Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Borders of The Cubital Fossa
Uploaded by
Sweäta DasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Borders of The Cubital Fossa
Uploaded by
Sweäta DasCopyright:
Available Formats
CUBITAL FOSSA
The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. It
is located as a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. It is homologous/similar to
the popliteal fossa of the lower limb.
The cubital fossa is triangular in shape, and thus has three borders:
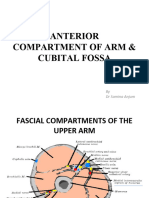
Borders of the cubital fossa :
• Lateral border – medial border of the brachioradialis muscle.
• Medial border – lateral border of the pronator teres muscle.
• Superior border – Imaginary line between the epicondyles of the humerus. ( Diagram at last page)
The floor of the fossa is formed by the brachialis muscle proximally, and the supinator
muscle distally — the roof (from superficial to deep) forms from the skin, fascia, and the bicipital
aponeurosis. In the roof of the fossa the median cubital vein, which can be accessed for
venepuncture.
Contents Of the Cubital Fossa :
The contents of the cubital fossa include vessels, nerves and the biceps tendon (lateral to medial):
• Radial nerve – this is not always strictly considered part of the cubital fossa, but is in the vicinity,
passing underneath the brachioradialis muscle. As it does so, the radial nerve divides into its deep
and superficial branches.
• Biceps tendon – runs through the cubital fossa, attaching to the radial tuberosity, just distal to the
neck of the radius.
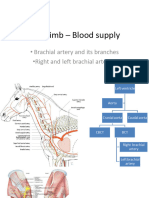
• Brachial artery – supplies oxygenated blood to the forearm. It bifurcates into the radial and ulnar
arteries at the apex of the cubital fossa.
• Median nerve – leaves the cubital between the two heads of the pronator teres. It supplies the
majority of the flexor muscles in the forearm.
Really Need Beer To Be At My Nicest.
Radial Nerve Biceps Tendon Brachial Artery Median Nerve
Dept of Physiotherapy, AWU
Rowriah,Jorhat Page 1
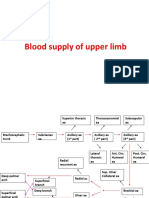
Blood Supply :
As stated above, the brachial artery passes through the cubital fossa, bifurcating into the
radial and ulnar arteries at the distal apex of the fossa. These arteries then continue down into the
forearm to supply the anterior and posterior aspects of the lower arm, ending with the deep and
superficial arches of the hand.
The two primary superficial veins of the arm have an essential communication in the roof
of the cubital fossa - the median cubital vein.
Muscles in the cubital fossa
1.Pronator teres forms the medial border of the fossa.
2.Brachioradialis forms the lateral border of the cubital fossa..
3.Brachialis forms the proximal aspect of the floor.
4. Supinator forms the distal aspect of the floor.
Dept of Physiotherapy, AWU
Rowriah,Jorhat Page 2
You might also like
- List of Video Lectures Available in Our Video BankDocument25 pagesList of Video Lectures Available in Our Video Bankzeeshannajeeb80% (10)
- Anatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiDocument69 pagesAnatomy of Thoracic Wall & Pleura-DikonversiFira TasyaNo ratings yet
- The Deep Hot Biosphere - Thomas GoldDocument359 pagesThe Deep Hot Biosphere - Thomas GoldKatherine Rodriguez100% (5)
- ForearmDocument58 pagesForearmRamon Jovi Lumayag100% (1)
- Anatomy Final ReviewDocument35 pagesAnatomy Final ReviewMarie100% (1)
- Anatomy of The ARMDocument17 pagesAnatomy of The ARMJacob MasikaNo ratings yet
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection ManualDocument5 pagesFrog Dissection Manualapi-230330590100% (1)
- Food Chain and Food Web PDFDocument6 pagesFood Chain and Food Web PDFA. ZNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ArmDocument22 pagesAnatomy of Armromaisa akhtarNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Upper LimbDocument36 pagesBlood Supply of Upper Limbteklay100% (2)
- Anatomy Summary From MooreDocument131 pagesAnatomy Summary From MooreNishma Malde100% (2)
- Upper and Lower LimbsDocument122 pagesUpper and Lower LimbsHamidreza RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure Blood Bank/ Blood Station: Approval SheetDocument28 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Blood Bank/ Blood Station: Approval Sheetddophlaak labdeptNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument33 pagesPlant Anatomy and Physiologymneilg100% (1)
- 6.blood Supply of Upper LimbDocument52 pages6.blood Supply of Upper LimbBlessed LoveNo ratings yet
- Cytopathologic Diagnosis of Serous Fluids - Shidham & AtkinsonDocument9 pagesCytopathologic Diagnosis of Serous Fluids - Shidham & Atkinsonvshidham100% (1)
- Session 4, L3 ARMDocument16 pagesSession 4, L3 ARMFirst LuckNo ratings yet
- UL4-armDocument26 pagesUL4-armfaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Veins of The Forearm and Arteries of The Arm.Document36 pagesAnatomy: Veins of The Forearm and Arteries of The Arm.Mercy AdeolaNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Upper Limb: Axilla & ArmDocument35 pagesBlood Supply of Upper Limb: Axilla & ArmfdjkvfjvNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The ArmDocument38 pagesAnatomy of The ArmAkomolede AbosedeNo ratings yet
- Arm - Anatomy - LecturioDocument17 pagesArm - Anatomy - LecturioElenaNo ratings yet
- The Profunda Brachii ArteryDocument1 pageThe Profunda Brachii ArteryIain FairbankNo ratings yet
- The Cubital FossaDocument19 pagesThe Cubital FossaSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Arm and Cubital FossaDocument40 pagesArm and Cubital FossaAbdelrhman AbubakrNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document1 pageDocument 3bomevah614No ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of The ArmDocument46 pagesAnterior Compartment of The ArmAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- The Upper ArmDocument4 pagesThe Upper ArmJerin XavierNo ratings yet
- Cubital FossaDocument12 pagesCubital FossaIjaz KhanNo ratings yet
- SGDDocument7 pagesSGDJanine Vega Calayo100% (1)
- Blood Supply and Nerve Supply of Upper LimbDocument94 pagesBlood Supply and Nerve Supply of Upper LimbthrrishaNo ratings yet
- S54 - Final Cubital Fossa IIDocument15 pagesS54 - Final Cubital Fossa IIVaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Front of ArmDocument23 pagesFront of ArmNicoleta PSNo ratings yet
- 323 Lecture 11Document45 pages323 Lecture 11Philip GituriNo ratings yet
- UL Drainage, Compartments CompliedDocument12 pagesUL Drainage, Compartments CompliedJasonLiewNo ratings yet
- Vessels of the Free Upper Limв (Engl.) Zharova n.V.Document25 pagesVessels of the Free Upper Limв (Engl.) Zharova n.V.Navneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb ArteriesDocument40 pagesUpper Limb Arteriesvivekk272002No ratings yet
- KUMC 18 Vascular Supply To UE StudentDocument36 pagesKUMC 18 Vascular Supply To UE StudentAzwarmuslimHasballahAminNo ratings yet
- Nerves and Arterial Supply of The Upper Limb: Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 pagesNerves and Arterial Supply of The Upper Limb: Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiMichelleNo ratings yet
- Vascular Supply To Upper ExtremityDocument36 pagesVascular Supply To Upper ExtremityFrancis ChegeNo ratings yet
- Biceps Brachii OriginDocument40 pagesBiceps Brachii OriginDanish GujjarNo ratings yet
- BRACHIUMDocument29 pagesBRACHIUMemanNo ratings yet
- Cubital FossaDocument19 pagesCubital FossaAhmed SharafNo ratings yet
- Topic: Antecubital Fossa: BoundariesDocument2 pagesTopic: Antecubital Fossa: BoundariesVINDHYA SHANKERNo ratings yet
- Discussion Topics IA1 AnatDocument9 pagesDiscussion Topics IA1 AnatPhysics TutionNo ratings yet
- Vascolarizzazione e Innervazione ArtiDocument11 pagesVascolarizzazione e Innervazione Artiwv4vwhrkpsNo ratings yet
- 3 Arm, Cubital Fossa & Elbow JointDocument25 pages3 Arm, Cubital Fossa & Elbow JointImkita MngqundanisoNo ratings yet
- Angiology: (LECTURE-3)Document6 pagesAngiology: (LECTURE-3)আহানাফ তাহমিদ শব্দNo ratings yet
- Axillary ArteryDocument28 pagesAxillary Arteryshrishti shadangiNo ratings yet
- Fore Limb - Blood SupplyDocument20 pagesFore Limb - Blood SupplyVignesh rajuNo ratings yet
- Anterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossaDocument24 pagesAnterior Compartment of Arm & Cubital FossakiranNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The Upper LimbDocument12 pagesBlood Supply of The Upper LimbMnashinatorNo ratings yet
- Kovacs Files AnatomyDocument124 pagesKovacs Files Anatomyshmirtb100% (2)
- Brachial Plexus Anatomy: Abdulaziz R. Alanzi Medical Student, Al-Imam University Riyadh, Saudi ArabiaDocument23 pagesBrachial Plexus Anatomy: Abdulaziz R. Alanzi Medical Student, Al-Imam University Riyadh, Saudi ArabiaArybaa MeerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document82 pagesAnatomy 1innyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document17 pagesAnatomy 1Uljana NasonovaNo ratings yet
- Cubital FossaDocument12 pagesCubital FossaAkinrotimi OluwadunsinNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionDocument13 pagesUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- Brachial DefDocument27 pagesBrachial DefMalak KhanNo ratings yet
- Axillary artery - نسخةDocument3 pagesAxillary artery - نسخةSaid Taysir AbdlJawadNo ratings yet
- Ombro 2Document5 pagesOmbro 2Sandro PinhoNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Head Neck16-2-20192nd YearDocument10 pagesBlood Supply of Head Neck16-2-20192nd Yearmikaelfelix627No ratings yet
- The Topography of Upper LimbDocument5 pagesThe Topography of Upper LimbLorena DobrescuNo ratings yet
- Vessels and Nerves of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDDocument43 pagesVessels and Nerves of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDTodesengelNo ratings yet
- Morphology and Physiology of BacteriaDocument9 pagesMorphology and Physiology of Bacteriaprashantshukla8280No ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesLaboratory Manual For Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualAlexMartinxfgr100% (56)
- Dwnload Full Before We Are Born Essentials of Embryology and Birth Defects 8th Edition Moore Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Before We Are Born Essentials of Embryology and Birth Defects 8th Edition Moore Test Bank PDFmariputwashercy4ca100% (15)
- AD14 Either Mankind Will Stop Monsanto or Monsanto Will Stop MankindDocument6 pagesAD14 Either Mankind Will Stop Monsanto or Monsanto Will Stop MankindAnton CloeteNo ratings yet
- Baylissascaris LarvisDocument136 pagesBaylissascaris LarvisAlejoDubertiNo ratings yet
- Reproduksi Sel RingkasanDocument2 pagesReproduksi Sel RingkasanMulyadi SPdNo ratings yet
- Life On Earth: by DR - Sanjay Banerji Founder Director/Dean of Amrita School of BusinessDocument2 pagesLife On Earth: by DR - Sanjay Banerji Founder Director/Dean of Amrita School of BusinessAravindan NeelakandanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report IDocument11 pagesLab Report IElle B.No ratings yet
- Activity 3 - The Human ReflexDocument2 pagesActivity 3 - The Human ReflexGOOKIEBOONo ratings yet
- Glasgow Theses Service Theses@gla - Ac.ukDocument94 pagesGlasgow Theses Service Theses@gla - Ac.ukKrupali JainNo ratings yet
- FTIR Spectroscopy PhotRes2009Document15 pagesFTIR Spectroscopy PhotRes2009DickyNo ratings yet
- Komunikasi Antar SelDocument39 pagesKomunikasi Antar SelMOCHILNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells - PeTa2Document6 pagesProkaryote and Eukaryote Cells - PeTa2Robin-chwanNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Time Since Death Ba PDFDocument6 pagesEstimation of Time Since Death Ba PDFCesar Augusto Rojas MachucaNo ratings yet
- Plasma Proteins 1Document72 pagesPlasma Proteins 1reuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Degradation and Enzyme Activities of Aspergillus Oryzae and Mucor Irregularis Isolated From Nigerian Crude Oil-Polluted SitesDocument19 pagesHydrocarbon Degradation and Enzyme Activities of Aspergillus Oryzae and Mucor Irregularis Isolated From Nigerian Crude Oil-Polluted SitesTassioNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Medicine: Definition of The Specialty and Scope of Nuclear MedicineDocument23 pagesNuclear Medicine: Definition of The Specialty and Scope of Nuclear MedicinePriya SalunkeNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Topic 1 Lifestyle, Health and Risk Exam Questions BookletDocument42 pagesYear 1 Topic 1 Lifestyle, Health and Risk Exam Questions BookletHazza KhanNo ratings yet
- Isopod BehaviorDocument4 pagesIsopod BehaviorCody Griffin100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration in Animals Plants Notes-2022-2023Document17 pagesCellular Respiration in Animals Plants Notes-2022-2023MARIA ISABILLE DUALLO MUSONGNo ratings yet
- Error Recognition: ToeicDocument47 pagesError Recognition: ToeicNargis Maulina17No ratings yet
- Histology of The Circulatory SystemDocument24 pagesHistology of The Circulatory SystemFatima Zehra YusefNo ratings yet
- ChalksDocument4 pagesChalksKenneth Garciano100% (3)