0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageUnderstanding Liver Function Tests
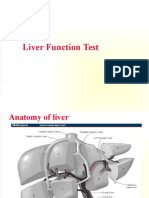
The document discusses liver function tests and what they indicate. It explains that AST is found everywhere but indicates liver damage when highest, while ALT is liver-specific. Alkaline phosphatase can be elevated in bone disease, pregnancy or liver diseases. GGT is liver-specific but may be elevated after alcohol. Bilirubin and albumin levels provide information on liver function and disease chronicity. Prothrombin time decreases in acute liver problems.
Uploaded by
karenmstamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageUnderstanding Liver Function Tests
The document discusses liver function tests and what they indicate. It explains that AST is found everywhere but indicates liver damage when highest, while ALT is liver-specific. Alkaline phosphatase can be elevated in bone disease, pregnancy or liver diseases. GGT is liver-specific but may be elevated after alcohol. Bilirubin and albumin levels provide information on liver function and disease chronicity. Prothrombin time decreases in acute liver problems.
Uploaded by
karenmstamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd