Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TLE Transes
TLE Transes
Uploaded by
jozelpiedraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TLE Transes
TLE Transes
Uploaded by
jozelpiedraCopyright:
Available Formats
Meat t.l.e. : cookery 10 s.y.
2023-2024
Introduction of meat (which require high temperatures
and dry heat).
• Meat is a term for the flesh of cattle (beef and
veal), sheep (lamb), and pigs (pork). Meat 7. Coating — The two basic coatings are:
comprises water, protein, fats, and various
amounts of minerals and vitamins. a) Flavor — coat the meat before
cooking; otherwise, the flavor
• Beef is divided into large sections called becomes sticky and unpleasant.
primal cuts. These beef primal cuts, or
"primal," are then broken down further into b) Bread crumbs — coat the meat in
individual steaks and other retail cuts. flour, then egg wash (egg wash is
made of a lightly beaten whole egg
Preparation of meat with a little water or milk), and finally
with the bread crumbs.
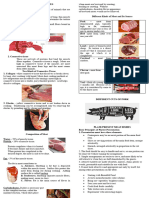
1. Washing — generally, the only occasion in
which you will have to wash meat is when it Types of meat
comes into contact with blood during
preparation. ➢ Cattle — Beef
➢ Pig — Pork
2. Skimming — most of the meat you dealt with ➢ Sheep — Lamb
has already been skinned by the supplier.
Tools needed for meat preparation
3. Dicing — meat is diced when it is cut into
cubes for various types of casseroles, stems, 1. French knife or chef's knife — for general
curries, and dishes, such as steak, kidney pie, purpose chopping, slicing, and dicing.
and pudding.
2. Utility knife — used for carving roast chicken
4. Trimming — Reasons for trimming: and duck.
a. Improve the appearance of the cut or 3. Boning knife — used for boning raw meats
joint. and poultry.
b. Leave as much of the meat intact as 4. Slicer — used for carving and slicing cooked
possible. meats.
c. Leave an even thickness of fat 5. Butcher knife — used for cutting, sectioning,
(where fat is to be left). How much and trimming raw meats in the butcher shop.
fat you trim off will depend on the
type of meat. 6. Scimitar or steak knife — used for the
accurate cutting of steaks.
5. Slicing — It is the cutting of meat by
determining the direction of the grain (the 7. Cleaver — used for cutting through bones.
muscle fiber) and cutting across the grain.
Composition of meat
6. Seasoning — it is the addition of salt and
1. Water —70% of muscle tissue.
white and black pepper to improve the flavor
of food.
2. Protein — 20% of muscle tissue.
a) Use of white pepper or cayenne
o Protein coagulates when it is heated.
pepper on food that you want to
keep attractive with a white color.
o It becomes firmer and loses
moisture.
b) Add salt to the roast and grill after
the meat has browned. Adding salt
3. Fat — 5% of muscle tissue.
before cooking will extract the juices
of the meat from the surface and
a) Juiciness — Marbling is fat that is
slow down the browning reactions
deposited in the muscle tissue.
Florenz Janus mina | 1
t.l.e. | 4th quarter // sir lesh-ter ayran
o Adding a flat surface is 4. Carabeef — meat from carabao.
called "barding" - surface
fats protect the meat from 5. Chevon — meat from deer or goat.
drying out during cooking.
6. Veal — flesh of a young calf, 4-5 months old.
b) Tenderness — marbling separates because of its age. It is considered by some
muscle fibers, making them easier to to be the finest meat.
chew.
Kinds of doneness of meat
c) Flavor — fat is the main source of
flavor in meat. 1. Rare - when pressed with a finger, the meat
is very soft with a jelly-like texture.
4. Carbohydrates — play a necessary part in
the complex reaction called the Malliard 2. Medium Rare - when pressed with a finger,
reaction, which takes place when meats are meat feels springy and resistant.
browned by roasting, broiling, or sautéing.
3. Medium - when pressed with a finger, the
o Without carbohydrates, the desired meat feels firm and there is a definite
flavor and appearance of browned resistance.
meats would not be achieved.
4. Well done - when pressed with a finger, the
Structure of meat meat feels hard and rough.
1. Muscle fibers — lean meat is composed of Nutrient contents of meat
long, thin muscle fibers bound together in
bundles. Meat consists of water, protein, and fat. with a few
minerals and some B vitamins.
o Fine — grained meat is composed of
1. Proteins — high-quality protein is the major
small fibers bound in small fibers.
constituent of meat after water, accounting for
about 20% of its weight. Meat contains 7
o Course — textured meat has large
grams of protein per ounce.
fibers.
2. Fats — content can vary widely, according to
2. Connective tissue — these are networks of
the grade of meat and its cut.
proteins that bind the muscle fibers together.
Connective tissue is tough.
3. Carbohydrates — meat contains very little
carbohydrates; glycogen, found in liver and
o Collagen — a white connective tissue
muscle tissue, is present when the animal is
that dissolves or breaks down by long,
alive, but glucose that makes up the glycogen
slow cooking liquid.
is broken down to lactic acid during and after
slaughter.
➢ Acid helps dissociate collagen.
4. Vitamins — meat is an excellent source of
o Elastin — a yellow connective tissue that
certain B vitamins. thiamine (B), riboflavin
is not broken down in cooking.
(B2), pyridoxine (B6), vitamin B12, niacin, and
some folate. Niacin is obtained from
Kinds of meat
tryptophan, an amino acid plentiful in meat
1. Pork — meat from domesticated pigs, and milk.
typically high in fat, commonly slaughtered
one year or less of age to ensure tender cuts. 5. Minerals — meat is an excellent source of
iron, zinc, copper, phosphorus, and a few
2. Beef — meat from cattle over one year old. other trace minerals.
3. Lamb — meat of domesticated sheep.
o Its texture is different from the age at
which it was slaughtered.
Florenz Janus mina | 2
t.l.e. | 4th quarter // sir lesh-ter ayran
Safe cooking temperature for meat
Meat °C °F
Beef, rare 52 125
Beef, medium 57 135
Beef, medium well 68 155
Beef, well done 71 160
Ground beef 74 165
Pork 71 160
Market form of meat
• Fresh meat — meat that has recently been
slaughtered, has not been preserved, or has
been frozen.
• Chilled meat — meat that is placed in a
chiller or is slightly cold.
• Cured meat — meat preserved by salting,
smoking, or aging.
• Processed meat — meat preserved by
chemical process.
Florenz Janus mina | 3
You might also like
- Dining On Babylon 5Document134 pagesDining On Babylon 5dluker2pi125667% (6)
- Cookery 10: Quarter 4 Las Number 1Document8 pagesCookery 10: Quarter 4 Las Number 1Edison Manuel91% (11)
- Cookery10 Q4 Week1 v4Document10 pagesCookery10 Q4 Week1 v4Maria Rose Tariga Aquino100% (4)
- 2010 - Studying The Influence of Package Shape and Colour On Consumer Expectations of Milk Desserts Using Word Association and ConjointDocument8 pages2010 - Studying The Influence of Package Shape and Colour On Consumer Expectations of Milk Desserts Using Word Association and ConjointvuongaiNo ratings yet
- Meat T.l.e.: Cookery 10Document5 pagesMeat T.l.e.: Cookery 10jozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- TLE ReviewerDocument3 pagesTLE Reviewerpogi junkyuNo ratings yet
- Meat LessonDocument16 pagesMeat LessondanicadagaragaNo ratings yet
- Q4 G10 Learning Outcome 1Document5 pagesQ4 G10 Learning Outcome 1asher daveNo ratings yet
- TleDocument5 pagesTleBianca MontalboNo ratings yet
- Cookero MeatDocument1 pageCookero MeatMiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Meat Lesson 1Document4 pagesReviewer Meat Lesson 1Rose Lynn100% (1)
- Activty in Tle 3Document7 pagesActivty in Tle 3bnw4z9g9yyNo ratings yet
- Q4 Module1 G10 CookeryDocument9 pagesQ4 Module1 G10 CookeryfishguadagraceNo ratings yet
- Cook 10 1Document8 pagesCook 10 1Jhoana Paula EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Las 1 q4 Perform Mise en PlaceDocument6 pagesLas 1 q4 Perform Mise en PlaceDump McDumpNo ratings yet
- 4 A 1 A 4 A 46 Ade 4Document62 pages4 A 1 A 4 A 46 Ade 4Ken ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Meat - Lesson 1Document25 pagesIntroduction of Meat - Lesson 1Ella Cagadas PuzonNo ratings yet
- Cookery10-Week1-7 (4th)Document27 pagesCookery10-Week1-7 (4th)mary grace manalang100% (2)
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics-Cookery Performing Mise' en PlaceDocument10 pagesTechnology and Livelihood Education: Home Economics-Cookery Performing Mise' en PlaceConstancia PerezNo ratings yet
- Dawata Akoang GugmaDocument3 pagesDawata Akoang GugmaJada CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Las Cookery 4TH Quarter - 083850Document19 pagesLas Cookery 4TH Quarter - 083850umlijamieeeNo ratings yet
- Tle 1o q4 ModuleDocument22 pagesTle 1o q4 ModuleRhea AnselmoNo ratings yet
- TleDocument5 pagesTleGwen MagtabogNo ratings yet
- EDITED - Lo1. Prepare Mise - en Place (Meat)Document46 pagesEDITED - Lo1. Prepare Mise - en Place (Meat)Christle Angelu CristobalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Prepare Meat Dishes NotesDocument2 pagesLesson 3 - Prepare Meat Dishes Notesabejarm7No ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 4 LAS Number 1 Weeks 1Document8 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 4 LAS Number 1 Weeks 1Leila Madelene LoyolaNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 MeatDocument2 pagesCOOKERY 10 MeatKC Tolentino CahanapNo ratings yet
- Module Quarter 4 CompiledDocument16 pagesModule Quarter 4 CompiledJoevic SuyodNo ratings yet
- Cookery - 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Document13 pagesCookery - 10 Quarter 4 Week 1CYRILNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Prepare and Cook Meat Meat: Than BeefDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Prepare and Cook Meat Meat: Than BeefFranz Russell TalosigNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET1Document3 pagesWORKSHEET1Shane PuertollanoNo ratings yet
- Culinary Mudule 10Document41 pagesCulinary Mudule 10Karen FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cook MeatDocument30 pagesPrepare and Cook MeatCarla RiveraNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cook MeatDocument65 pagesPrepare and Cook MeatARLENE MORADA100% (1)
- Quarter 4 TLE 10 L 1Document34 pagesQuarter 4 TLE 10 L 1Kennard GundranNo ratings yet
- TLE LAS Cookery 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Document8 pagesTLE LAS Cookery 10 Quarter 4 Week 1Edgar RazonaNo ratings yet
- April 162024 Asyncronous TaskDocument3 pagesApril 162024 Asyncronous Taskariannealcaraz6No ratings yet
- 4th Quarter HandoutsDocument5 pages4th Quarter Handoutsjenny sumayoNo ratings yet
- 10 Cookerylas 1Document3 pages10 Cookerylas 1Althea RejaeNo ratings yet
- Cookery - 10-Quarter 4-Week-1Document12 pagesCookery - 10-Quarter 4-Week-1Ereca Mae Papong100% (1)
- Cookery10 Week1-2 Q4Document5 pagesCookery10 Week1-2 Q4StephanieNo ratings yet
- MEATPPTDocument29 pagesMEATPPTAshly AragonNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 MEATDocument2 pagesActivity 1 MEATAshly AragonNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document12 pagesWeek 1KISHANo ratings yet
- LO1PPTGR10Document53 pagesLO1PPTGR10Ashly AragonNo ratings yet
- Tle Cookery-10 - 4TH QuarterDocument34 pagesTle Cookery-10 - 4TH QuarterPatrick Dave San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet (Las) : Cookery 10Document8 pagesLearning Activity Sheet (Las) : Cookery 10criselda desistoNo ratings yet
- Week 1&2 CookeryDocument33 pagesWeek 1&2 CookeryJonabel DacilloNo ratings yet
- Tle - 9 - Prepare and Cook MeatDocument7 pagesTle - 9 - Prepare and Cook MeatJeff Ubana Pedrezuela0% (1)
- Preparing Meat For CuringDocument2 pagesPreparing Meat For CuringAsia VelascoNo ratings yet
- TLE ReviewerDocument6 pagesTLE ReviewerRamil NebrilNo ratings yet
- Weeks 31 and 32Document59 pagesWeeks 31 and 32G3 ODL Kim Angela BernardoNo ratings yet
- Meatcuts 1Document23 pagesMeatcuts 1annaliza barondaNo ratings yet
- Beef Poultry and EggsDocument17 pagesBeef Poultry and EggsAira RamonNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Cook MeatDocument62 pagesPrepare and Cook MeatSthepanie Badillo75% (8)
- PREPARE Meat DishesDocument37 pagesPREPARE Meat DishesThea Jeonieesa GarayNo ratings yet
- TLE Group 2Document23 pagesTLE Group 2Janet C. RamosNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ReportDocument14 pagesGroup 2 ReportNoire LeeNo ratings yet
- Cook 10 02Document6 pagesCook 10 02Jhoana Paula EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Module MeatDocument2 pagesModule Meatpio.barrettoNo ratings yet
- Saln2022form Aj Ferrer 2023Document2 pagesSaln2022form Aj Ferrer 2023jozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument2 pagesMusicjozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- MarsoulWare2 0Document3 pagesMarsoulWare2 0jozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- CL ReviewerDocument2 pagesCL ReviewerjozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- Lessonon Holy RosaryDocument5 pagesLessonon Holy RosaryjozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CLDocument4 pagesReviewer CLjozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- Recipe Plan TLEDocument3 pagesRecipe Plan TLEjozelpiedraNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Eapp Week 1-2Document4 pagesAnswer Sheet Eapp Week 1-2Karla Joy Corpuz Marciano50% (2)
- Uncountable Nouns: This News Is Very ImportantDocument10 pagesUncountable Nouns: This News Is Very ImportantbianevalerioNo ratings yet
- Guess The Mystery Object - ObservationDocument3 pagesGuess The Mystery Object - ObservationMark Eddieson Ong ArancelNo ratings yet
- The Ritz Restaurant Breakfast Menu PDFDocument4 pagesThe Ritz Restaurant Breakfast Menu PDFPutu Rana JanendraNo ratings yet
- Product Mix of Nestle India LTD.: Sales and Distribution ReportDocument9 pagesProduct Mix of Nestle India LTD.: Sales and Distribution ReportNikita Sanghvi100% (1)
- Adler AD 6019 Bread MakerDocument64 pagesAdler AD 6019 Bread MakerDulauCiprianNo ratings yet
- Clean Label - BreadDocument5 pagesClean Label - BreadJonyBlessingNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP GIỮA KÌ 2-ANH 9Document6 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP GIỮA KÌ 2-ANH 9ngaNo ratings yet
- Activities - Earth SciDocument5 pagesActivities - Earth Scirufino delacruzNo ratings yet
- 4753-Article Text-10548-3-10-20191214Document5 pages4753-Article Text-10548-3-10-20191214MARY ROSE HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Soal PTS 1 B.inggris Kelas IX K13Document7 pagesSoal PTS 1 B.inggris Kelas IX K13Romy Apriliani AhmadNo ratings yet
- MenuDocument7 pagesMenuQuarantinaholics CompanyNo ratings yet
- Doctor ResignationDocument1,320 pagesDoctor ResignationNaomi Jeck MoocNo ratings yet
- Teachingvocabulary Hungryathalf Time Describingfood Materialspack2Document7 pagesTeachingvocabulary Hungryathalf Time Describingfood Materialspack2RezkianiNo ratings yet
- Data:: Patient Name Gender Age Weight BP HeightDocument4 pagesData:: Patient Name Gender Age Weight BP HeightMuhammad HasnatNo ratings yet
- Yule Log Nigellas Recipes Nigella LawsonDocument4 pagesYule Log Nigellas Recipes Nigella LawsonНаталья УлановаNo ratings yet
- Lengua Extranjera: Comunidad Y SociedadDocument22 pagesLengua Extranjera: Comunidad Y SociedadEDITH.MARISA6932No ratings yet
- Potato and White Bean Puttanesca Soup Recipe - NYT CookingDocument1 pagePotato and White Bean Puttanesca Soup Recipe - NYT Cookingjpl.guedes6842No ratings yet
- Sergio S Sarava at Shaker Square LunchDocument3 pagesSergio S Sarava at Shaker Square LuncheatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- IDIN-3 DTV3 Extra Grammar Exercises I PARTIALDocument4 pagesIDIN-3 DTV3 Extra Grammar Exercises I PARTIALrobert martinezNo ratings yet
- Meal Management: By: Maricris BastidaDocument29 pagesMeal Management: By: Maricris BastidaRaymond GarciaNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 6 q4 w6Document7 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q4 w6Pamela BulawitNo ratings yet
- Pryll BusinessDocument7 pagesPryll BusinessPrecious YasayNo ratings yet
- Mango Graham Shake: SupremacyDocument18 pagesMango Graham Shake: SupremacyZayn RauiNo ratings yet
- PROJECT-PALM-Princess BalisiDocument5 pagesPROJECT-PALM-Princess BalisiPRINCESS BALISINo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet BPP (LAS) 1Document6 pagesLearning Activity Sheet BPP (LAS) 1Precious Andoy-MegabonNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Golden BellDocument50 pages4th Grade Golden BellrerrroarNo ratings yet
- A Healthy Diet For Runners: Meal Plan Week 1Document4 pagesA Healthy Diet For Runners: Meal Plan Week 1ana beaverhousenNo ratings yet