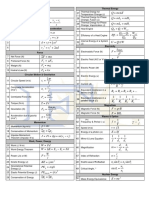
0625 IGCSE Physics Formula Sheet
Cosmo
April 22, 2024
Contents
1 General Physics 2
1.1 Force . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.2 Motion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.3 Density . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.4 Momentum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.5 Hooke’s Law . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.6 Moments Of Force . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.7 Energy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.8 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.9 Efficiency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.10 Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.11 Collisions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Thermal Physics 5
2.1 Kelvin Conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.2 Boyle’s Law . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.3 Heat Energy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3 Waves 6
3.1 Wave Formula . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.2 Law of Reflection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4 Electricity 6
4.1 Circut Formulae . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4.2 Resistors in Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4.3 Resistors in Parallel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4.4 Transformer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
5 Astrophysics 7
5.1 Orbital Velocity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
5.2 Hubble Constant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1
�1 General Physics
1.1 Force
F = ma
W = mg
F →
− force (N )
m→
− mass (kg)
− acceleration (m/s2 )
a→
W →
− weight (N )
− acceleration due to freefall // gravitational field strength (m/s2 )
g→
1.2 Motion
d
v=
t
dtotal
vaverage =
ttotal
v→
− velocity/speed (m/s)
d→
− displacement/distance m
t→
− time taken (s)
1.3 Density
m
ρ=
V
− density (kg/m3 )
ρ→
− volume (m3 )
V →
m→
− mass (kg)
2
�1.4 Momentum
p = mv
p
F =
t
I = Ft
p→
− momentum (kgm/s)
v→
− velocity/speed (m/s)
m→
− mass (kg)
F →
− force (N )
t→
− time taken (s)
I→
− impulse (N s)
1.5 Hooke’s Law
F = kx
F →
− force (N )
k→
− spring constant (N/m)
x→
− extension (m)
1.6 Moments Of Force
Moment = F d
F →
− force (N )
d→
− distance (m)
1.7 Energy
1
Ek = mv 2
2
EGP = mgh
W = Fd
Ek →
− kinetic energy (J)
EGP →
− gravitational potential energy (J)
W →
− work done (J)
3
� F →
− force (N )
d→
− distance (m)
v→
− velocity/speed (m/s)
m→
− mass (kg)
− acceleration due to freefall // gravitational field strength (m/s2 )
g→
h→
− height (m)
1.8 Power
E
P =
t
W
P =
t
P →
− power (W )
W →
− work done (J)
E→
− energy (J)
t→
− time taken (s)
1.9 Efficiency
NOTE: The symbol for efficiency is η, however you are not required to know
this, I have used it purely for simplicity.
useful energy output
η=
useful energy input
useful power output
η=
useful power input
Remember to multiply by 100 to convert to a percentage if needed.
1.10 Pressure
F
p=
A
p = ρgh
− pressure (N/m2 )
p→
F →
− force (N )
− area (m2 )
A→
− acceleration due to freefall // gravitational field strength (m/s2 )
g→
h→
− height (m)
4
�1.11 Collisions
m1 u1 + m2 u2 = m1 v1 + m2 v2
v→
− velocity/speed (m/s)
m→
− mass (kg)
2 Thermal Physics
2.1 Kelvin Conversion
T = θ + 273
T →
− temperature in Kelvin (K)
θ→
− temperature in degrees celsius
2.2 Boyle’s Law
pV = constant
p1 V1 = p2 V2
− pressure (N/m2 )
p→
− volume (m3 )
V →
2.3 Heat Energy
Q = mc∆θ
Q→
− heat energy (J)
m→
− mass (kg)
c→
− specific heat capacity (J/kg deg C
θ→
− temperature in degrees celsius
5
�3 Waves
3.1 Wave Formula
v = fλ
1
T =
f
v→
− velocity/speed (m/s)
f→
− frequency (Hz)
λ→
− wavelength (m)
T →
− time period (s)
3.2 Law of Reflection
i=r
r→
− angle of reflection
i→
− angle of incidence
4 Electricity
4.1 Circut Formulae
Q
I=
t
V
R=
I
V = IR
P =VI
V2
P =
R
P = I 2R
E = IV t
E = Pt
I→
− current (A)
6
� V →
− voltage (V )
R→
− resistance (Ω)
P →
− power (W )
E→
− energy (J)
t→
− time taken (s)
4.2 Resistors in Series
R = R1 + R2 + ... + Rn
R→
− resistance (Ω)
4.3 Resistors in Parallel
1 1 1 1
= + + ... +
R R1 R2 Rn
R→
− resistance (Ω)
4.4 Transformer
Pin = Pout
Vp Np Is
= =
Vs Ns Ip
P →
− power (W)
V →
− voltage in primary (P) or secondary (S) (V)
I→
− current in primary (P) or secondary (S) (A)
N→
− number of turns in primary (P) or secondary (S)
5 Astrophysics
5.1 Orbital Velocity
2πr
v=
T
v→
− orbital velocity/speed (m/s)
r→
− orbital radius (m)
T →
− orbital time period (s)
7
�5.2 Hubble Constant
v = Ho d
Ho →
− hubble constant
v→
− recession speed (m/s)
d→
− distance from galaxy (m)