Professional Documents
Culture Documents
X Rays
X Rays
Uploaded by
zubair syedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
X Rays
X Rays
Uploaded by
zubair syedCopyright:
Available Formats
X-Rays
Friday, 7 January 2022 8:18 PM
PEDIATRICS VIVA-VOCE: X-RAY
-Dr.Ashray S Patel
Ph No: 9482141673
E-mail: patel1995ash@gmail.com
INTERPRETATION
NEONATOLOGY
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
CVS
GIT
GENITOURINARY SYSTEM
BONE
BASICS OF X-RAY INTERPRETATION:
How to Systematically Interpret the X-ray film?
• Plain/Contrast X-ray
• Comment on which part of the
body X-ray is taken
• Name/Age/Sex/Date
• Side Marker
• View: AP/PA/Lateral/Oblique
• Exposure
• Centring of the Film
• Inspiratory/Expiratory Film
• Systematically Examine Each Part
of the X-ray
• Commenting on any Abnormality
AP vs PA View:
EXPOSURE: Under/Correct/Over Exposure
ROTATION:
• Both Medial ends of Clavicle should be equidistant
from midline, vertical drawn through the centre of
T1-T5 vertebral bodies.
• Rotation: medial end of one of the clavicle further
away from the vertical line.
INSPIRATORY/EXPIRATORY Film:
Systematically Examine each part of the X-ray:
INSIDE OUT APPROACH
• TRACHEA/CARINA/BRONCHUS
• SUPERIOR MEDIASTINUM
• AORTIC ARCH
• AORTIC KNUCKLE
• HILAR SHADOWS: MPA dividing into Right PA
and Left PA.
• Comment on the Cardia
• Diaphragm and below diaphragm
• Costo-Phrenic Angle
• Chest wall
• Compare Lung Zones
Commenting on any Abnormality:
• Unilateral/Bilateral
• Symmetric/Assymetric
• Focal/Diffuse
• Radiolucent/Opaque
• Focal/Diffuse
NEONATOLOGY
RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME:
• Fine granular appearance
• Ground Glass Appearance
• White Out Lung
• Bilateral and Symmetrical
• Air Bronchograms extending Peripherally
• Stages:
1. Reticulogranular Pattern
2. Air Bronchograms
3. Decreased transperancy+Blurry Diaphragm
and Heart
4. Whiteout Lung
TRANSIENT TACHYPNEA OF NEWBORN:
• Hyperinflation of the lungs
• Interstitial edema: peri-hilar
streaks(Sunray Appearance)
• Prominent fissure of Right
upper Lobe.
• Rarely Cardiomegaly.
MECONIUM ASPIRATION SYNDROME:
• Bilateral, Diffuse,
Heterogeneous Fluffy
Opacities
• This is suggestive of patchy
areas of atelectasis and
emphysema from air
trapping.
• Hyperinflated
• Air leak
ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA:
Tracheo-Esophageal Fistula Isolated Esophageal Atresia
CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA:
• Ipsilateral Hemithorax contains
bowel loops filled with gas.
• Ispilateral lung is hypoplastic.
• Mediastinal Shift to opposite
side.
DUODENAL ATRESIA:
• Simultaneous distension
of stomach and first part
of duodenum.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM:
ANATOMY:
INFECTIONS:
VIRAL SPECTRUM:
• Hyperinflated Lung Fields
• Flattening of diaphragm
• Translucent lung fields
• Parahilar Peribronchial Infiltrates
Streaky or Reticular Bilateral nodular, fluffy,
infiltrates radiating from patchy or rarely consolidave
hilar regions into the changes.
parenchyma
BACTERIAL:
LOCALIZATION IS USUALLY POSSIBLE
COLLAPSE:
• White Homogenous Opacity
• Compensatory over-inflation of
the adjacent lobes
• Trachea or mediastinal shift to
affected side
• Vessels are more spread out
• Luftsichel Sign: sickle shaped
air crescent noticed around
aortic knuckle due to
compensatory hyperinflation
of upper part of left lower
lobe.
PNEUMOTHORAX:
• Absent vascular
markings
• Increased size and
licence of the involved
hemithorax
• Shift of mediastinum to
opposite side
• Flattening of ipsilateral
diaphragm
PLEURAL EFFUSION:
• Blunting of Costco-phrenic
and Cardio-phrenic angle
• Opacification
• S shaped curve of Ellis
• Shift of mediastinum to the
opposite side
CARDIO-VASCULAR SYSTEM:
ANATOMY:
CARDIOMEGALY:
Cardio-Thoracic Ratio of more than:
• 0.6 in newborns and infants
• 0.5 in older children
RV ENLARGEMENT:
• Upturned Apex: apex is laterally
and upwardly displaced and
elevated from diaphragm
• D-TGA
• ASD with Eisenmenger Syndrome
• TAPVC
• ASD
• VSD with PAH
RIGHT ATRIAL ENLARGEMENT:
• A prominent convexity on right
side
• Right atrial shadow occupies
more than 2.5 interspaces
• Distance from midline to right
heart border will be more than
4cm.
• Severe PS, Ebstein’s Anamoly,
Tricuspid Atresia.
LEFT ATRIAL ENLARGEMENT:
• Straightening of left heart
border
• PDA
• VSD
• MR
• MITRAL STENOSIS
LEFT VENTRICULAR ENLARGEMENT:
• Apex is shifted down and
out
• Large VSD
• Significant MR, AR
• PDA, with large shunt
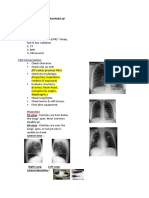
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE:
1) TETRALOGY OF FALLOT:
• Boot shaped heart or
“Coeur en Sabot”
• Upturned apex without
Cardiomegaly
• Pulmonary Oligemia
2) TRANSPOSITION OF GREAT ARTERIES:
• EGG ON STRING
APPEARANCE
• RV apex/Right atrial
enlargement
• Increased pulmonary
vascularity
3) EBSTEIN’s ANAMOLY:
• Massive Cardiomegaly
• Huge RA
• Dilated RVOT
• BOX SHAPED HEART
4) TOTAL ANAMOLOUS PULMONARY VENOUS
CONNECTION:
• FIGURE OF 8 APPEARANCE/
SNOWMAN APPEARANCE
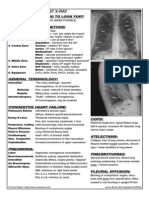
CARDIAC FAILURE: Pulmonary Edema
INTERSTITIAL STAGE:
• Reticular lines, followed by
increasing haziness and
generalised opacity of the
lungs.
• B Lines: small transverse lines
located in the costo-phrenic
sulci
• A Lines: longer lines running
outward from the hilar regions
ALVEOLAR STAGE:
• Nodular or diffuse
haziness
• Usually accumulates in the
parahilar regions sparing
apical region
• BUTTERFLY/BATWING
Appearance
GASTRO-INTESTINAL SYSTEM:
HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS:
• Single Bubble Appearance
Sonography is diagnostic:
• Muscle thickness > 3mm
• Channel length > 15mm
• Diameter > 8mm
HIRSCHSPRUNG’s DISEASE:
• Distended bowel loops
throughout the abdomen
• Rectum is more dilated than
sigmoid normally.
• Rectum is narrow, sigmoid is
dilated.
PNEUMOPERITONIUM:
• Air under Diaphragm
• Intestinal Perforation
INTUSSUSCEPTION:
• Claw Sign
GENITOURINARY SYSTEM:
VESICOURETERAL REFLUX:
POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVE:
BONE:
RICKETS:
• Generalized Osteopenia
• Cupping
• Fraying: irregular margins of the
metaphysis
• Splaying: widening of metaphysical
ends
• Bending of bones, lateral bowing
SCURVY:
• Pencil thin cortex
• Ground glass appearance of the
shaft
• Ring Epiphysis/Wimberger Sign
• White line of Frenkel
• Scorbutic Zone
• Pelken Spurs
You might also like
- 2024 MYMAXICARE BROCHURE RatesDocument17 pages2024 MYMAXICARE BROCHURE RatesJuliet CoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Dr. Osama Mahmoud PDFDocument91 pagesRespiratory Dr. Osama Mahmoud PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNo ratings yet
- Approach To Head CTDocument31 pagesApproach To Head CTElisabeth F. Ojha100% (2)
- Diagnostic TestsDocument70 pagesDiagnostic TestssimpforaiahNo ratings yet
- Thorax PatologisDocument72 pagesThorax PatologisAida Fitriyane HamdaniNo ratings yet
- 18 - Thoracic & CardiovascularDocument31 pages18 - Thoracic & CardiovascularAbhijith J PuttananickalNo ratings yet
- Thorax RadiologyDocument31 pagesThorax Radiologyshanti kiranaNo ratings yet
- Moodle Course On Chest ImagingDocument54 pagesMoodle Course On Chest ImagingStanley ShanNo ratings yet
- Basicinterpretationofcxr 110913060449 Phpapp01Document84 pagesBasicinterpretationofcxr 110913060449 Phpapp01Alexandra DîrțuNo ratings yet
- NoseDocument15 pagesNoseArooshaNo ratings yet
- Chest X - RayDocument49 pagesChest X - RayLyk TiglaoNo ratings yet
- Chest X Ray SessionDocument110 pagesChest X Ray SessionzakiyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Interpretation of CXRDocument84 pagesBasic Interpretation of CXRAbdiqani Mohamed AdanNo ratings yet
- Basic CXR Interpretation Learning Material 2018Document74 pagesBasic CXR Interpretation Learning Material 2018Slindy Noty MtetwaNo ratings yet
- Respirasi System ImagingDocument98 pagesRespirasi System ImagingRereNo ratings yet
- L3 - IM - Correlated Lecture (Sept0922)Document12 pagesL3 - IM - Correlated Lecture (Sept0922)Maria Carmela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray Abnormalities - Costophrenic Angle BluntingDocument2 pagesChest X-Ray Abnormalities - Costophrenic Angle Blunting89znnw5k85No ratings yet
- Stenotic Valvular Heart Disease and Its Anaesthetic ManagementDocument75 pagesStenotic Valvular Heart Disease and Its Anaesthetic ManagementDr MounicaNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Ent 1.07 NoseDocument4 pagesShanz - Ent 1.07 NosePetrina XuNo ratings yet
- ENT Radiology ADocument64 pagesENT Radiology AMitulsinh M RavaljiNo ratings yet
- PleureziileDocument18 pagesPleureziilep3tru_mzqNo ratings yet
- CXR Reading Made EasyDocument94 pagesCXR Reading Made EasyMiaMDNo ratings yet
- Local Exam 5Document68 pagesLocal Exam 5drnasir31No ratings yet
- DR Marcel Blok 18Document39 pagesDR Marcel Blok 18vaiyenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress HandoutDocument1 pageRespiratory Distress HandoutLuciaNo ratings yet
- Pns CT For Fess HandoutDocument14 pagesPns CT For Fess HandoutRonald Justin Joseph RagasaNo ratings yet
- Chest Interpretation in Emergency CaseDocument49 pagesChest Interpretation in Emergency CaseLuh Leni AriniNo ratings yet
- BST TraumaDocument41 pagesBST TraumavereriNo ratings yet
- DR Marcel Blok 18Document39 pagesDR Marcel Blok 18vaiyenNo ratings yet
- Clinical Radiology: The Thorax: Naveen Nair Gangadaran (0402005198)Document48 pagesClinical Radiology: The Thorax: Naveen Nair Gangadaran (0402005198)Chubii Luph DokhitNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)Document55 pagesAneurysm Final (Bentals Procedure)tejuteju067100% (1)
- Pleual ConditionsDocument61 pagesPleual ConditionsKandarp TrivediNo ratings yet
- Life Threatening Brain PathologiesDocument33 pagesLife Threatening Brain Pathologiesnithin shenoiNo ratings yet
- Chest Examination New SsDocument16 pagesChest Examination New SsNAINo ratings yet
- Respirations 1Document42 pagesRespirations 1api-3697326No ratings yet
- Lecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologyDocument94 pagesLecture - Dr. Subagia - Neuro RadiologySyaimee Annisa AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Neuroradiology: Dr. Dhanti Erma, SP - RadDocument64 pagesNeuroradiology: Dr. Dhanti Erma, SP - RadizzkibipNo ratings yet
- Chest X-RayDocument31 pagesChest X-RayPraneetha NouduriNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi Dasar Foto Thoraks: Basuki Rachmat ICU Anak PJN HK JakartaDocument42 pagesInterpretasi Dasar Foto Thoraks: Basuki Rachmat ICU Anak PJN HK JakartaMashudi SyaikhanNo ratings yet
- Benign Larnygeal LesionDocument6 pagesBenign Larnygeal Lesionwan amiera wan malekNo ratings yet
- Radiologic AssessmentDocument7 pagesRadiologic AssessmentEloisa Marie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Systematic in Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-RayDocument60 pagesSystematic in Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-RayDian Oktaria SafitriNo ratings yet
- 6 Radiology Under GraduateDocument80 pages6 Radiology Under GraduateJavier Gutiérrez CastilloNo ratings yet
- 1 Approachtoheadct 130418093230 Phpapp01Document71 pages1 Approachtoheadct 130418093230 Phpapp01Sikandar Shahzad YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiomegaly, CCF, Pulmonary EdemaDocument20 pagesCardiomegaly, CCF, Pulmonary EdemarajhiniNo ratings yet
- Survival Rad 15 - Lung HandoutDocument41 pagesSurvival Rad 15 - Lung HandoutLorraineYongNo ratings yet
- CHEST X-RayDocument82 pagesCHEST X-Raytarakeeshbai1802No ratings yet
- SurgeryspecimensDocument81 pagesSurgeryspecimensHimanshu BadjatyaNo ratings yet
- ENT RadiologiDocument70 pagesENT RadiologiyowwwNo ratings yet
- Thoracic 428 Edited2Document87 pagesThoracic 428 Edited2Mihary RamanandraitsioryNo ratings yet
- Radiology in ENT-1Document64 pagesRadiology in ENT-1SahilNo ratings yet
- NCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument128 pagesNCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Ent 1.02 Middle EarDocument3 pagesShanz - Ent 1.02 Middle EarPetrina XuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - LarynxDocument20 pagesLecture 7 - LarynxkotekingNo ratings yet
- By Prof - DR.: Ahmed AllamDocument84 pagesBy Prof - DR.: Ahmed Allamdrqazi777No ratings yet
- Scut Report: Chest X-RayDocument1 pageScut Report: Chest X-RayJames Booth100% (4)
- ICD Case 2: Clinical Clerk Ben Paolo C. RabaraDocument12 pagesICD Case 2: Clinical Clerk Ben Paolo C. RabaraBen Paolo RabaraNo ratings yet
- Respi 2Document11 pagesRespi 2Jeno SigamaniNo ratings yet
- Template (Mukmin)Document15 pagesTemplate (Mukmin)Amirul MukminNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies: Dr. Mark Louie M. LantingDocument64 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies: Dr. Mark Louie M. Lantinglouie10279098No ratings yet
- Tumors of The Head and NeckDocument5 pagesTumors of The Head and NeckMiguel CuevasNo ratings yet
- Sha00180 Cutason-5mg English Leaflet 175mmDocument1 pageSha00180 Cutason-5mg English Leaflet 175mmAgnesa MunishiNo ratings yet
- Mymaxicare Brochure 2022 1.5.22Document16 pagesMymaxicare Brochure 2022 1.5.22Charie GemaoNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsDocument31 pagesCare of Clients With Physiologic and Psychosocial AlterationsAesThetiC SagittariusNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia 2Document22 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia 2carosegurallNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument27 pagesAir PollutionJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray - Pulmonary Disease - Bronchiectasis and Cystic FibrosisDocument1 pageChest X-Ray - Pulmonary Disease - Bronchiectasis and Cystic FibrosisNang KhamNo ratings yet
- NMPST Month, Day, YeanmppkrDocument5 pagesNMPST Month, Day, Yeanmppkrsylvania heniNo ratings yet
- Target BeneficiariesDocument6 pagesTarget BeneficiariesTommy SoleraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan GraffitiDocument7 pagesLesson Plan GraffitiMeig Angelo CatiilNo ratings yet
- HSC4555 0001 Fall17 SyllabusDocument6 pagesHSC4555 0001 Fall17 SyllabusDilly RijoNo ratings yet
- BNB Syllabus 2020Document4 pagesBNB Syllabus 2020Hengame SJNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Resp DiseaseDocument28 pagesLecture Notes Resp DiseaseWan Razin Wan HassanNo ratings yet
- Rujuk MeiDocument180 pagesRujuk MeiGemma AyuNo ratings yet
- The Following Invitation Is For Question No 4-5Document4 pagesThe Following Invitation Is For Question No 4-5lissa rositaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1438463921000225 MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S1438463921000225 Mainrendiprasetya014No ratings yet
- Manual of Canine and Feline Cardiology PDFDocument450 pagesManual of Canine and Feline Cardiology PDFNovanAndrian100% (1)
- Syllab of Dip in Life Ins UnderwritingDocument17 pagesSyllab of Dip in Life Ins Underwritinganon_303912439100% (1)
- MRCP Part 1 SyllabusDocument18 pagesMRCP Part 1 SyllabusAggamemnon populosNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Biology Chapter 14 NotesDocument23 pagesClass 12 Biology Chapter 14 NotesSyed Atta Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Department Triage Prediction Ofclinical Outcomes Using Machine Learning Models PDFDocument13 pagesEmergency Department Triage Prediction Ofclinical Outcomes Using Machine Learning Models PDFOscar Julian Perdomo CharryNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Respiratory Disease A Case Study Approach To Patient Care 3rd Edition Wilkins PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Respiratory Disease A Case Study Approach To Patient Care 3rd Edition Wilkins PDF Full Chapterondogram.betulinpwl1gz100% (20)
- Raw Q3 Las 1Document15 pagesRaw Q3 Las 1Abegail CastilloNo ratings yet
- KNR University of Health Sciences: Telangana: Some of The Dissertations Topics Submitted For The Year 2016,2017Document337 pagesKNR University of Health Sciences: Telangana: Some of The Dissertations Topics Submitted For The Year 2016,2017Movie addictNo ratings yet
- After Effects of COVID 19 and Repair of LungsDocument13 pagesAfter Effects of COVID 19 and Repair of LungsAthenaeum Scientific PublishersNo ratings yet
- Ena Respiratory EmergenciesDocument30 pagesEna Respiratory Emergencieseng78ineNo ratings yet
- ERS MONOGRAPH - PULMONARY MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES/ Artritis ReumatoideaDocument24 pagesERS MONOGRAPH - PULMONARY MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES/ Artritis ReumatoidearocioanderssonNo ratings yet
- Healing The LungsDocument59 pagesHealing The LungsJeesuNo ratings yet
- Educational Case Asthma Clinical Features and MorpDocument5 pagesEducational Case Asthma Clinical Features and MorpZhailyn Joy DumlaoNo ratings yet