Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L.O 9
L.O 9
Uploaded by
hassan hamedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L.O 9
L.O 9
Uploaded by
hassan hamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Earth’s Natural Resources
Section 1 Electricity and Your Community
What Do You See?
Learning Outcomes Think About It
In this section, you will Electricity is a key part of life in the United States. Factories,
• Compare energy resources stores, schools, homes, and most recreational facilities depend
used to generate electricity upon a supply of electricity. The unavailability of electricity
in the United States to other
almost always makes the news.
countries.
• Identify the major energy • What is electric energy?
sources used to produce
• What are some consequences of not having electricity when
electricity in the United
States and your state.
it is needed?
• Identify trends and patterns Record your ideas about these questions in your Geo log. Be
in electricity generation. prepared to discuss your responses with your small group
• Understand the difference and the class.
between electric power and
electric energy.
Investigate
• Describe commonly used
methods of generating Part A: Global and United States Electricity Generation
electric power.
1. Use the data table showing world net electricity generation
by type to answer the questions on the following page.
726
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 726 7/13/11 12:25:13 PM
Section 1 Electricity and Your Community
Table 1: World Net Electricity Generation by Type, 2008 (in billion-kilowatt hours)
Region Geothermal
Fossil Fuels Hydropower Nuclear Total
Country and Other1
North America
Canada 152.706 378.644 89.253 11.723 632.326
Mexico 189.689 38.786 9.314 7.727 245.516
United States 2926.731 254.831 806.208 137.905 4125.675
The Caribbean and South America
Bolivia 3.547 2.258 0.000 0.177 5.982
Brazil 55.633 365.861 13.970 19.366 454.830
Puerto Rico 20.765 0.156 0.000 0.000 20.921
Venezuela 31.425 86.705 0.000 0.000 118.130
Western Europe
France 51.644 63.089 417.495 11.528 543.756
Spain 178.164 23.265 56.024 37.169 294.622
Switzerland 0.844 35.676 26.315 2.329 65.164
United Kingdom 290.975 5.116 49.862 17.171 363.124
Eastern Europe and Former U.S.S.R.
Bulgaria 24.306 2.796 14.742 0.131 41.975
Romania 34.316 17.023 10.662 0.028 62.029
Russia 665.115 163.115 154.176 2.863 985.269
Middle East
Cyprus 4.696 0.000 0.000 0.013 4.709
Saudi Arabia 191.948 0.000 0.000 0.000 191.948
Africa
Angola 0.140 3.804 0.000 0.000 3.944
Egypt 108.501 14.535 0.000 0.884 123.920
Ethiopia 0.439 3.263 0.000 0.013 3.715
Morocco 18.421 0.920 0.000 0.283 19.624
Far East and Oceania
China 2618.558 522.423 65.325 14.875 3221.181
Japan 667.942 75.477 245.222 28.513 1017.154
Malaysia 84.536 7.384 0.000 0.001 91.921
Mongolia 3.896 0.000 0.000 0.000 3.896
Nepal 0.010 3.042 0.000 0.000 3.052
1
Geothermal and Other consists of geothermal, solar, wind, wood, and waste generation.
Source: Adapted from the Energy Information Administration/International Energy Annual 2009 report
a) List the three countries that generate d) What type of electricity generation is
the most electricity. used most by these areas? Which type
is used least?
b) What type of electricity generation is
used most by these areas? Which type e) How do the resources for electricity
is used least? generation differ between the top
and bottom regions? How do you
c) List the three countries that generate
account for the differences?
the least electricity.
727
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 727 7/13/11 12:25:14 PM
Chapter 7 Earth’s Natural Resources
2. Consider electricity generation by b) What energy resources are used to
fuel type. generate electricity in your state?
a) Without including the United States, c) Which energy resource does your
rank global electricity generation by state depend upon the most to
fuel type from highest to lowest. generate electricity?
b) Rank United States electricity d) What are the trends in energy
generation by fuel type from resource use for electric power
highest to lowest. generation in your state over time?
c) How does the electricity generation e) How has the generation of electricity
in the United States match global changed in your state over time?
electricity generation? Why do you How much has it grown in the most
think this is so? recent 10-year period? What is the
annual rate of growth?
3. Devise a way to represent the data for
the United States graphically (either a f) How does the growth in electricity
pie chart or a histogram). generation in your state compare to
the rate of population growth in your
a) Complete your graph in your
state? How might you explain the
Geo log.
relationship between them?
Part B: Investigating Electricity g) How do the types of resources
Generation in Your State used by your state for electricity
1. Go to the EarthComm Web site at generation compare with the averages
http://www.agiweb.org/education/ for the world and the United States,
earthcomm2/ to visit the Department which you looked at in Part A?
of Energy’s Energy Information h) What sector (residential, commercial,
Administration Web page. Click industrial, or other) consumes the
on your state to obtain your “state most energy for electricity in your
electricity profile.” Use the information state? What sector consumes the
to answer the following questions: least energy?
a) Is your state a net importer or net i) What resources does your state
exporter of electricity? What does use most for residential and
this mean? commercial purposes? For
transportation? For industry?
2. Review the data and figures for the
electricity profile for your state.
a) How do they help you to meet your
Chapter Challenge?
728
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 728 7/13/11 12:25:14 PM
Section 1 Electricity and Your Community
Digging Deeper
MEETING ELECTRICITY NEEDS
Energy Resources
The world’s population continues to grow. This means that the need for
energy will likely grow as well. Energy is needed for heating or cooling.
It is needed to generate electricity. It is used in industrial processes. It
is also used for transportation. Different energy resources can be used
for many different purposes. Energy resources include coal, natural Geo Words
gas, and petroleum. Hydropower, nuclear fission, solar, wind, waste nuclear fission: the
biomass, wood, and oceanic power are other sources. Nuclear fusion has process by which an
atomic nucleus splits
been proposed as the long-term source. However, the progress made in into two or more
research to make this possible has been very slow. large fragments of
comparable mass,
simultaneously
producing additional
neutrons and vast
amounts of energy.
nuclear fusion: a
nuclear process that
releases energy when
lightweight nuclei
combine to form
heavier nuclei.
electric power:
power associated
with the generation
and transmission of
electricity.
electric energy:
energy associated
with the generation
and transmission of
electricity.
Figure 1 Nuclear power can come from the fission of uranium, plutonium, or
thorium or the fusion of hydrogen into helium.
Generating Electric Energy
Energy resources are used to generate electricity. Electricity is an energy
source with which you are very familiar. Electric power is the rate at
which electricity does work. It is measured at a point in time. The unit of
measure for electric power is a watt (W). The rate at which an appliance
transforms electric energy is called its capacity. You can check the tags
or labels on electrical appliances for this information. For example, you
might see a “1200-W hair dryer” or “40-W stereo receiver.” Electric
energy is the amount of work that can be done by electricity. Its unit
of measure is the watt-hour (Wh). A 1200-W hair dryer used for 15 min
would require 300 Wh of electric energy.
729
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 729 7/13/11 12:25:14 PM
Chapter 7 Earth’s Natural Resources
Geo Words
fossil fuel: fuel Fossil fuels can be burned to generate electricity. Fossil fuels supply about
derived from 70 percent of the electricity in the United States. Coal, petroleum, and
materials (mainly natural gas are examples of fossil fuels. They are the main ones used by the
coal, petroleum, and
natural gas) that were electrical power industry. When these fuels are burned, a variety of gases
generated from fossil and particles are formed. Pollution-control equipment can be used to catch
organic matter and these. If they are not caught, they are let out into the atmosphere. Other
stored deep in Earth sources of energy can also be used for electricity. These sources include
for geologically long
times. water, geothermal energy, solar thermal energy, photovoltaic energy,
geothermal energy: and biomass. They have many advantages over fossil fuels.
energy derived from
hot rocks and/or
Fossil Fuels and Nuclear Energy
fluids beneath Earth’s Most of the electricity in the United States is produced in steam turbines.
surface.
A turbine converts the kinetic energy of a moving fluid (liquid or gas) to
photovoltaic energy: mechanical energy. In a fossil-fueled steam turbine, the fuel is burned in
energy associated
with the direct a boiler to produce steam. The steam then turns the turbine blades. The
conversion of solar blades turn the shaft of the generator to produce electricity. In a nuclear-
radiation powered steam turbine, a reactor replaces the boiler. The reactor contains
to electricity. a core of nuclear fuel. (The fuel is mostly enriched uranium.) The fission of
turbine: a rotating uranium produces the heat in the reactor. The heat is used to make steam.
machine or device
that converts the The steam is then passed through the turbine generator to produce
mechanical energy electricity. This is the same as what occurs in the fossil-fueled steam
of fluid flow into turbine. Figure 2 shows the nuclear power plant locations and uranium
mechanical energy of resources available in the United States.
rotation of a shaft.
Figure 2 The location of nuclear power plants and uranium
resources in the continental United States.
730
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 730 7/13/11 12:25:14 PM
Section 1 Electricity and Your Community
Hydroelectric Power Geo Words
Water is the top renewable resource used to generate electric power. renewable resource: a
Hydroelectric power is generated when flowing water spins a turbine. resource that can be
The turbine is connected to a generator. Hydroelectric plants are located replaced in nature at
a rate close to its rate
where suitable waterways are available. Many of the best of these sites of use.
have already been developed. (Figure 3 shows the hydroelectric plants hydroelectric power:
developed in the United States.) Seventy percent of the hydroelectric electrical power
power in the United States is generated in the Pacific and Rocky derived from the flow
Mountain states. There are two basic types of hydroelectric systems. One of water on Earth’s
surface.
is based on falling water. The other is based on a natural river current.
In a falling-water system, water builds up in reservoirs created by dams.
This water then falls through large pipes. The falling water applies
pressure against the turbine blades. The blades drive the generator to
produce electricity. The second system is called a run-of-the-river system.
In it, the force of the river current applies pressure to the turbine blades
to produce electricity. Because they do not store water, these systems
depend upon seasonal changes and stream flow.
Using water to generate electricity has advantages. Water is a renewable
resource and is a source of cheap power. Compared to fossil fuels,
there is little air pollution. That is because there is no fuel combustion.
Also, there is limited thermal pollution compared to nuclear plants.
Hydroelectric power plants can start generating electricity quickly.
They do not need to wait for water to be heated into steam. Also, the
flow of water can be adjusted to make quick changes in power output
during peak demands for electricity. Like other energy sources, the
use of water has
drawbacks. These
include impacts on
the environment
caused by damming
rivers and streams.
Dams affect the
habitats of the
local plants and
animals. Another
drawback to some
hydroelectric power
plants is that they
depend upon the
flow of water.
This can vary with
seasons and during
droughts. Figure 3 The location of hydroelectric power plants relative
to major waterways in the continental United States.
731
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 731 7/13/11 12:25:15 PM
Chapter 7 Earth’s Natural Resources
Other Resources Used to Generate Electricity
At this time, renewable resources (other than water) and geothermal
Geo Words energy supply less than 4 percent of the electricity generated by electric
nonrenewable companies. Renewable resources include solar, wind, and biomass power.
resource: a resource
(Biomass consists of wood, municipal solid waste, agricultural waste, and
that exists in a fixed
amount or is used so on.) Although geothermal energy is a nonrenewable resource, it will
faster than it can be not run out. It comes from heat energy buried beneath the surface of
replaced in nature. Earth. Most of this heat is at depths beyond current drilling methods. In
some areas of the country, magma flows close enough to the surface of
Earth to produce steam. That steam can then be used in steam-turbine
Checking Up plants. Figure 4 shows the locations of geothermal plants within the
1. What is the United States. Most are found in the western United States. There, magma
difference between
is close enough to the surface to supply steam.
electric energy and
electric power?
2. Compare and
contrast steam
turbine versus
hydroelectric
power generation.
How are they
similar? How are
they different?
3. From an
Earth systems
perspective, what
are the advantages
and disadvantages
of hydroelectric
power?
4. In your own
words, explain
why biomass and Figure 4 The location of geothermal power plants and source
wind are called temperatures in continental United States.
renewable energy
sources.
Think About It Again
At the beginning of this section, you were asked the following:
• What is electric energy?
• What are some consequences of not having electricity when it is needed?
Record your ideas about these questions now. Refer to the various energy
resources used to generate electricity in your answer.
732
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 732 7/13/11 12:25:15 PM
Section 1 Electricity and Your Community
Reflecting on the Section and the Challenge
In this section, you looked at the different types of resources that are used to generate
electricity in the United States and around the world. You also investigated the trends in
energy resource use and electricity generation in your state. Knowing where and how your
state uses energy resources to generate electricity will help you to think about how to meet
the energy needs of an expanding population.
Understanding and Applying
1. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions about the generation of
electricity in the United States:
a) Which of the energy sources listed are nonrenewable? What percentage of energy
consumed to produce electricity in 2009 did they represent?
b) Which of the energy sources listed are renewable? What percentage of energy
consumed to produce electricity in 2009 did they represent?
c) Compare the value for energy consumed to produce electricity versus gross
generation of electricity in 2009. What is the overall efficiency of electricity
generation systems in the United States?
d) Conversion losses accounted for 24.61 “quads” of the energy consumed to generate
electricity. Explain what this means in relation to your answer to Question 3.c).
733
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 733 7/13/11 12:25:15 PM
Chapter 7 Earth’s Natural Resources
2. Converting one form of energy into another comes with a loss in usable energy (waste
heat). The “net efficiency” of a multi-step process is the product of the efficiencies of
each step. For example, if each step in a two-step process was 50 percent efficient, the
net efficiency would be (0.50 × 0.50) = 0.25 = 25 percent.
a) Use the information below to calculate the net efficiency of a home water heater.
b) The lowest efficiency of this process is the generation of electricity. Why do you
think this is so?
Step Efficiency (in percent)
Production of coal 96
Transporting coal to power plant 97
Generating electricity 33
Transmission of electricity (from plants to homes) 85
Heating efficiency of the hot water heater 70
Net Efficiency ?
3. Each year, the United States uses more than 71 trillion Btu of solar energy. One
million Btu equals 90 lb of coal or 8 gallons of gasoline.
a) How many metric tons (2204.62 lb) of coal per year does this equate to?
b) How many gallons of gasoline does this equate to?
c) If the United States increased its use of solar energy 5 percent annually, how many
metric tons of coal would this equate to during the next 10 years?
4. Preparing for the Chapter Challenge
Write a short paper in which you review the energy resources used in your community
and how their use affects your community. Be sure to include information on how
energy resources are used to generate electricity and fuel in your community, which
of the current means of producing power your community relies on most, and which
seems the least important. This paper will help you to think about what resources your
community is using before the population increase.
Inquiring Further
1. Storage of solar energy
Electricity from solar energy offers a clean, reliable, and renewable source of energy for
home use. Batteries are used to store electrical energy for use at night or when bright
sunlight is not available. Research recent advances in technologies used to store solar
energy. How do car batteries perform in comparison to solar batteries in solar systems?
Present your report to the class.
734
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 734 7/13/11 12:25:15 PM
Section 1 Electricity and Your Community
2. Energy from the oceans
Three novel ways have been proposed to use the energy of the oceans for electrical
generation: tides, waves, and vertical temperature differences. Choose one of these,
and research the theory and techniques involved in its use for generating electricity.
3. Other methods of generating electricity
Research one of the following methods of generating electricity. How do they work?
Where are they being used? What are the ideal conditions for using these alternatives?
What are the advantages of these methods over fossil fuels? What are the disadvantages
or limitations? Visit the EarthComm Web site at http://www.agiweb.org/education/
earthcomm2/ for sources of information.
• photovoltaics
• geothermal
• solar thermal
The Rance Tidal Power System in France has been operating since 1966 and is the first tidal
power station.
735
EarthComm
EC_Natl_SE_C7.indd 735 7/13/11 12:25:15 PM
You might also like
- Soorya Bala SangramayaDocument4 pagesSoorya Bala SangramayaSaurabh Himkar100% (1)
- CoalDocument29 pagesCoalrashmi sahooNo ratings yet
- Book 5Document3 pagesBook 5anonyeNo ratings yet
- Inustrial Structure of Power Sector in India: Sr. No. Topic No. Topic Details No. 1Document15 pagesInustrial Structure of Power Sector in India: Sr. No. Topic No. Topic Details No. 1malini72No ratings yet
- Space and Climate ChangeDocument30 pagesSpace and Climate ChangeHammadNo ratings yet
- ISO Country Code WORLD TOTAL Others (IndividualsDocument46 pagesISO Country Code WORLD TOTAL Others (Individualsapi-26006336No ratings yet
- Sector-Level Energy Demand Decomposition (EXAMPLE)Document2 pagesSector-Level Energy Demand Decomposition (EXAMPLE)Goh Kay YunNo ratings yet
- 5.developed and Underdevelped CountriesDocument16 pages5.developed and Underdevelped CountriesNishantNo ratings yet
- World-Wide Direct Uses of Geothermal Energy 2000: John W. Lund, Derek H. FreestonDocument40 pagesWorld-Wide Direct Uses of Geothermal Energy 2000: John W. Lund, Derek H. FreestonGloria Luciana Muñoz VillalobosNo ratings yet
- 195 Countries in The WorldDocument9 pages195 Countries in The WorldpradeepNo ratings yet
- GDP Per CapitaDocument481 pagesGDP Per CapitaShree KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- What's App PricingDocument2 pagesWhat's App PricingSATISH WORDBOXNo ratings yet
- GDP 2017Document4 pagesGDP 2017khanhhuyen4979No ratings yet
- World Data SetDocument2 pagesWorld Data SetJ HerbertNo ratings yet
- Eurostat - Electricity From Renew. 2011-2020Document10 pagesEurostat - Electricity From Renew. 2011-2020pierucci93No ratings yet
- New Consumption TableDocument2 pagesNew Consumption TableAldo BontáNo ratings yet
- India Is The Largest CountryDocument2 pagesIndia Is The Largest CountryJagdish BendkarNo ratings yet
- Portfolio ContempDocument12 pagesPortfolio ContempJim Russel SangilNo ratings yet
- Notes 5 Soil DegradationDocument10 pagesNotes 5 Soil DegradationJohn BildanNo ratings yet
- World Is Open For BusinessDocument37 pagesWorld Is Open For BusinessSajjad HussainNo ratings yet
- The World Is Open For Business. Yours.: An Overview of The U.S. Commercial ServiceDocument37 pagesThe World Is Open For Business. Yours.: An Overview of The U.S. Commercial ServiceSyaibatul HamdiNo ratings yet
- US Exports OverviewDocument22 pagesUS Exports OverviewRaza AliNo ratings yet
- EnergyConsumption 2022Document687 pagesEnergyConsumption 2022Sladjan UgrenovicNo ratings yet
- G Berbari GEC 2012 Presentation Rev 2Document46 pagesG Berbari GEC 2012 Presentation Rev 2mohamadNo ratings yet
- Vaccinations MetabaseDocument11 pagesVaccinations MetabaseAnand Anubhav DataAnalyst Batch48No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th Edition-1021-1030Document10 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 7th Edition-1021-1030Andres Eduardo Diaz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Mechatronics and Electronics, Lac Hong University, Bien Hoa, VietnamDocument23 pagesFaculty of Mechatronics and Electronics, Lac Hong University, Bien Hoa, VietnamMạnh KhangNo ratings yet
- GDP CountryDocument2 pagesGDP CountryPratik DodiaNo ratings yet
- Description: Tags: Fws-ReadingDocument2 pagesDescription: Tags: Fws-Readinganon-179223No ratings yet
- State Bank of Pakistan: Statistics and Data Warehouse DepartmentDocument2 pagesState Bank of Pakistan: Statistics and Data Warehouse DepartmentMuhammad Babar ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Introduction To Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument2 pagesAssignment 3 Introduction To Financial Markets and InstitutionsVenkatNo ratings yet
- Tablas White Flujo de FannoDocument5 pagesTablas White Flujo de FannoCarlos Alejandro Mendoza SilvaNo ratings yet
- TablasDocument8 pagesTablasDavid PiscoyaNo ratings yet
- List Countries by Past and Projected Gross Domestic Product (Nominal) Per Capita Estimates Between 2010 and 2019Document1 pageList Countries by Past and Projected Gross Domestic Product (Nominal) Per Capita Estimates Between 2010 and 2019Anandashifa FauziahNo ratings yet
- PA8 SolutionDocument21 pagesPA8 SolutionHelenNo ratings yet
- Countries in The WorldDocument10 pagesCountries in The WorldKaveriNo ratings yet
- SJ PDF 1 JTR 10.1177 - 00472875211036194Document8 pagesSJ PDF 1 JTR 10.1177 - 00472875211036194imam fachriNo ratings yet
- 03 Presentation Adriana RoldanDocument33 pages03 Presentation Adriana RoldanJoshMooreNo ratings yet
- Book TGT Solar AllDocument36 pagesBook TGT Solar AllAsad Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Proprieta' Termiche Dell'Aria A Elevate Temperature: Thermal Properties of Air at Elevated TemperaturesDocument1 pageProprieta' Termiche Dell'Aria A Elevate Temperature: Thermal Properties of Air at Elevated TemperaturesSebastian Rodrigo Octaviano0% (1)
- Optical Distortion, Inc. (A)Document8 pagesOptical Distortion, Inc. (A)SergiNo ratings yet
- Description: Tags: Recip-FseogDocument2 pagesDescription: Tags: Recip-Fseoganon-405829No ratings yet
- Forty Key Trends For The Next DecadeDocument23 pagesForty Key Trends For The Next DecadeVivekNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Solar FirmsDocument7 pages2.2 Solar FirmsBuddy The LabNo ratings yet
- Total GDP 2006: (Millions of Ranking Economy US Dollars)Document4 pagesTotal GDP 2006: (Millions of Ranking Economy US Dollars)420No ratings yet
- Book 4Document6 pagesBook 4anonyeNo ratings yet
- MalaBabaganaGutti LevellingSurveyDocument12 pagesMalaBabaganaGutti LevellingSurveyyosuf ShazadaNo ratings yet
- Country, Total Cse NW Cse TTL Dths Recovered Active: World 1,763,577 64,742 107,779 397,053 1,258,745Document13 pagesCountry, Total Cse NW Cse TTL Dths Recovered Active: World 1,763,577 64,742 107,779 397,053 1,258,745Abdulsaboor ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Renewable DieselDocument5 pagesRenewable DieselShin ShinNo ratings yet
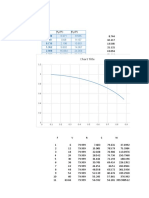
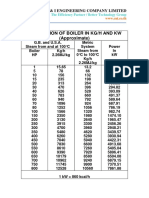
- KB - Conversion of Boiler in KGDocument2 pagesKB - Conversion of Boiler in KGChiragNo ratings yet
- AMR AsnmntDocument14 pagesAMR Asnmntsnjb13459969No ratings yet
- Stowage Factor Conversion TableDocument3 pagesStowage Factor Conversion TableGary LampenkoNo ratings yet
- Largest Countries in The WorldDocument6 pagesLargest Countries in The WorldSATHIASEELAN SIVANANDAM, AdvocateNo ratings yet
- Please Read: An Urgent Appeal From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy WalesDocument6 pagesPlease Read: An Urgent Appeal From Wikipedia Founder Jimmy WalesPradeep TiwariNo ratings yet
- Loans Outstanding of Universal and Commercial BanksDocument56 pagesLoans Outstanding of Universal and Commercial BankszpmellaNo ratings yet
- Sector-Level Energy Intensity Decomposition (EXAMPLE)Document3 pagesSector-Level Energy Intensity Decomposition (EXAMPLE)Goh Kay YunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document27 pagesChapter 14moniqueNo ratings yet
- Población Según El FMIDocument14 pagesPoblación Según El FMIAlexVianaNo ratings yet
- Global Registrations or Sales of New Vehicles - All Types: Jan-June 2020 Jan-June 2021Document11 pagesGlobal Registrations or Sales of New Vehicles - All Types: Jan-June 2020 Jan-June 2021Sanket PawarNo ratings yet
- United States Census Figures Back to 1630From EverandUnited States Census Figures Back to 1630No ratings yet
- Earth and Space Science Model 2019Document16 pagesEarth and Space Science Model 2019hassan hamedNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For ES.3.08 (STEM Elfayoum)Document11 pagesLesson Plan For ES.3.08 (STEM Elfayoum)hassan hamedNo ratings yet
- L.O 12Document15 pagesL.O 12hassan hamedNo ratings yet
- L.O 11Document13 pagesL.O 11hassan hamedNo ratings yet
- Revisiog 10Document6 pagesRevisiog 10hassan hamedNo ratings yet
- EU Renewable Energy Directive RevisionDocument10 pagesEU Renewable Energy Directive RevisionThe International Council on Clean TransportationNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Annual Repor - 022Document103 pagesCaterpillar Annual Repor - 022Sandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- PV DatasheetDocument5 pagesPV DatasheetRafdi Dzulfikar RNo ratings yet
- Asia 2020Document16 pagesAsia 2020meldi suhatrilNo ratings yet
- 3.3-12KW - India - COC-IEC 62116 IEC61727Document2 pages3.3-12KW - India - COC-IEC 62116 IEC61727firas abou sharafNo ratings yet
- Micro GridsDocument23 pagesMicro GridsJin JiangNo ratings yet
- Green Banking Report - Final PDFDocument46 pagesGreen Banking Report - Final PDFSelim KhanNo ratings yet
- Sample PBLDocument10 pagesSample PBLMABINI Hanna SchaneNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions On Energy-Ktustudents - inDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On Energy-Ktustudents - insruthyNo ratings yet
- Airport Solar Guide Print PDFDocument162 pagesAirport Solar Guide Print PDFraduNo ratings yet
- 1) A Leader Is Born Not Made: The More Knowledge You Gain, The More Enlightened Your Vision Becomes"Document32 pages1) A Leader Is Born Not Made: The More Knowledge You Gain, The More Enlightened Your Vision Becomes"poorvika natarajNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Applications of MCADocument32 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Applications of MCACamilaNo ratings yet
- People's Republic of Bangladesh Preparatory Survey On Renewable Energy Development Project Final ReportDocument310 pagesPeople's Republic of Bangladesh Preparatory Survey On Renewable Energy Development Project Final ReportShahin NescoNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Technologies (Elective) Sample Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document4 pagesRenewable Energy Technologies (Elective) Sample Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Lakshman Naik100% (1)
- Ppa Status List PDFDocument4 pagesPpa Status List PDFIts meNo ratings yet
- Electric Cars in NZ-mastersthesisDocument240 pagesElectric Cars in NZ-mastersthesisnzekdahlNo ratings yet
- Joint Initiative of Govt of India and OrissaDocument70 pagesJoint Initiative of Govt of India and OrissaPuspak MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Final Report TemplateDocument13 pagesFinal Report TemplateRias SahulNo ratings yet
- Does Renewable Electricity Supply Match With Energy Demand 1-S2.0-S0306261921014914-MainDocument20 pagesDoes Renewable Electricity Supply Match With Energy Demand 1-S2.0-S0306261921014914-MainCarlos PintoNo ratings yet
- Future Northwest Capacity Shortages by Randy Hardy and Larry Kitchen I. Recent Events Affecting The Mid-Term Pacific Northwest (PNW) Capacity OutlookDocument8 pagesFuture Northwest Capacity Shortages by Randy Hardy and Larry Kitchen I. Recent Events Affecting The Mid-Term Pacific Northwest (PNW) Capacity OutlookIan ClarkNo ratings yet
- Project 1Document9 pagesProject 1Karthikeyan AnbalganNo ratings yet
- Stem B Group 9 Final Capstone Paper 5 1 PDFDocument64 pagesStem B Group 9 Final Capstone Paper 5 1 PDFYuan Andrei Santos100% (2)
- Hydroreview201407 DLDocument140 pagesHydroreview201407 DLErick PerezNo ratings yet
- Presentation-4 - Flexibility of Thermal Power Plants - v2 - FPE - V2Document77 pagesPresentation-4 - Flexibility of Thermal Power Plants - v2 - FPE - V2Juniko ParhusipNo ratings yet
- Nep 2022 32 Final Gazette-1Document316 pagesNep 2022 32 Final Gazette-1Anomitra SarkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - WorkbookDocument10 pagesUnit 5 - WorkbookMaii MendiiölaNo ratings yet
- Owerri 2.5kva Solar SoutionDocument1 pageOwerri 2.5kva Solar SoutionFetuga AbiodunNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Temperature On The Performance of A Photovoltaic Solar System in Eastern NigeriaDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Temperature On The Performance of A Photovoltaic Solar System in Eastern NigeriainventyNo ratings yet