0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views20 pagesMetacentric Height Experiment Guide
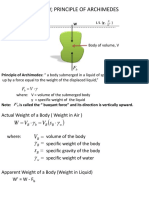
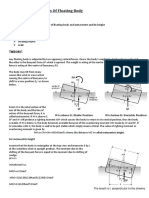
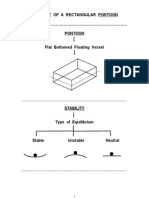
This document provides instructions and procedures for conducting a laboratory experiment to determine the metacentric height of a floating body. Students will use a pontoon apparatus and measure how it tilts at different positions as weights are adjusted. They will collect data, perform calculations, and analyze the results to find the metacentric height and stability of the pontoon.
Uploaded by
Devia PadulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
74 views20 pagesMetacentric Height Experiment Guide
This document provides instructions and procedures for conducting a laboratory experiment to determine the metacentric height of a floating body. Students will use a pontoon apparatus and measure how it tilts at different positions as weights are adjusted. They will collect data, perform calculations, and analyze the results to find the metacentric height and stability of the pontoon.
Uploaded by
Devia PadulCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd