0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views8 pagesGrade 8 Measurement
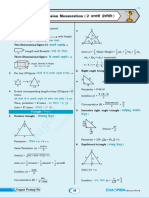
The document discusses different geometric shapes including polygons, circles, and perimeters. Polygons include regular polygons and special quadrilaterals. Circles are defined and parts like radii, diameters, arcs, and sectors are explained. Formulas are provided to calculate the perimeters of squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles. Examples and exercises on finding perimeters of various shapes are also included.
Uploaded by
Mar RichCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views8 pagesGrade 8 Measurement
The document discusses different geometric shapes including polygons, circles, and perimeters. Polygons include regular polygons and special quadrilaterals. Circles are defined and parts like radii, diameters, arcs, and sectors are explained. Formulas are provided to calculate the perimeters of squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles. Examples and exercises on finding perimeters of various shapes are also included.
Uploaded by
Mar RichCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd