Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atria - It Is A Chamber of The Heart Receiving Blood From The Veins Superior Heart Chamber
Atria - It Is A Chamber of The Heart Receiving Blood From The Veins Superior Heart Chamber
Uploaded by
Zyrah Ziska ZafraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atria - It Is A Chamber of The Heart Receiving Blood From The Veins Superior Heart Chamber
Atria - It Is A Chamber of The Heart Receiving Blood From The Veins Superior Heart Chamber
Uploaded by
Zyrah Ziska ZafraCopyright:
Available Formats
IV.
Definition of Terms
1) Apnea- cessation of breathing
2) Atria – it is a chamber of the heart receiving blood from the veins; superior heart
chamber.
3) Bronchioles- smallest of the conducting passageways
4) Dead space volume- it is when much of the air that enters the respiratory tract remains
in the conducting zone passageways and never reaches the alveoli.
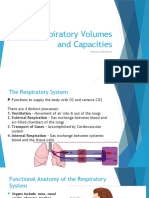
5) ERV (Expiratory Reserve Volume)- the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled
after a tidal expiration.
6) Hypoxia- a condition in which inadequate oxygen is available to tissues.
7) IRV (Inspiratory Reserve Volume)- the amount of air that can be taken in forcibly
over the tidal volume.
8) Mediastinum- the region of the thoracic cavity between the lungs
9) Pericardium – membranous or double-walled sac enveloping the heart.
10) Rheumatic Fever – is an inflammatory disease that can develop as a complication of
inadequately treated strep throat or scarlet fever. It is caused by an infection with
group a streptococcus.
11) Rheumatic Heart Disease – is a complication of rheumatic fever in which the heart
valves are damaged.
12) Rheumatic Heart Disease in Failure – is a complication wherein the heart is already
failing to function.
13) TV (Tidal volume)- amount of air inhaled or exhaled with a normal breath.
14) Ventricles – it is a discharging chamber of the heart; cavities within the brain.
15) VC (Vital Capacity)- it is the sum of the TV + IRV + ERV.
You might also like
- Humulin RDocument1 pageHumulin RZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- 3805 Topper 21 101 3 1 7508 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Up201606291134 1467180285 4454Document8 pages3805 Topper 21 101 3 1 7508 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Up201606291134 1467180285 4454saracastic123No ratings yet
- Pulmonology: Dr. Okon MRCSDocument28 pagesPulmonology: Dr. Okon MRCSEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Ventilation: Dr. Mohamed HassanDocument29 pagesPulmonary Ventilation: Dr. Mohamed HassanSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: I. Olfactory CellsDocument10 pagesRespiratory System: I. Olfactory CellsTJ HarrisNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Respiratory Systemno nameNo ratings yet
- MODULE 22 HANDOUTS Repiratory SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 22 HANDOUTS Repiratory SystemMichaela PoNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesUnit VI Lecture NotesSteve Sullivan100% (1)
- Respiratory System: Answers and ExplanationsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: Answers and ExplanationsManan ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesWeek 3 Respiratory SystemangeliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Act 11Document7 pagesAnatomy Act 11Nevado, Jonamae Ivee D.No ratings yet
- ImrozDocument57 pagesImrozSyed Imroz KhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Lesson 1Document7 pagesRespiratory System Lesson 1Gabriela RamírezNo ratings yet
- Science Review 1 - Respi-CircDocument3 pagesScience Review 1 - Respi-CircRuby Grace Cari GalvezNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 3 Respirasi + CardiovasculerDocument73 pagesKuliah 3 Respirasi + CardiovasculerNindya Alfa DichaNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الجاهزة 4،5 فسيو بلك التنفسيDocument43 pagesالمحاضرة الجاهزة 4،5 فسيو بلك التنفسيbessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- Science 9 First Quarter ALL NotesDocument9 pagesScience 9 First Quarter ALL Notesliannicole884No ratings yet
- Respiratory: Welcome!Document119 pagesRespiratory: Welcome!Majo ParagasNo ratings yet
- Lung Volume Measurement: Notes To Chapter 11 (Ventilation) 11 Ed. SlidesDocument22 pagesLung Volume Measurement: Notes To Chapter 11 (Ventilation) 11 Ed. SlidesChristina GonezNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Biology Class - 11Document8 pagesPoints To Remember: Biology Class - 11AnitaNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Lecture Notes - Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesUnit VI Lecture Notes - Respiratory SystemSteve Sullivan100% (3)
- The Respiratory System and Its DisordersDocument16 pagesThe Respiratory System and Its DisordersZea Leyan J. LopezNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY-SYSTEM pptx1137Document32 pagesRESPIRATORY-SYSTEM pptx1137Jerick Sevilla SearesNo ratings yet
- Breating and ExchangeDocument3 pagesBreating and Exchangedamon salvatoreNo ratings yet
- Airway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2Document49 pagesAirway and Its Maintenance Hand Out2agatakassaNo ratings yet
- Biology IIRespiratory SystemDocument28 pagesBiology IIRespiratory SystemSustiguer Estelle FaithNo ratings yet
- Handout Respiratory and Circdulatory SystemDocument2 pagesHandout Respiratory and Circdulatory SystemJerick EpantoNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument9 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesAksa Merlin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Alterations in OxygenationDocument104 pagesAlterations in OxygenationMelchor Felipe Salvosa100% (1)
- Spirometry RV and RCDocument19 pagesSpirometry RV and RCMâřâh MöHămmădNo ratings yet
- Breathing & Exchange of GasesDocument16 pagesBreathing & Exchange of GasesUttam SinghNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument25 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesSureshNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument55 pagesThe Respiratory SystemChuy Cantu RdzNo ratings yet
- Practical PhysiologyDocument14 pagesPractical PhysiologyOmar AymanNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange Notes-2Document11 pagesBreathing and Exchange Notes-2manshibhaskar09No ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument10 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument16 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMoses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument13 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesTanmayee MuppaneniNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Post LabDocument3 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEM Post LabVeronica AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemAlloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Parts/Functions/ Respiration Process/ Respiratory Problem /taking Care of The Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesThe Respiratory System: Parts/Functions/ Respiration Process/ Respiratory Problem /taking Care of The Respiratory SystemChandy Faye SisonNo ratings yet
- L - 2 Physiology of Respiration IIDocument25 pagesL - 2 Physiology of Respiration IIkaukab azimNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument9 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMukesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Pulmunology FADocument39 pagesPulmunology FAJaankiNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument19 pagesScience ReviewerfluyuuyyyNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 17 REspiratory SystemBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Module 13 Thorax and LungsDocument18 pagesModule 13 Thorax and LungsKristine Angie RamosNo ratings yet
- RT 321 Chest and AbdomenDocument85 pagesRT 321 Chest and Abdomenpntrdzj75wNo ratings yet
- Buku DyspneaDocument12 pagesBuku DyspneaAmi DhaniaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Bullet PointsDocument5 pagesRespiratory System Bullet PointsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Respiratory SysDocument3 pagesTest 1 Respiratory SysJaskirat SinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi RespirasiDocument22 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi RespirasinortonaingNo ratings yet
- Basic Respiratory Mechanics (DR Arif)Document36 pagesBasic Respiratory Mechanics (DR Arif)Rizqi Luqmanul HakimNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument3 pagesRespiration Noteseshoukat353No ratings yet
- DR Sakher Al-Khaderi Consultant Radiologist AmcDocument85 pagesDR Sakher Al-Khaderi Consultant Radiologist AmcionululNo ratings yet
- Therespiratorysystem 130524022043 Phpapp01 TestDocument21 pagesTherespiratorysystem 130524022043 Phpapp01 TestMergel GeconcilloNo ratings yet
- 3 Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument20 pages3 Lung Volumes and CapacitiesNimra TariqNo ratings yet
- Breathing N Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesBreathing N Gas Exchangemariamfernandes6No ratings yet
- Roses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.Document249 pagesRoses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.MabesNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument249 pagesRespiratoryBulborea MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- Vii. Health History History of Present Illness: The Client Was Admitted To CLMMRH On January 13, 2015 at 11:50 AmDocument2 pagesVii. Health History History of Present Illness: The Client Was Admitted To CLMMRH On January 13, 2015 at 11:50 AmZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- II. ObjectivesDocument1 pageII. ObjectivesZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- PiptazDocument2 pagesPiptazZyrah Ziska Zafra100% (1)
- Acute Appendicitis: Zyrah Ziska Z. ZafraDocument3 pagesAcute Appendicitis: Zyrah Ziska Z. ZafraZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis NCSDocument25 pagesAppendicitis NCSZyrah Ziska ZafraNo ratings yet