Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cosmology Practice Test (Solutions)
Uploaded by
aimeesantillana08Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cosmology Practice Test (Solutions)
Uploaded by
aimeesantillana08Copyright:
Available Formats
Cosmology Science Test Practice
What is cosmology?
a) The study of how the sun affects the Earth
b) A sequence in the star life cycle
c) The study of the universe, including its origin and future
d) A form of cloud dust that surrounds the universe
What is the Big Bang theory?
The Big Bang theory states that the universe began from a single point with a big explosion and that all the universe
is moving out from this point. As with all objects in the universe, the Earth was created as a result of the Big Bang.
Describe gravity.
Gravity is the force of attraction between two objects.
Describe nebulas and state what forms from a nebula.
A nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas in space. Stars are formed from nebula.
What is a star? Circle all that are appropriate.
a) A ring that circles around a planet
b) A luminous ball of gas
c) It is made of hydrogen and helium
d) The sun
What do astronomers find out from the colour of a star?
The colour of a star gives us information about the size of the star, its temperature and where it is in its lifecycle.
Outline the difference between apparent and absolute magnitude.
The apparent magnitude of a star is how bright the star appears when viewed from Earth. The absolute magnitude
of a star is how bright the star actually is and this is measured as if the star were a certain fixed distance from the
Earth and the same fixed distance is used when calculating the absolute magnitude of all stars.
Define a light year and a parsec. Write down their formulas of conversion.
A light year is the distance that light will travel in one year.
A parsec is equivalent to 3.26 light years (it is based on parallax).
To convert from ly to pc divide by 3.26.
To convert from pc to ly multiply by 3.26.
Define an error of parallax. Why don’t astronomers use parallax to measure the distances to other galaxies?
An error of parallax is caused by the position of the observer when taking a measurement. Stellar parallax is very
small for stars that are very far away and so cannot be used to measure the distance to the star.
Which of the following pieces of evidence can be used to prove that the universe is expanding?
a) Blue shift
b) Telescope Imagery
c) Chemical reactions
d) Red shift
How does ___red shift____________ show that the universe is expanding?
When stars are moving away from us, light shifts towards the red end of the spectrum because the wavelengths are
lengthened. Since everything in the universe is expanding according to the Big Bang theory, stars are moving away
and therefore light coming from them is red-shifted.
Which of the following solidifies the theory of the Big Bang?
a) Cosmic wave background radiation
b) Blue shift
c) Mathematics
d) Telescope imagery
With the answer you chose above, define it.
There is measurable background low-frequency radiation in the universe which is a result of the Big Bang explosion.
Fill in the blanks.
Gamma ultraviolet infrared radiowaves
rays
X-rays Visible microwaves
light
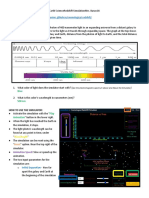
What is an electromagnetic spectrum?
It is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation.
Define the following types of waves.
Type Definition
Radio waves Long wave radiation. Emitted by radio stations and by stars.
Microwaves Long wave radiation. Used in microwave ovens to cook food and used by astronomers to
provide information about the structures of galaxies.
Infrared Long wave radiation. Better known as heat.
Visible
The light that can be detected by human eyes.
Ultraviolet Shortwave radiation. Emitted by the sun (and all stars).
X-rays Shortwave radiation. Used to take images of bones and teeth.
Gamma-rays Short wave radiation.
Categorize the following pictures according to their type of wave.
Possibly heat UV Visible
Radio Describe Radio
(infrared Xrays light
waves waves
radiation) from
the engine?
nuclear fusion and explain how it occurs in stars.
Nuclear fusion occurs when two hydrogen nuclei fuse. This occurs inside stars due to the enormous temperature
inside a star.
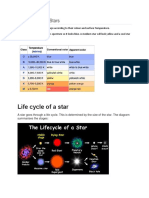
State the life cycle for medium sized or main sequence stars.
nebula protostar main sequence star red giant planetary nebula white dwarf black dwarf
Explain why black dwarf is still a theory.
A black dwarf cannot be seen as no light escapes a black dwarf but the effect of a black dwarf on other objects can
be detected.
State the life cycle for high mass stars.
nebula protostar main sequence high mass star supergiant supernova black hole or neutron star
Define a neutron star.
Neutron stars are the remains of high mass stars.
Define a black hole. Describe a method to identify a black hole.
The most massive stars become black holes when they die. After a large star explodes the gravity is so strong that
gas is pulled inwards into a smaller and smaller space. Eventually the gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not
even light.
What colour are Type A stars? What colour are Type G stars?
a) Blue a) Yellow-white
b) Yellow b) Blue-white
c) White c) Orange
d) Pink d) Yellow
What colour are Type K stars? What colour are Type O stars?
a) Red a) Red
b) Blue b) Blue
c) Red c) Blue-white
d) Orange d) Orange
Why are light years more appropriate to use than kilometers when measuring the distance to stars?
The distance to stars is so great that kilometers are too small as a unit. (the closest star is 4 x 10 13 km away)
Explain why we cannot observe more than 13.7 billion light years of the universe.
Possibly because it is so far away that there hasn’t been enough time passed for light to reach us from so great a
distance.
What characteristics of Cepheid variables makes them useful in measuring distances to other galaxies?
You don’t need to know this for the exam.
Cepheid variable stars are stars which pulsate in a predictable way. In addition, a Cepheid star's period (how often it
pulsates) is directly related to its luminosity or brightness.
Define the following.
Red Giant A star produced when the core of a small to medium
sized star runs out of hydrogen.
White Dwarf A hot dense star that is the remains of a red giant.
Black Dwarf Cold dark remains of a white dwarf.
Blue Supergiant Stars that are ten or more times more massive than the
sun
Supernova A giant explosion that occurs when a star much larger
than our sun runs out of fuel
Alpha Centauri is the brightest star we see in our sky, although it is only a medium sized star similar to our sun.
Betelgeuse is a much bigger star, but it doesn’t not appear to be as bright as Alpha Centauri. Use these examples
to explain the difference between absolute and apparent magnitude.
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears to an observer on Earth and it depends on the size of the
star and the distance that it is from Earth. Absolute magnitude is the actual brightness of the star. This is compared
for all stars as if they were the same distance from Earth. Betelgeuse does not appear as bright as Alpha Centauri
because Betelgeuse is further from Earth.
Heat causes objects in space to expand, State the factor which prevents a star from blowing apart due to the
explosive power of the nuclear reaction occurring in the star.
gravity
You might also like
- D Astrophysics TSOKOSDocument49 pagesD Astrophysics TSOKOSCalvin Kong88% (8)
- Ease Sci.i Module 18 StarsDocument23 pagesEase Sci.i Module 18 StarsBoy SawagaNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Notes - Year 10 Victorian Curriculum 2022Document4 pagesAstronomy Notes - Year 10 Victorian Curriculum 2022boa0004No ratings yet
- Classification of StarsDocument6 pagesClassification of StarsAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Study Guide AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 21 Study Guide AnswersElizabeth LuxNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect WorksheetDocument2 pagesDoppler Effect WorksheetNaz Khalili0% (1)
- Midterm SolutionsDocument12 pagesMidterm Solutionsozworld3100% (1)
- Physical Chap 24Document22 pagesPhysical Chap 24Chavez ShalomNo ratings yet
- Multiwavelength Universe Poster All 8x11 PDFDocument10 pagesMultiwavelength Universe Poster All 8x11 PDFnabilanabnabNo ratings yet
- Astronomy 104, Spring 2018: Test 1Document11 pagesAstronomy 104, Spring 2018: Test 1None OfUrBizNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Astronomy Questions AnswersDocument20 pagesGrade 9 Science Astronomy Questions Answersmarkjethro.tomas.gsNo ratings yet
- Final 071212 WithAnswerKeyDocument20 pagesFinal 071212 WithAnswerKeyChuah Chong YangNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Practice PapersDocument11 pagesAstronomy Practice PaperstausarpaoNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in Chemistry Project Space ChemistryDocument22 pagesFdocuments - in Chemistry Project Space ChemistryLip UtNo ratings yet
- All About StarsDocument3 pagesAll About StarsrishNo ratings yet
- Option d1 PagesDocument9 pagesOption d1 PagesMohammad SuliemanNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics SummaryDocument10 pagesAstrophysics SummaryHafsah PirzadaNo ratings yet
- Presentation-WPS Office 081647Document72 pagesPresentation-WPS Office 081647Katherine NicoleNo ratings yet
- Option D - Astrophysics - IB PhysicsDocument18 pagesOption D - Astrophysics - IB PhysicsVinisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 PDFDocument36 pagesLecture 11 PDFZachNo ratings yet
- Astronomy 111 Review Problems Solutions: Problem 1Document7 pagesAstronomy 111 Review Problems Solutions: Problem 1Chitsimran Singh AroraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AstrophyicsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To AstrophyicsJohn Rick VasolNo ratings yet
- Malou Ass Tungkol Sa StarsDocument4 pagesMalou Ass Tungkol Sa Starstom_donato_1No ratings yet
- SPACE Notes 4 and 5Document16 pagesSPACE Notes 4 and 5Shashwat TripathiNo ratings yet
- Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument5 pagesStars and Galaxies in The UniverseMei Shuen CheamNo ratings yet
- Lecture14 ElmsDocument60 pagesLecture14 ElmsDanny BrewerNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of A StarDocument8 pagesLife Cycle of A StarHriditi HowladerNo ratings yet
- Created By-: Sheikh Khalilur RahmanDocument23 pagesCreated By-: Sheikh Khalilur RahmanKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Star and Its PropertiesDocument4 pagesStar and Its PropertiesRemond BalabaNo ratings yet
- Outlines: - Chapter 15 "Surveying The Stars"Document97 pagesOutlines: - Chapter 15 "Surveying The Stars"New1122No ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document7 pagesChapter 14Aaron LisandrioNo ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument22 pagesChem ProjectAnthony LowNo ratings yet
- Week 8 ConstellationsDocument50 pagesWeek 8 ConstellationsRechie Marie Porras PeralesNo ratings yet
- 27 - Stars and GalaxiesDocument45 pages27 - Stars and GalaxiesNor AdinaNo ratings yet
- Module P7 L6Document19 pagesModule P7 L6geth jonesNo ratings yet
- PHYSUICADocument37 pagesPHYSUICAAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- Soal Osk Astro 2014Document5 pagesSoal Osk Astro 2014Sang Ayu VirgayaniNo ratings yet
- Carrie Weeks Pd2: Star BasicsDocument5 pagesCarrie Weeks Pd2: Star BasicsFifinessNo ratings yet
- History of The Universe: Or, Following Stephen HawkingDocument47 pagesHistory of The Universe: Or, Following Stephen HawkingRANJITHNo ratings yet
- The Earth and BeyondDocument14 pagesThe Earth and Beyondaungnaingoo44No ratings yet
- The Earth and BeyondDocument14 pagesThe Earth and Beyond1221No ratings yet
- Star Distances - ActivitiesDocument2 pagesStar Distances - ActivitiesbinduNo ratings yet
- Sample 1Document12 pagesSample 1KhamNo ratings yet
- Week 7 StarsDocument41 pagesWeek 7 StarsBEA ANGELINE RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document8 pagesUnit 5Raiyad RezaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3, WK 8-9, Module 6Document16 pagesScience: Quarter 3, WK 8-9, Module 6Geraldine GalceranNo ratings yet
- Astronomy and CosmologyDocument40 pagesAstronomy and CosmologyDropplet MaggotNo ratings yet
- Review Exam 2Document110 pagesReview Exam 2Jeremy DedmanNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Astronomy Olympiad 2012Document5 pagesBangladesh Astronomy Olympiad 2012Science Olympiad Blog87% (15)
- Google Meet 2A 21 October 2020: Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseDocument15 pagesGoogle Meet 2A 21 October 2020: Stars and Galaxies in The UniverseAthirah SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Constituents and StructuresDocument18 pagesConstituents and StructuresHassan BareachNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument9 pagesSample Questionsbabarrayyan292No ratings yet
- 5054 Space Physics Practice QuestionsDocument14 pages5054 Space Physics Practice QuestionsSoya BeansNo ratings yet
- 8 PlanetsDocument41 pages8 PlanetsBblabsLlameraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Properties of Stars - Michael KDocument30 pagesChapter 17 - Properties of Stars - Michael KMickyOvshievichNo ratings yet
- Cosmology Revision - 2013 SolutionsDocument4 pagesCosmology Revision - 2013 Solutionsmxq88557No ratings yet
- The UniverseDocument10 pagesThe UniverseAaron YogurtNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 5 & UNIT - 6 NotesDocument7 pagesUNIT - 5 & UNIT - 6 Notessharkfin1403No ratings yet
- P1 - 5 - Use of Waves QsDocument7 pagesP1 - 5 - Use of Waves QsTim LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essentials of Geology Fourth EditionDocument15 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Geology Fourth Editionminhkhoit8cua3No ratings yet
- Modified Esb U9 Investigating Redshift and Blueshift Portfolio Worksheet and Rubric 1Document6 pagesModified Esb U9 Investigating Redshift and Blueshift Portfolio Worksheet and Rubric 1Lyndsee WeibleNo ratings yet
- HubbleslawDocument11 pagesHubbleslawSajib IslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Origin and Structure of The EarthDocument15 pagesChapter 1 Origin and Structure of The EarthCheska Marie B. OlivaNo ratings yet
- Early Universe Universe Some Time Later: Astronomy Assessment and TPS Questions: Expansion of The UniverseDocument11 pagesEarly Universe Universe Some Time Later: Astronomy Assessment and TPS Questions: Expansion of The UniversemanaNo ratings yet
- JahskajhasDocument6 pagesJahskajhasVen Viv Gumpic0% (1)
- EG From DG - K.M.L.L Van Spaendonck - ISBN 9789402158601 PDFDocument62 pagesEG From DG - K.M.L.L Van Spaendonck - ISBN 9789402158601 PDFKoen Van SpaendonckNo ratings yet
- New DLL Physical ScienceDocument55 pagesNew DLL Physical ScienceGirl from the NorthNo ratings yet
- Sol Barbara Ryden Cap 4 PDFDocument6 pagesSol Barbara Ryden Cap 4 PDFCarlos A GarcíaNo ratings yet
- PCS181 Notes Class 4Document3 pagesPCS181 Notes Class 4Marc MNo ratings yet
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems - From Stellar To Satellite NavigationDocument168 pagesGlobal Navigation Satellite Systems - From Stellar To Satellite NavigationDavid BrownNo ratings yet
- PythonTutorial MetivierDocument11 pagesPythonTutorial MetivierLillyOpenMindNo ratings yet
- The Big Bang Theory SummaryDocument13 pagesThe Big Bang Theory Summarypauline cunananNo ratings yet
- Unzicker 0708.3518 PDFDocument15 pagesUnzicker 0708.3518 PDFHelmut SoehnNo ratings yet
- Planetisimal TheoryDocument3 pagesPlanetisimal Theorymakoy29826578No ratings yet
- Amitabha Ghosh-Origin of Inertia - Extended Mach's Principle and Cosmological Consequences-Apeiron (2000) PDFDocument161 pagesAmitabha Ghosh-Origin of Inertia - Extended Mach's Principle and Cosmological Consequences-Apeiron (2000) PDFderaj1No ratings yet
- Olbers ParadoxDocument4 pagesOlbers ParadoxPrakash SankerNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Grade 12 Term 2 1Document120 pagesPhysical Sciences Grade 12 Term 2 1Linda Mnisi100% (1)
- Special Theory of Relativity Reviewer PDFDocument2 pagesSpecial Theory of Relativity Reviewer PDFJeremy Joshua EvocesNo ratings yet
- D3 - CosmologyDocument6 pagesD3 - CosmologyArun MuddamsettyNo ratings yet
- Big Bang TheoryDocument29 pagesBig Bang TheoryNo NameNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Space Physics KnowIT GCSEDocument37 pagesAQA Physics Space Physics KnowIT GCSEAvrian PradiptyaNo ratings yet
- Christina Latorre - Redshift Simulator Activity Sheet VirtualDocument3 pagesChristina Latorre - Redshift Simulator Activity Sheet VirtualChristina LatorreNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics TimelineDocument34 pagesModern Physics TimelineJhetr CledrNo ratings yet
- The Expanding UniverseDocument3 pagesThe Expanding UniverseMary Francia RicoNo ratings yet
- Astrophysics PDFDocument29 pagesAstrophysics PDFWilliam ChongNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument60 pagesPhysics Notespicard82No ratings yet
- BigBangTheory PDFDocument22 pagesBigBangTheory PDFPrince KumarNo ratings yet