Chem 114 Worksheet: Calorie Counting
The human body consumes food as source of energy to fuel the system for its daily activities.
We get different amounts of energy from different types of food and drinks and this energy is
measured in terms of Calorie. An ideal daily intake of calories varies depending on age,
metabolism and levels of physical activity, among other things. Below is an estimate of amounts
of calories needed to maintain energy balance for various gender and age groups at three
different levels of physical activity. This is based on Estimated Energy Requirements (EER) from
the Institute of Medicine Dietary Reference Intakes macronutrients report.
Table 1. Estimated calorie needs for energy balance
b
Sedentary: light physical activity associated with typical day-to-day life
c
Moderately active: includes physical activity such as walking about 1.5-3mi per day at 3-4mi per
hour, in addition to the light physical activity associated with typical day-to-day life
d
Active: includes physical activity more than that of moderately active, in addition to the light
physical activity associated with typical day-to-day life.
Caloric intake can also affect how we maintain, gain or lose body weight. However, this is not the
sole factor to consider when making up your diet plans. Still, you may consider monitoring your
caloric counts to see if you are consuming enough for what your body requires. Food packages
contain nutrition labels which states the amount of calorie per serving for a specific food product.
There are also websites and apps that can be used for calorie counting and monitoring.
In this activity, you will monitor your daily calorie intake by listing down the foods and drinks you
consume for 5 days. A worksheet is provided where you will write the foods and drinks you had
per meal. You will compute for your daily caloric intake by referring to product labels of foods or
you can also go to https://www.myfitnesspal.com/food/search and enter the food you need to
search including the serving sizes.
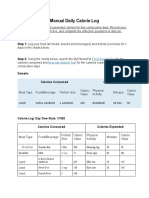
�Chem 114 Lab Worksheet: Calorie Counting
Name: _____________________________
Year and Section: _____________
Directions: List down the foods and drinks you had per meal and the corresponding calories.
Compute for the total daily calorie intake and compare this with your ideal calorie intake based on
Table 1.
Calorie Count Tracker
Total
Breakfast Lunch Dinner Snacks Calorie
Count
Day 1
Day 2
Day 3
Day 4
Day 5
� Average Calorie Count
Problems on Calorimetry
Directions: Show your complete solution for each question the box or encircle your final answers.
1. How much heat, in Joules, must be added to a 500-g iron skillet pan to increase its
temperature from 25 °C to 250 °C? The specific heat of iron is 0.451 J/g °C.
2. A 1.0 g of fructose, a sugar commonly found in fruits, is burned in a bomb calorimeter. The
temperature of the calorimeter increases by 1.58 °C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter
and its contents is 9.90 kJ/°C, what is q for this combustion?
3. A teaspoon of common sugar contains 16 Calories (16 kcal). What is the mass of one
teaspoon if the average number of Calories for carbohydrates is 4.1 Calories/g?
4. A serving of a breakfast cereal contains 3 g of protein, 18 g of carbohydrates, and 6 g of fat.
What is the Calorie content of a serving of this cereal if the average number of Calories for fat
is 9.1 Calories/g, for carbohydrates is 4.1 Calories/g, and for protein is 4.1 Calories/g?