Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer Ed9
Uploaded by
Lourd Hundryx Abara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views4 pagesReviewer Ed9
Uploaded by
Lourd Hundryx AbaraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Acquire New Knowledge found but is used as a means to
accomplish intended goals.
The Curriculum: Definition, Nature
and Scope Robert M. Hutchins views curriculum
as permanent studies where rules of
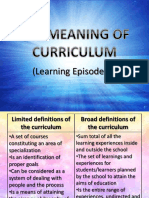
Definitions of curriculum
grammar, reading, rhetoric, logic and
The New International Dictionary mathematics for basic education are
defines curriculum as the whole body of emphasized.
a course in an educational institution or
The 3Rs should be emphasized in basic
by a department.
education while liberal education should
Oxford English Dictionary defines be emphasis in college.
curriculum as courses taught in schools
Arthur Bestor as an essentialist
or universities.
believes that the mission of the school
Curriculum is a planned and guided set should be intellectual training, hence
of learning experiences and intended curriculum should focus on the
outcomes, formulated through the fundamental intellectual disciplines of
systematic reconstruction of knowledge grammar, literature and writing. It should
and experiences under the auspices of include mathematics, science, history
the school, for the learners’ continuous and foreign language.
and willful growth in personal social
Joseph Schwab thinks that the sole
competence (Tanner, D.1980 in Bilbao,
source of curriculum is a discipline, thus
et al, 2015).
the subject areas such as Science,
Curriculum is what is taught in school, Mathematics, Social Studies, English
as a set of subjects, a content, a and many more, In college, academic
program of studies, asset of materials, a disciplines are labelled as humanities,
sequence of courses, a set of sciences, languages, mathematics
performance objectives, everything that among others. He coined the word
goes within the school. discipline as a ruling doctrine for
curriculum development.
Curriculum from Traditional Points of
View Phillip Phenix asserts that curriculum
should consist entirely of knowledge
Curriculum can be defined as a field of
which comes from various disciplines.
study. It is highly academic and is
concerned with broad historical, From a traditional view, curriculum is
philosophical, psychological and social mostly written documents such as
issues. It is mostly written documents syllabus, course of study, books and
such as syllabus, course of study, books references where knowledge is found
and references where knowledge is but is used as a means to accomplish
intended goals.
Curriculum from Progressive Points 1. Curriculum as a content or Body
of View of Knowledge
A progressive view of curriculum is the The focus is in the body of knowledge to
total learning experiences of the be transmitted to students using
individual. A listing of school subjects, appropriate teaching method. Teaching
syllabi, course of study and specific is limited to the acquisition of facts,
discipline does not make a curriculum. concepts, and principles of the subject
matter; however, the content or subject
John Dewey believes that education is
matter can also be taken as a means to
experiencing. Reflective thinking is a
an end.
means that unifies curricular elements
that are tested by application. Four ways of presenting the content
in the curriculum
Holin Caswell and Kenn Campbell
viewed curriculum as all experiences 1. Topical approach, where much
children have under guidance of content is based on knowledge and
teachers. experiences are included.
Othaniel Smith, William Stanley and 2. Concept approach with fewer topics
Harlan Shore likewise defined in clusters around major and sub-
curriculum as a sequence of potential concepts and their interactions, with
experiences, set up in schools for the relatedness emphasized;
purpose of disciplining children and
3. Thematic approach as a
youth in group ways of thinking and
combination of concepts that develop
acting.
conceptual structures, and
Colin Marsh and George Willis also
4. Modular approach that leads to
viewed curriculum as all the experiences
complete units of instruction.
in the classroom which are planned and
enacted by the teacher and also learned Criteria in the Selection of Content
by the students.
1. Significance. Content should
Three Ways of Approaching a contribute to ideas, concepts, principles
Curriculum and generalization that should attain the
overall purpose of the curriculum.
Curriculum can be approached or seen
in three ways. It can be defined as a 2. Validity. The authenticity of the
content, a process or an outcome. If you subject matter forms its validity.
examine the definitions provided by the
3. Utility. Usefulness of the content in
experts in the field, there are three ways
the curriculum is relative to the learners
of approaching a curriculum.
who are going to use these. It is relative
to time.
4. Learnability. The complexity of the 2. Articulation. As the content
content should be written the range o complexity progresses with the
experiences of the learners. educational levels, vertically or
horizontally, across the same discipline
5. Feasibility. The subject to be learned
smooth connection or bridging should be
is within the time allowed, resources
provided.
available, expertise of the teachers and
the nature of learners. West Visayas 3. Sequence. The logical arrangement
State University Lambunao Campus of the content refers to sequence or
College of Education Lambunao, Iloilo order.
17
4. Integration. Content in the curriculum
6. Interest. The content must be has relatedness or connectedness to
interesting to the learners. Interest is other contents.
one of the driving forces for students to
5. Continuity. Content should
learn better.
continuously flow as it was before, to
Guides in the Selection of the where it is now, and where it will be in
Content in the curriculum the future. It should be perennial. It
endures time.
1. Commonly used in the daily life.
2.Curriculum as a Process Curriculum
2. Appropriate to the maturity levels and
abilities of the learners. is seen as an action. It is an interaction
among the teachers, students, and
3. Valuable in meeting the needs and
content. Pedagogical Content
competencies of the future career.
Knowledge or PCK.
4. Related to other subject fields or
Guiding Principles when curriculum
discipline for complementation and
is approached as a process
integration.
1. Curriculum process in the form of
5. Importance in the transfer of learning
teaching methods or strategies are
to other disciplines.
means to achieve the end.
Basic Principles of Curriculum Content
2. There is no single best process or
In 1952, Palma proposed the principle of
method.
BASIC as a guide in addressing content
in the curriculum. BASIC refers to 3. Curriculum process should stimulate
Balance, Articulation, Sequence, the learners’ desire to develop the
Integration, and Continuity. cognitive, affective, psychomotor
domains in each individual.
1. Balance. Content should be fairly
distributed in depth and breadth.
4. In the choice of methods, learning the selection and organization of
and teaching styles should be content, the selection and organization
considered. of learning experiences or activities and
the selection of the assessment
5. Every method or process should
procedure and tools to measure
result to learning outcomes which can
achieved learning outcomes.
be described as cognitive, affective and
psychomotor. 3. Curriculum Implementing is putting
into action the plan which is based on
6. Flexibility in the use of the process or
the curriculum design in the classroom
methods should be considered. An
setting or the learning environment.
effective process will always result to
learning outcomes. 4. Curriculum Evaluating determines
the extent to which the desired
7. Both teaching and learning are the
outcomes have been achieved.
two important process in the
implementation of the curriculum.
3.Curriculum as a Product
Product is what the students desire to
achieve as a learning outcomes. The
product from the curriculum is a student
equipped with the knowledge, skills and
values to function effectively and
efficiently.
Curriculum Development Process
Curriculum development is a dynamic
process involving many different people
and procedures. Development connotes
changes which is systematic. A change
for the better means alteration,
modification, or improvement of existing
condition.
Phases of Curriculum Development
Process
1. Curriculum Planning considers the
school vision, mission and goals.
2. Curriculum Designing is the way
curriculum is conceptualized to include
You might also like
- M2 - Lesson 1 The School CurriculumDocument7 pagesM2 - Lesson 1 The School CurriculumJirk Jackson Esparcia89% (19)
- Module 1 - The Teacher and School CurriculumDocument17 pagesModule 1 - The Teacher and School CurriculumSienna Mae AgringoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 LESSON 2 Aprroaches To School CurriculumDocument8 pagesMODULE 2 LESSON 2 Aprroaches To School Curriculumprincess pauline laizNo ratings yet
- The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumDocument38 pagesThe Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumAlyssa AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 The Teacher As A Knower of Curriculum - RheuDocument13 pagesModule 2 The Teacher As A Knower of Curriculum - Rheuqrhe30gswNo ratings yet
- Module 2 EuDocument37 pagesModule 2 EuRhea Tamayo CasuncadNo ratings yet
- The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumDocument48 pagesThe Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumLee Jay TesingNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development Module 2 Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesCurriculum Development Module 2 Lesson 1 and 2Jireh Albay100% (1)
- Professional Education: Curriculum Development: Bilbao Et - Al. 2009)Document9 pagesProfessional Education: Curriculum Development: Bilbao Et - Al. 2009)SlodineNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The School Cirruculum: Lesson 2.2Document39 pagesApproaches To The School Cirruculum: Lesson 2.2Mariel Mae PolancosNo ratings yet
- Module 2.1Document20 pagesModule 2.1Maila Calimpong AsimNo ratings yet
- Model Didik HiburDocument23 pagesModel Didik Hibursuzzy romilusNo ratings yet
- 01 TCUR111 Course Unit 2Document5 pages01 TCUR111 Course Unit 2Sunako ClaesNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Valdez & Legaspi Module 4 Approaches To School CurriculumDocument2 pagesGroup 2 Valdez & Legaspi Module 4 Approaches To School CurriculumLycea ValdezNo ratings yet
- Educ 202 ADocument3 pagesEduc 202 A2022201035No ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Approaches To School CurriculumDocument33 pagesLesson 2: Approaches To School CurriculumChristyNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Finally 123Document36 pagesStudy Guide Finally 123Krizza Aubrey Orias AmparadoNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The School CurriculumDocument3 pagesThe Teacher and The School CurriculumPat HortezanoNo ratings yet
- Module-2-The-Teacher-as-a-knower-of-curriculum FDocument20 pagesModule-2-The-Teacher-as-a-knower-of-curriculum FResyn Faye CortezNo ratings yet
- L 2.2 Educ 4 The Teacher and The School Curriculum - 044817Document7 pagesL 2.2 Educ 4 The Teacher and The School Curriculum - 044817dianarose.beldadNo ratings yet
- PROF ED 30 CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT FinalDocument38 pagesPROF ED 30 CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT FinalRainiel Victor M. CrisologoNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 30 Curriculum Development FinalDocument38 pagesProf Ed 30 Curriculum Development FinalclarisseNo ratings yet
- Concept and Need of CurriculumDocument36 pagesConcept and Need of CurriculumShyam Bihari100% (1)
- Approaches To School CurriculumDocument15 pagesApproaches To School CurriculumMeriel JagmisNo ratings yet
- PROF ED 5 LectureDocument9 pagesPROF ED 5 LectureMelody CastroNo ratings yet
- Educ 8 Module 3Document8 pagesEduc 8 Module 3EDETH SUBONGNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Approaches To School CurriculumDocument9 pagesModule 4 Approaches To School Curriculumbonitdanilo1968No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2Document4 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 2HeheNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and CurriculumDocument11 pagesThe Teacher and CurriculumAudremie DuratoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document2 pagesLesson 2John Mari Lloyd DaosNo ratings yet
- C1 M2 Lesson 2.2Document7 pagesC1 M2 Lesson 2.2Kath Leen IbacitasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 EGLOSODocument4 pagesLesson 2.2 EGLOSOMathew EglosoNo ratings yet
- Tugas MK Elt Curriculum - 1Document4 pagesTugas MK Elt Curriculum - 1Adi Wicaksono WidjayaNo ratings yet
- Report 2 Ms - SealmoyDocument4 pagesReport 2 Ms - SealmoyRegine QuijanoNo ratings yet
- St103 Group 2 FinalDocument48 pagesSt103 Group 2 FinalJudyl Arciga CamoNo ratings yet
- Module 26Document7 pagesModule 26Kel LumawanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumDocument10 pagesModule 2 - The Teacher As A Knower of CurriculumVannessa LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- 2 - CurrIntroDocument52 pages2 - CurrIntroandrie sajarah salilamaNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The School Curriculum Manuscript Final EditedDocument116 pagesThe Teacher and The School Curriculum Manuscript Final EditedClaire RedfieldNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The School Curriculum: Lesson 2.2Document6 pagesApproaches To The School Curriculum: Lesson 2.2Liza MaramagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecture NotesDocument1 pageChapter 2 Lecture NotesCariza AndaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 &5 SEd Prof 311 October 5, 2020 Chapter 1Document9 pagesModule 4 &5 SEd Prof 311 October 5, 2020 Chapter 1aetheticNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development A SummaryDocument22 pagesCurriculum Development A SummaryMSLI 50No ratings yet
- Module 2 The Teacher and The School CurriculumDocument14 pagesModule 2 The Teacher and The School CurriculumRoberto AlvarezNo ratings yet
- fs2 Group 1Document21 pagesfs2 Group 1Mella CañezoNo ratings yet
- EDUC 205 Review (F2F NOTES)Document20 pagesEDUC 205 Review (F2F NOTES)Princess Ann DomingoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Lesson 1Document3 pagesCHAPTER 2 Lesson 1HeheNo ratings yet
- Historical Philosophical PerspectivesDocument7 pagesHistorical Philosophical Perspectivesbello fatimaNo ratings yet
- Approaches About School Curriculum - Prof Ed 5Document23 pagesApproaches About School Curriculum - Prof Ed 5Minette Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Educ 106Document34 pagesEduc 106Jay RicNo ratings yet
- Integrative ReviewerDocument12 pagesIntegrative ReviewerBrittany VenturaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ED 5Document6 pagesModule 2 ED 5Karla Dao-ayNo ratings yet
- Assignment AnuDocument11 pagesAssignment AnuanushadaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Curriculum DevelopmentDocument15 pagesLecture Notes in Curriculum DevelopmentJishan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide 1 in BPEd 71Document30 pagesLearning Guide 1 in BPEd 71Xyra V YponNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - AddendumDocument25 pagesModule 1 - AddendumJomarie V. PauleNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The School Curriculum Three Ways of Approaching A CurriculumDocument5 pagesApproaches To The School Curriculum Three Ways of Approaching A CurriculumMichelle SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Lesson1 and 2Document14 pagesUnit 2 Lesson1 and 2Analo Miranda AntigaNo ratings yet
- College Teaching: Studies in Methods of Teaching in the CollegeFrom EverandCollege Teaching: Studies in Methods of Teaching in the CollegeNo ratings yet
- General EdDocument16 pagesGeneral EdLourd Hundryx AbaraNo ratings yet
- Abara ReportDocument7 pagesAbara ReportLourd Hundryx AbaraNo ratings yet
- FulltextDocument42 pagesFulltextLourd Hundryx AbaraNo ratings yet
- GradesDocument1 pageGradesLourd Hundryx AbaraNo ratings yet
- L o U R D: Oud When I'm Happy Utgoing and Excited Nderstanding and Quite NoisyDocument1 pageL o U R D: Oud When I'm Happy Utgoing and Excited Nderstanding and Quite NoisyLourd Hundryx AbaraNo ratings yet
- Eksrhyky Usg: JK"V H Izks - KSFXDH Lalfkku Bykgkckn Iz KXJKT Bykgkckn &211004 HKKJRDocument2 pagesEksrhyky Usg: JK"V H Izks - KSFXDH Lalfkku Bykgkckn Iz KXJKT Bykgkckn &211004 HKKJRKrishna sahNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument98 pagesReviewerdiarydenieNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2Vijayakumar KNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan-INSET 2020Document5 pagesGroup 6 - PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan-INSET 2020Tara BautistaNo ratings yet
- ED 209 - Assessment in Learning 2Document15 pagesED 209 - Assessment in Learning 2Rochyll Angel GaleciaNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Batangas City South Senior High SchoolDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Batangas City South Senior High Schoolmarinella borbonNo ratings yet
- Characteristics, Strengths, and WeaknessesDocument30 pagesCharacteristics, Strengths, and WeaknessesErica Canon100% (1)
- Science Quarter 1 Module 1Document33 pagesScience Quarter 1 Module 1Xyril GalendezNo ratings yet
- Role of Social Class in Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument12 pagesRole of Social Class in Consumer Buying Behaviour27abhisekcooldude27758No ratings yet
- Report - Classifications of Assessment.Document4 pagesReport - Classifications of Assessment.jyNo ratings yet
- Virtual Labs - Computer Science & EngineeringDocument3 pagesVirtual Labs - Computer Science & EngineeringNeeraj JainNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Department of EducationDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Department of EducationKay BelgaNo ratings yet
- Resume Fahmi Fathur RahmanDocument1 pageResume Fahmi Fathur Rahmanbimo prabowoNo ratings yet
- Integration of Circular Economy in The Surf Industry - A Vision Aligned With The Sustainable Development GoalsDocument1 pageIntegration of Circular Economy in The Surf Industry - A Vision Aligned With The Sustainable Development GoalsVladan KuzmanovicNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document4 pagesQuiz 1J A.100% (1)
- Hodge 2018Document7 pagesHodge 2018Ines Arias PazNo ratings yet
- Containment Theory: Jayson Ivan TorreonDocument11 pagesContainment Theory: Jayson Ivan TorreonShane TorrieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Review of Related LiteratureDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Review of Related LiteratureLoraine Platilla100% (2)
- Project DefenceDocument13 pagesProject DefenceGame4FunNo ratings yet
- Nature of GeographyDocument241 pagesNature of GeographyIndrajit PalNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Culture and Arts Education 2018 2019Document2 pagesBachelor of Culture and Arts Education 2018 2019Theresa Manglicmot PanemNo ratings yet
- Crop Yield Prediction Using Machine Learning TechniquesDocument5 pagesCrop Yield Prediction Using Machine Learning TechniquesArshanday UkundamayNo ratings yet
- The Audiolingual MethodDocument3 pagesThe Audiolingual MethodHà Đặng Nguyễn NgânNo ratings yet
- Постер Вітчук Вадим РомановичDocument1 pageПостер Вітчук Вадим Романовичmmoney.work.01No ratings yet
- IARE BRM Lecture NotesDocument79 pagesIARE BRM Lecture NotesAkarsh DhimanNo ratings yet
- Reflections (Transfer of Learning)Document2 pagesReflections (Transfer of Learning)ShaniceNo ratings yet
- Test Measurement and Evaluation in SportsDocument9 pagesTest Measurement and Evaluation in Sportsavik mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Black Pregnant Women "Get The Most Judgment" A QualitativeDocument19 pagesBlack Pregnant Women "Get The Most Judgment" A QualitativeFatmawati SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PPT LAC Final (A, B, C)Document64 pagesUnit 2 PPT LAC Final (A, B, C)Leena GadkariNo ratings yet
- Classification With Quantum Machine Learning: A Survey: 1 - IntroductionDocument16 pagesClassification With Quantum Machine Learning: A Survey: 1 - IntroductionArtūrs PriedītisNo ratings yet