Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.9 Photosynthesis
2.9 Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Ariadna AlvarengaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.9 Photosynthesis
2.9 Photosynthesis
Uploaded by
Ariadna AlvarengaCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2.
9: PHOTOSynTHESIS
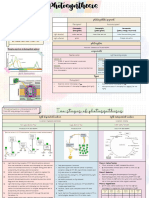
Photosynthesis Light Spectrum
Photosynthesis involves the use of light energy to synthesise Visible light has a range of wavelengths (~ 400 – 700 nm)
organic compounds from inorganic molecules • Violet has the shortest wavelength, red has the longest
Light The Visible Spectrum
6 CO2 + 12 H2O C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O
Chlorophyll
Carbon Water Glucose Oxygen Water
dioxide 700 nm 400 nm
Light Absorption
Pigments are required for the conversion of light energy into chemical energy in photosynthetic organisms
Chlorophyll is the main photosynthetic pigment, although other accessory pigments also exist (e.g. carotenoids)
• Chlorophyll absorbs red light and blue light most effectively and reflects green light more than other colours
An absorption spectrum (left) indicates the wavelengths of light absorbed by each photosynthetic pigment (e.g. chlorophyll)
An action spectrum (right) indicates the overall rate of photosynthetic activity at each wavelength of light
Relative absorption
Photosynthetic rate
carotenoid
chlorophyll a
chlorophyll b
400 500 600 700 400 500 600 700
Wavelength of light (nm) Wavelength of light (nm)
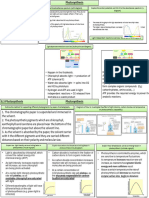
Stages of Photosynthesis
Light Dependent Reactions Light Independent Reactions
Light energy is converted into chemical energy Carbon compounds are made from the chemical energy
• Light is absorbed by chlorophyll to produce ATP • ATP and hydrogen are fixed with carbon dioxide
• The photolysis of water forms oxygen and hydrogen • This results in the formation of organic molecules
Light energy Carbon dioxide NADPH ATP
Water Chlorophyll Chemical energy
Carbon fixation
e–
Oxygen Hydrogen NADPH ATP Organic compounds Cell Processes
Chromatography Limiting Factors
Pigments can be separated by chromatography When a process depends on more than one condition, the
• Pigments are dissolved in fluid rate will be limited by the factor nearest its minimum value
• The fluid is passed through a static material
Limiting factors in photosynthesis include:
• Pigments are separated according to size
• Temperature (influences photosynthetic enzymes)
A retardation factor (Rf value) is calculated: • Light intensity (required for chlorophyll photoactivation)
Rf = distance of pigment ÷ distance of solvent • Carbon dioxide concentrations (CO2 is a core substrate)
You might also like
- PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesPhotosynthesispixholic100% (2)
- PhotosynthesisDocument29 pagesPhotosynthesisAB CloydNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsDocument15 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis: - Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - NewDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis - Newsanjay prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Pesticide FormulationsDocument6 pagesPesticide FormulationsMD FARUKNo ratings yet
- Poly (Butylene Succinate) and Its Copolymers: Research, Development, and IndustrializationDocument15 pagesPoly (Butylene Succinate) and Its Copolymers: Research, Development, and IndustrializationfaridehNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesPhotosynthesisyusfa khildhaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionJovelyn GuerraNo ratings yet
- 8 Coenzymes and Vitamins (كيمياء حيوية صيدلانية (1 PDFDocument74 pages8 Coenzymes and Vitamins (كيمياء حيوية صيدلانية (1 PDFmaher100% (1)
- Chemistry Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesDocument32 pagesChemistry Higher Level Paper 3: Instructions To CandidatesJuan Camilo VargasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: B. Carbon Metabolism 1. C3 2. C4 3. CAM C. Factors Regulating The ProcessesDocument94 pagesPhotosynthesis: B. Carbon Metabolism 1. C3 2. C4 3. CAM C. Factors Regulating The ProcessesJonathanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document52 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Ella Mae CelestinoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biology: PhotosynthesisDocument31 pagesAdvanced Biology: Photosynthesiszorbax100% (2)
- GBT-1220-2007-stainless Steel BarsDocument23 pagesGBT-1220-2007-stainless Steel BarsKepeNo ratings yet
- Apex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchDocument35 pagesApex Institute of Management Studies and ResarchSHEKHAR PRASADNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument53 pagesPhotosynthesis: Powerpoint Lectures ForSean JonesNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document68 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Capili, Princess Jenelle D.No ratings yet
- PDF Modul 7 Amp 8 Bahasa Indonesia - CompressDocument29 pagesPDF Modul 7 Amp 8 Bahasa Indonesia - CompressHasti PrastikasariNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: A2 Biology (9700) 2022-2023Document31 pagesPhotosynthesis: A2 Biology (9700) 2022-2023Youssef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - HussDocument43 pagesPhotosynthesis - HussTrish Austria50% (2)
- C13 Photosynthesis - RedactedDocument48 pagesC13 Photosynthesis - RedactedDevRushi VyasNo ratings yet
- 8 Photosynthesis 1Document45 pages8 Photosynthesis 1ThiệnÂnDươngNo ratings yet
- 2022F PP2 Photosynthesis Light DarkDocument100 pages2022F PP2 Photosynthesis Light Dark啦啦啦啦No ratings yet
- L5 - PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesL5 - PhotosynthesisLanz TaminNo ratings yet
- SDFSDFDocument68 pagesSDFSDFXexAriasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 02-11-02 14Document33 pagesPhotosynthesis 02-11-02 14Eanne HavenNo ratings yet
- Chapter7 Photosynthesisarespiration 281 29Document30 pagesChapter7 Photosynthesisarespiration 281 29NameNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document16 pagesLecture 02darshanpandaNo ratings yet
- Light - Independent Reaction 5Document46 pagesLight - Independent Reaction 5Dandena Gelmesa SobokaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Photosynthesis CPDocument21 pagesLecture Photosynthesis CPpranav.biophdNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument68 pagesPhotosynthesisJhigo Villar Franco PascualNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 02-11-02 14Document43 pagesPhotosynthesis 02-11-02 14Soemi BarrientosNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument11 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISDRISTIE KALITANo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Den Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- SL Photosynthesis Summary CompleteDocument2 pagesSL Photosynthesis Summary CompletePhuong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis A Level BiologyDocument88 pagesPhotosynthesis A Level Biologyeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- BIO 324-Chap7,8Document61 pagesBIO 324-Chap7,8yarabeaini1No ratings yet
- CH 2 - PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesCH 2 - PhotosynthesisnawarakanNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2.0 Chapter 8Document3 pagesBio Notes 2.0 Chapter 8farrisya zulyazanNo ratings yet
- Energy Can Be Transformed From One Form To AnotherDocument35 pagesEnergy Can Be Transformed From One Form To AnotherLatha MahendraNo ratings yet
- PhotosynDocument55 pagesPhotosynSANSKRITI 3928No ratings yet
- Photos YnDocument55 pagesPhotos YnSANSKRITI 3928No ratings yet
- 3.2 The Light-Dependent Reaction: PhotosynthesisDocument20 pages3.2 The Light-Dependent Reaction: PhotosynthesisazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation IN Eukaryotic CellDocument28 pagesEnergy Conservation IN Eukaryotic CellJohn TinambacanNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Document35 pagesBy The End of This Lecture You Will Be Able To:: Light-Dependent Reactions (I.e., Light Reactions)Diganta Kr DasNo ratings yet
- Almost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsDocument15 pagesAlmost All Plants Are Photosynthetic Autotrophs, As Are Some Bacteria and ProtistsDandena Gelmesa SobokaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ADocument15 pagesPhotosynthesis ABALQIS NURAZIZAHNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ADocument15 pagesPhotosynthesis AJust EllaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8 Photosynthesis F17Document70 pagesCh. 8 Photosynthesis F17bae loonaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Botany Laboratory: Exercise 15: PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesPharmaceutical Botany Laboratory: Exercise 15: PhotosynthesisZyreeneNicoleNo ratings yet
- Flame PhotometeryDocument7 pagesFlame PhotometeryMooma fatimaNo ratings yet
- WK 9 PhotosynthesisDocument22 pagesWK 9 PhotosynthesisKuku MandavaNo ratings yet
- BIO C6 @notastpm04Document152 pagesBIO C6 @notastpm04Huey KaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis EllaDocument42 pagesPhotosynthesis EllaElla AgyeiNo ratings yet
- NitrificationDocument20 pagesNitrificationamargokul143No ratings yet
- 6.0 PhotosynthesisDocument15 pages6.0 Photosynthesisa200812No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument45 pagesPhotosynthesisUmarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: The Process That Feeds The BiosphereDocument50 pagesPhotosynthesis: The Process That Feeds The BiosphereMicaszen MendozaNo ratings yet
- RB Cagmat Review Center - Cs-Photosynthesis PDFDocument33 pagesRB Cagmat Review Center - Cs-Photosynthesis PDFBergo AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Biology 11 Class Federal BoardDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Biology 11 Class Federal BoardMuhammad MustafaNo ratings yet
- Living Things Run On BatteriesDocument17 pagesLiving Things Run On BatteriesAzfar ZackNo ratings yet
- CHP 5 PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesCHP 5 PhotosynthesisSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- FOTOSINTESISDocument56 pagesFOTOSINTESISskoswara100% (1)
- 1.1 Oxidation and Reduction Part 1Document76 pages1.1 Oxidation and Reduction Part 1Rabbi 08No ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Liquid Chromatography Analysis of Synthetic PolymersDocument280 pagesRecent Advances in Liquid Chromatography Analysis of Synthetic PolymersAnderson CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual FSI 12803 Exp 3 7.11.2022Document4 pagesLab Manual FSI 12803 Exp 3 7.11.2022alyea atiraNo ratings yet
- Nature - Goodenough - Oxide Ion Conductors by DesignDocument2 pagesNature - Goodenough - Oxide Ion Conductors by Designavinash patelNo ratings yet
- Tehnički List - PLUG VRDocument2 pagesTehnički List - PLUG VRMARKO MATUHANo ratings yet
- Titration - Dry Lab - 2020Document6 pagesTitration - Dry Lab - 2020MariaPaulaGonzalezRojasNo ratings yet
- Latmer ExerciciosDocument7 pagesLatmer ExerciciosLilian WeitzelNo ratings yet
- Test - 3 Single Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesTest - 3 Single Choice QuestionsGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- AOChem Sanfoundry CompiledDocument176 pagesAOChem Sanfoundry CompiledChastine CruzNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical AnalysisDocument19 pagesPharmaceutical AnalysisDeepak VermaNo ratings yet
- Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and TechnologyDocument40 pagesCritical Reviews in Environmental Science and TechnologyMathilda PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDocument45 pagesChapter 3. The Structure of Crystalline SolidsDiego AbadNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument228 pagesUntitledDeepanshu digari100% (2)
- TantalumDocument2 pagesTantalumAaron Ana MayNo ratings yet
- AiTECH 4.3.-Chemical-Reactions-and-Chemical-EquationsDocument26 pagesAiTECH 4.3.-Chemical-Reactions-and-Chemical-EquationsRyan PazonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Od Acids & BasesDocument6 pagesWorksheet Od Acids & BasesAreeba IftikharNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Lectures 4, 5, 6 and 7 CHE1010Document77 pagesStoichiometry Lectures 4, 5, 6 and 7 CHE1010Wayne MachinguraNo ratings yet
- 7 Transition Elements WSDocument73 pages7 Transition Elements WSRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Pictures of Elements: Hydrogen - Element 1Document33 pagesPictures of Elements: Hydrogen - Element 1Praveen JoshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document51 pagesChapter 14Varalaxmi BandariNo ratings yet
- Important Terms and Concepts: ReferencesDocument7 pagesImportant Terms and Concepts: ReferencesABDELRHMAN ALINo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance Table: Page 1 of 14Document14 pagesChemical Resistance Table: Page 1 of 14FreddyPerazaNo ratings yet
- Rheflat Plus PDB EngDocument2 pagesRheflat Plus PDB EngJose AlejandroBlanco100% (1)
- Recent Advances in Nanocomposite Soft Magnetic Materials A ReviewDocument6 pagesRecent Advances in Nanocomposite Soft Magnetic Materials A Reviewshameem siddiqueNo ratings yet
- Polymers: Natural Rubber Latex Foam Reinforced With Micro-And Nanofibrillated Cellulose Via Dunlop MethodDocument16 pagesPolymers: Natural Rubber Latex Foam Reinforced With Micro-And Nanofibrillated Cellulose Via Dunlop MethodRini Ananda SiagianNo ratings yet