Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Profunda Brachii Artery
Uploaded by
Iain FairbankOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Profunda Brachii Artery
Uploaded by
Iain FairbankCopyright:
Available Formats
The Profunda Brachii Artery
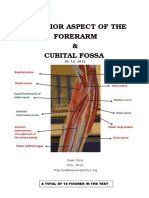
This is the largest branch of the brachial artery, and has the most superior origin. It accompanies the radial nerve in its posterior course in the radial groove. Posterior to the humerus, the profunda brachii artery (or deep brachial artery) divides into anterior and posterior ascending branches. These help form the arterial anastomoses of the elbow region.
Branches.The branches of the brachial artery are: Profunda Brachii. Superior Ulnar Collateral. Nutrient. Inferior Ulnar Collateral.
The Profunda Brachii Artery
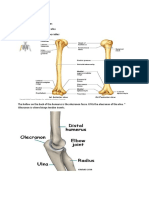
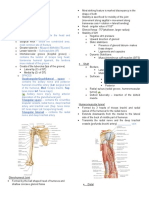
This artery begins at the inferior border of the teres major muscle as the continuation of the axillary artery. It runs inferiorly and slightly laterally on the medial side of the biceps brachii muscle to the cubital fossa, where it ends opposite the neck of the radius. It is superficial and palpable throughout its whole length. At first it lies medial to the humerus and then anterior to it. It lies anterior to the triceps brachii and brachialis muscles, and is overlapped by the biceps brachii and coracobrachialis muscles. It accompanies the median nerve, which crosses it anteriorly at the middle of the arm. Under the cover of the bicipital aponeurosis, the brachial artery divides into the radial and ulnar arteries. The brachial artery gives rise to many unnamed muscular branches, mainly from its lateral side. The named branches of the brachial artery are the profunda brachii artery, the nutrient humeral artery, and the ulnar collateral arteries (superior and inferior).
The Brachialis Muscle
The brachial artery is continuation of the axillary artery, it descends along the medial side of the humerus,divides into the radial and ulnar arteries at the level of the neck of radius.
This is a flattened, fusiform muscle that lies posterior to the biceps brachii. Proximal attachments are: distal half of anterior surface of humerus. Distal attachments are: coronoid process and tuberosity of ulna. Innervation: musculocutaneous nerve (C5 and C6) The strong brachialis is the main flexor of the forearm. It flexed the forearm in all positions and in slow or quick movements. When the forearm is being extended slowly, the brachialis steadies the movement by slowly relaxing. It always contracts during flexion of the elbow joint and is primarily responsible for maintaining flexion. Because of this, it is the workhorse among the flexor muscles if the elbow joint.
You might also like
- Anatomy 1Document82 pagesAnatomy 1innyNo ratings yet
- Nerves of Upper LimbDocument24 pagesNerves of Upper LimbShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Borders of The Cubital FossaDocument2 pagesBorders of The Cubital FossaSweäta DasNo ratings yet
- 323 Lecture 11Document45 pages323 Lecture 11Philip GituriNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Upper Limb: Axilla & ArmDocument35 pagesBlood Supply of Upper Limb: Axilla & ArmfdjkvfjvNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower LimbsDocument122 pagesUpper and Lower LimbsHamidreza RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Anterior Aspect of The Forearm Cubital Fossa 2012Document28 pagesAnterior Aspect of The Forearm Cubital Fossa 2012Elena IftimiNo ratings yet
- Biceps Brachii OriginDocument40 pagesBiceps Brachii OriginDanish GujjarNo ratings yet
- Nerves and Arterial Supply of The Upper Limb: Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesNerves and Arterial Supply of The Upper Limb: Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiMichelleNo ratings yet
- The Upper ArmDocument4 pagesThe Upper ArmJerin XavierNo ratings yet
- The Arm Bone of The Arm-The Humerus Trochlea Articulates With The Ulna Capitulum Articulates With The RadiusDocument11 pagesThe Arm Bone of The Arm-The Humerus Trochlea Articulates With The Ulna Capitulum Articulates With The RadiussmexiiloriNo ratings yet
- UL4-armDocument26 pagesUL4-armfaraNo ratings yet
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy Head and Abdomen: Mandibular AngleDocument17 pagesGeneral Anatomy Head and Abdomen: Mandibular AnglesdsddsdsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Summary From MooreDocument131 pagesAnatomy Summary From MooreNishma Malde100% (2)
- Anatomy of The ArmDocument38 pagesAnatomy of The ArmAkomolede AbosedeNo ratings yet
- Ancross MateriDocument6 pagesAncross MateriAnnaNo ratings yet
- The Cubital FossaDocument19 pagesThe Cubital FossaSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionDocument13 pagesUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- Session 4, L3 ARMDocument16 pagesSession 4, L3 ARMFirst LuckNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Final ReviewDocument35 pagesAnatomy Final ReviewMarie100% (1)
- BRACHIUMDocument29 pagesBRACHIUMemanNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document1 pageDocument 3bomevah614No ratings yet
- 2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDocument3 pages2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDi CanNo ratings yet
- DMS (PBL3) Mohamad Arbian Karim FMUI20Document24 pagesDMS (PBL3) Mohamad Arbian Karim FMUI20Mohamad Arbian KarimNo ratings yet
- Kovacs Files AnatomyDocument124 pagesKovacs Files Anatomyshmirtb100% (2)
- Upper Limb NotesDocument14 pagesUpper Limb NotesSwasChanCNo ratings yet
- Forearm Note DR SharewDocument8 pagesForearm Note DR SharewsharewdelelegnNo ratings yet
- Axillary ArteryDocument7 pagesAxillary Arteryavinash dhameriyaNo ratings yet
- KH BasicDocument64 pagesKH BasicTomNo ratings yet
- Axilla Boundaries and ContentDocument47 pagesAxilla Boundaries and Contentchzaheer72No ratings yet
- UL Drainage, Compartments CompliedDocument12 pagesUL Drainage, Compartments CompliedJasonLiewNo ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy of The Upper LimbDocument3 pagesSurface Anatomy of The Upper LimbIrvin JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of The ArmDocument46 pagesAnterior Compartment of The ArmAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Vascolarizzazione e Innervazione ArtiDocument11 pagesVascolarizzazione e Innervazione Artiwv4vwhrkpsNo ratings yet
- The Topography of Upper LimbDocument5 pagesThe Topography of Upper LimbLorena DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Brachial Plexus (Compatibility Mode)Document58 pagesBrachial Plexus (Compatibility Mode)Daniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb ArteriesDocument40 pagesUpper Limb Arteriesvivekk272002No ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument7 pagesMuscles of The BackDon RaulNo ratings yet
- SG3 Ortho PresentationDocument199 pagesSG3 Ortho PresentationPrincess Noreen SavellanoNo ratings yet
- The Arm PDFDocument19 pagesThe Arm PDFMayra FlorNo ratings yet
- Abdomen Wall: Rex L. Barza MD,, FPCS, FPSGS, FpalesDocument101 pagesAbdomen Wall: Rex L. Barza MD,, FPCS, FPSGS, Fpaleskira santosNo ratings yet
- Periodic Paralysis Group 4 DraftDocument10 pagesPeriodic Paralysis Group 4 DraftCassandra ColigadoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentDocument56 pagesDr. Eman El Sawaf: Anatomy & Embryology DepartmentKareem DawoodNo ratings yet
- Lungs and PleuraDocument7 pagesLungs and PleuraArvin ArliandoNo ratings yet
- Ana 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Document119 pagesAna 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Favour OnyeaboNo ratings yet
- Topography of The Upper Limb: Dr. Muh. Iqbal Basri, M.Kes, SP.SDocument53 pagesTopography of The Upper Limb: Dr. Muh. Iqbal Basri, M.Kes, SP.SFiraNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy of The Human BodyDocument18 pagesGeneral Anatomy of The Human BodyVarenLagartoNo ratings yet
- Vascularization of Lower and Upper ExtermitesDocument40 pagesVascularization of Lower and Upper Extermiteszainab sawan100% (1)
- Membrul Superior MGDocument118 pagesMembrul Superior MGMihai OpreaNo ratings yet
- External Anatomy of Frog 2Document25 pagesExternal Anatomy of Frog 2STEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoNo ratings yet
- Abdomen MusclesDocument26 pagesAbdomen MusclesSepehr ShahimNo ratings yet
- Posterior Compartment of Arm 9 Mar 2024Document25 pagesPosterior Compartment of Arm 9 Mar 2024aamna.nadeem101No ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Upper LimbDocument36 pagesBlood Supply of Upper Limbteklay100% (2)
- Anatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiFira TasyaNo ratings yet
- Radial and Median NervesDocument33 pagesRadial and Median NervesveegeerNo ratings yet
- Name: Laiba Asghar Class: DPT Section-A STUDENT ID: 70112377 Subject: Anatomy Submitted To: Dr. Mehreen JabbarDocument14 pagesName: Laiba Asghar Class: DPT Section-A STUDENT ID: 70112377 Subject: Anatomy Submitted To: Dr. Mehreen JabbarLaiba AsgharNo ratings yet
- Elbow Joint & Anastomosis Around Elbow Joint: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesElbow Joint & Anastomosis Around Elbow Joint: Objectiveschittsat39610% (1)
- 34-Nerves & Vessels of PelvisDocument48 pages34-Nerves & Vessels of Pelvistesfaye mekonnenNo ratings yet