Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electronics and Communication Digital Electronics
Uploaded by
Praveen KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronics and Communication Digital Electronics
Uploaded by
Praveen KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION Digital electronics
1. Flip flop and their working. What is metastable state in flip-flops? 2. Construct a d flip-flop from a t flip-flop.Differentiate b/w flip-flop and latches 3. What is totem pole? 4. Draw the state graphs for a given problem like sequence generator, flip flop etc 5. Implement Boolean expressions using MUX (2 to 4,3 to 8,etc) 6. Design a decade counter 7. Explain internal organization of memory chips 8. What is a bit? What is CMOS? Draw the circuit of an adder using NAND gate 9. What is a Karnaugh map? 10. What are the four methods to reduce a Boolean? 11. What is the difference b/w half adder and full adder? 12. What are the advantages of CMOS and TTL?What technology is used in CMOS logic? What are VLSI and ULSI? What is the number of components in both? 13. Explain synchronous and asynchronous counter 14. Minimize the function using Quine McClusky:f=xy+xy+yz+xyz 15. What is prime implicant? Which is the universal flip-flop? 16. What is SRAM and DRAM? Compare the two, relative cost of the two. 17. What will happen in the case of a power failure for the above? 18. What is tristate or high impedance state? 19. What are the difference between open collector output and totem pole out put? 20. Find the highest clocking frequency of a digital circuit give the rise time ,fall time and propagation delay?
Electronic Devices & circuits
1. Obtain a square wave from sine wave from Zener diodes. 2. What is the difference between oscillator and multivibrator? 3. What is emitter follower? What is an opamp? 4. What is the ideal gain of an opamp? 5. How is amplification possible in a transistor? 6. Classify power amplifiers 7. How does a diode look(internally)? Explain the working using internal diagram 8. Explain processes taking place in the depletion junction of a forward biased diode 9. What is a buffer? What is the gain of a buffer? 10. What is an oscillator? 11. How do you forward bias a transistor? 12. What are the practical applications of a transistor? 13. What is reverse recovery time and how does it affect a diode?
14. Draw and explain the working of a monostable vibrator using op amp 15. State Thevenins theorem and Nortons theorem. What are their applications? 16. What is the virtual ground in an op amp? 17. Differentiate between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor
Power Electronics
1. What is a thyristor and differentiate between thyristor and a diode 2. Switching action of an SCR and triggering. Draw the diagram of thyristor 3. Draw an internal block diagram of a normal voltage stabilizer 4. What is a reference variable?
Control Systems
1. Define control systems. Why are they so important? 2. What are the different types of control systems? 3. Explain open loop with block diagram examples 4. What are the advantages and drawbacks of closed loop? 5. How can you design a stable system? Explain different stability criteria 6. Explain Ruth-Hurwitz rule in one sentence. What are poles and their significance? 7. Is there any control system in this room(interview hall)? 8. Draw the block diagram of a control system and write its transfer function 9. What is ROC? Explain transformation between s and z planes 10. Differentiate between open and closed loop control systems 11. What is meant by adaptive control system?
12. Find the transfer function of a given RLC circuit Communication
1. What is packet switching and circuit switching? What is the protocol used in telephone network? 2. What is modulation? Why is needed? What are the various types?Compare AM,FM, PM.Which waves will travel a longer distance- FM or AM and why? 3. What is the mode of transmission of television signals? 4. Compare the bandwidth requirements of AM and FM 5. What do you know about antennae? 6. Why is linking up frequency greater than the down linking frequency?
Modern trends and general questions
1. What is a modem? Draw its internal diagram 2. What is VoIP? 3. What is the most important advantage of Bluetooth? 4. What is wave studio? What is Bit rate? 5. What is the difference between mp3 and WAV formats? 6. What is sampling? What is a database? What is VHDL? What is a complier?
7. What is FSF? Cite any current relevance 8. Volume control in TV is logarithmic. Why? 9. What is the mathematics used in DSP and from which domain to which domain is it converted? 10. Differentiate between macros and functions in C .Explain the booting process of a computer.What is round robin technique of interrupt arbitration
Read more: http://www.careers-india.com/2008/02/18/interview-question-asked-interviewquestion-for-electronics-and-communication-engineering/#ixzz1fjJmnEJS
1. What is the frequency at which bluetooth operates? 2. Give an example for a 1 port microwave network. 3. What is the basic difference between an active and passive device? 4. What is the multiple access and duplexing scheme used in GSM?
5.Is diode an active device or passive device? 6. If we tie up J and K ports of the JK flip flop, it will act like a______ flip flop. 7.In microprocessor terminology what does SIM stand for?
8. What all factors the resistance depends on? 9.Where is the energy stored in a capacitor? 10. What is the significance of 8 in 8-bit processor?
1. 2.4 GHz 2. Antenna 3. Active device is capable of amplifying (has gain) or processing signals (has directivity) whereas passive device is not. 4. TDMA/FDD 5. Active device because it has directivity 6. T flip flop 7. Set Interrupt Mask 8. Length and area of cross section (R=resistivity X L/A) 9. In the electric field existing between the plates 10. 8= number of datalines in the processor.
1. The third generation mobile phones satisfy which specifications of the International Telecommunication union?
2. What does the circle around a transistor indicate?
3. Which BJT transistor configuration is also known as 'Emitter Follower'? 4. To which category does the single side band modulation(SSB) technique fall? Digital or analog? 5. What sort of an interfacing is provided by Intel 8259 to Intel 8085 microprocessor?
6. In network theory, what are the branches of a co-TREE made out of the graph of a circuit called?
7. What is the laplace transform of an impulse signal? 8. What is the fundamental difference between Laplace transform and Ztransform? 9. What is the knee voltage of Schottky diodes? 10. What does IMEI number of a mobile phone stand for?
ANSWERS
1. International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) 2. Indicates that the transistor is a discrete component. 3. Common Collector 4. Analog 5. Programmable Interrupt Controller 6. Links 7. 1 8. Laplace transform is for continuous signals and Z-transform is for digital signals. 9. 0.2 V 10. International Mobile Equipment Identity number1. What does LED stand for?
Light Emitting Display Low Energy Display Light Emitting Diode Light Emitting Detector 2. Name the three leads of a common transistor Collector Bias Omitter Base Collector Case
Emitter Collector Bias Collector Base Emitter 3. Connecting a lead from the negative to the positive of a battery will produce: A high resistance circuit A short circuit A low current path An open circuit 4. What is the approximate characteristic voltage that develops across a red LED?
1.7v 3.4v 0.6v 5v 5. If two resistors are placed in series, is the final resistance: Higher Lower The same Cannot be determined 6. Which is not a "common" value of resistance: 2k7 1M8
330R 4k4 7. If a small value of capacitance is connected in parallel with a large value, the combined capacitance will be: The same Higher Lower 8. If the voltage on the base of a transistor increases, does it: Turn on Turn off Not enough information Remain the same 9. The resistor identified in brown is called the:
Base Bias Resistor Load Resistor Emitter Feedback Resistor Bypass Resistor
10. A 100n capacitor in parallel with 10n produces: 90n 100n
110n Cannot be determined 11. A resistor with colour bands: red-red-red-gold, has the value: 22k 5% 2k2 5% 220R 5% 22R 5% 12. The lead marked with the arrow is: The Collector The Base The Emitter The case 13. A 10k resistor in parallel with 10k produces: 10k 5k 20k Cannot be determined 14. The symbol is:
NPN Transistor PNP Transistor Photo Transistor Field Effect Transistor
15. Two 3v batteries are connected as shown. The output voltage is:
3v 0v 6v 16. 4 resistors in ascending order are: 22R 270k 2k2 1M 4k7 10k 47R 330k 3R3 4R7 22R 5k6 100R 10k 1M 3k3 17. The closest value for this combination is: 4k7 2k3 9k4 18. This stage is called:
Common Base Common Collector Common Emitter Emitter Follower
19. The four symbols are:
Capacitor, Microphone, Potentiometer, Electrolytic Electrolytic, Microphone, Resistor, Capacitor Capacitor, Piezo, Resistor, Electrolytic Electrolytic, Coil, Resistor, Capacitor 20. The value of the combination is: 100n 200n 50n 21. The resistor marked in red is:
Base Bias Resistor Load Resistor Emitter Feedback Resistor Bypass Resistor
22. A resistor and capacitor in series is called a: Pulse Circuit Timing Circuit/Delay Circuit Oscillator Circuit/Frequency Circuit Schmitt Circuit
23. A red-red-red-gold resistor in series with an orange-orange-orange-gold resistor produces: 5k5 35,200 ohms 55k None of the above 24. Name the 4 components:
Photo transistor, switch, capacitor, coil Transistor, mercury switch, piezo, coil Photo transistor, reed switch, piezo, coil Photo darlington transistor, reed switch, piezo, coil 25. To obtain a higher value of resistance, resistors are connected in:
Reverse Forward Parallel Series 26. A capacitor and coil in parallel is called: A Tuned Circuit A Timing Circuit
A Delay Circuit A Schmitt Circuit 27. When the base is raised, the emitter will:
Rise Fall Remain Fixed Oscillate
28. What is 1,000p? 0.01n 0.001u 0.1n 1n 29. The current in a circuit is 45mA. This is: 0.045Amp 0.00045A 0.0045A 0.45A 30. A 100n capacitor can be expressed as: 0.1u 0.01u u = microfarad
0.001u none of the above 31. 1mA is equal to: 0.001A 0.00001A 0.01A 0.1A 32. 1,200mV is equal to: 12v 1.2v 0.12v 0.0012v 33. If a 10k resistor is placed across a 10v supply, the current will be: 10mA 1mA 0.01mA 0.1mA 34. This arrangement is called:
Common Emitter Common Collector/Emitter Follower Common Base
35. Identify the correctly connected LED:
A B C D 36. Identify the correct statement:
The cathode lead is longer. It goes to the negative rail The cathode lead is shorter. It goes to the negative rail The cathode lead is shorter. It goes to the positive rail The cathode lead is longer. It goes to the positive rail 37. The current requirement of a LED is: 1.7mA 25mA Between 3 and 35mA 65mA 38. The signal at the collector will be . . .
Inverted . . . In-phase . . . . . . with the base.
39. The purpose of the capacitor:
To pass AC on the input to the base To allow the transistor to self-bias Block DC from the input line To allow the stage to operate
40. The direction of conduction for a diode is:
A B C 41. A DC voltage . . . rises and falls is a sinewave remains constant is an audio waveform 42. A CRO is a
Cathode Ray Oscillator Cathode Ray Oscilloscope Capacitor-Resistor Oscillator Capacitor-Resistor Output 43. These jargon terms mean: (Jargon = language peculiar to a 'mickey' 'electro' 'cap' 'puff'; trade)
mighty, electronic, capper, picofarad microfarad, electronic, capacitor, picofarad microfarad, electrolytic, capacitor, picofarad microfarad, electrolyte, capping, blow 44. The tolerance bands: gold; silver; brown, represent: 10%, 5%, 1% 5%, 10%, 2% 5%, 10%, 1%
10%, 5%, 2% 45. 223 on a capacitor represents: 0.022u 22n 22,000p u = microfarad n = nanofarad p = picofarad
All of the above 46. Arrange these in ascending order: n, p, u p, u, n, n, u, p
p, n, u 47. Name this symbol: A buffer A NOR gate A NAND gate A Schmitt Trigger 48. The number "104" on a capacitor indicates: 0.1u 100n 1n 10n 49. What is the multimeter detecting:
The output voltage of the Schmitt Trigger The delay across the capacitor The voltage across the capacitor The current through the capacitor 50. For the XOR gate, what is the output when both inputs are HIGH:
HIGH LOW Can be HIGH or LOW Cannot be determined
Q1. What is impedance? A. The electric charge stored by a capacitor B. The inverse of resistance C. The opposition to the flow of current in an AC circuit D. The force of repulsion between two similar electric fields Q2. What is reactance? A. Opposition to the flow of direct current caused by resistance B. Opposition to the flow of alternating current caused by capacitance or inductance C. A property of ideal resistors in AC circuits D. A large spark produced at switch contacts when an inductor is deenergized Q3. Which of the following causes opposition to the flow of alternating current in an inductor? A. Conductance B. Reluctance C. Admittance D. Reactance Q4. Which of the following causes opposition to the flow of alternating current in a capacitor? A. Conductance B. Reluctance C. Reactance D. Admittance Q5. How does a coil react to AC? A. As the frequency of the applied AC increases, the reactance decreases
B. As the amplitude of the applied AC increases, the reactance increases C. As the amplitude of the applied AC increases, the reactance decreases D. As the frequency of the applied AC increases, the reactance increases Q6. How does a capacitor react to AC? A. As the frequency of the applied AC increases, the reactance decreases B. As the frequency of the applied AC increases, the reactance increases C. As the amplitude of the applied AC increases, the reactance increases D. As the amplitude of the applied AC increases, the reactance decreases Q7. What happens when the impedance of an electrical load is equal to the internal impedance of the power source? A. The source delivers minimum power to the load B. The electrical load is shorted C. No current can flow through the circuit D. The source can deliver maximum power to the load Q8. Why is impedance matching important? A. So the source can deliver maximum power to the load B. So the load will draw minimum power from the source C. To ensure that there is less resistance than reactance in the circuit D. To ensure that the resistance and reactance in the circuit are equal Q9. What unit is used to measure reactance? A. Farad B. Ohm C. Ampere D. Siemens Q10. What unit is used to measure impedance? A. Volt B. Ohm C. Ampere D. Watt Q11. Why should core saturation of a conventional impedance matching transformer be avoided? A. Harmonics and distortion could result B. Magnetic flux would increase with frequency C. RF susceptance would increase D. Temporary changes of the core permeability could result Q12. What is one reason to use an impedance matching transformer? A. To reduce power dissipation in the transmitter
B. To maximize the transfer of power C. To minimize SWR at the antenna D. To minimize SWR in the transmission line Q13. Which of the following devices can be used for impedance matching at radio frequencies? A. A transformer B. A Pi-network C. A length of transmission line D. All of these choices are correct Q14. Which of the following describes one method of impedance matching between two AC circuits? A. Insert an LC network between the two circuits B. Reduce the power output of the first circuit C. Increase the power output of the first circuit D. Insert a circulator between the two circuits Q15. A two-times increase or decrease in power results in a change of how many dB? A. 2 dB B. 3 dB C. 6 dB D. 12 dB Q16. How does the total current relate to the individual currents in each branch of a parallel circuit? A. It equals the average of each branch current B. It decreases as more parallel branches are added to the circuit C. It equals the sum of the currents through each branch (Kirchoff's Current Law) D. It is the sum of the reciprocal of each individual voltage drop
You might also like
- Ultrasonic Inspection Standards for Wrought MetalsDocument44 pagesUltrasonic Inspection Standards for Wrought Metalsdomsoneng100% (1)
- XII Practicals Viva QDocument8 pagesXII Practicals Viva QAnshul Sharma100% (1)
- Modulus of Subgrade Reaction KsDocument1 pageModulus of Subgrade Reaction KsmohamedabdelalNo ratings yet
- The Essence of Success - Earl NightingaleDocument2 pagesThe Essence of Success - Earl NightingaleDegrace Ns40% (15)
- Question Bank For Power System Transients1Document5 pagesQuestion Bank For Power System Transients1Prabha KaruppuchamyNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFDocument8 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFVenkata SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Tuned Collector Oscillator - Electronic Circuits and Diagram-Electronics Projects and DesignDocument6 pagesTuned Collector Oscillator - Electronic Circuits and Diagram-Electronics Projects and DesignSuhaila ctNo ratings yet
- Method Statement of Static Equipment ErectionDocument20 pagesMethod Statement of Static Equipment Erectionsarsan nedumkuzhi mani100% (4)
- VLSI Interview QuestionDocument17 pagesVLSI Interview QuestionamiteshtripathiNo ratings yet
- Transients in Power SystemDocument10 pagesTransients in Power SystemMATHANKUMAR.SNo ratings yet
- Storage Reservior and Balancing ReservoirDocument19 pagesStorage Reservior and Balancing ReservoirNeel Kurrey0% (1)
- LNGC Q-Flex Al Rekayyat - Imo 9397339 - Machinery Operating ManualDocument581 pagesLNGC Q-Flex Al Rekayyat - Imo 9397339 - Machinery Operating Manualseawolf50No ratings yet
- Interview QuesDocument12 pagesInterview Quesvlsi_asicNo ratings yet
- Anna University Affiliated Colleges Be Eee Semester Vi Ee2353 - High Voltage Engineering Unit - Iover Voltages in Electrical Power SystemsDocument6 pagesAnna University Affiliated Colleges Be Eee Semester Vi Ee2353 - High Voltage Engineering Unit - Iover Voltages in Electrical Power Systemspvanitha143No ratings yet
- Books 2738 0Document12 pagesBooks 2738 0vinoohmNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 ReportDocument9 pagesLab 2 Reportsherub wangdiNo ratings yet
- Interview Technical QuestionsDocument2 pagesInterview Technical QuestionsAndreaBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Viva QuestionsDocument9 pagesComprehensive Viva Questionsraju83650% (2)
- Electric Circuits and Electron Devices Question BankDocument3 pagesElectric Circuits and Electron Devices Question BankVenkatesh ShankarNo ratings yet
- Edec Question Paper-IDocument8 pagesEdec Question Paper-IarunfriendsNo ratings yet
- Me2255-Electronics & Microprocessor: Question Bank Ii Year / Iv Semester / MechanicalDocument5 pagesMe2255-Electronics & Microprocessor: Question Bank Ii Year / Iv Semester / Mechanical28217728No ratings yet
- Assignment - Interview Questions - ECE - 3Document4 pagesAssignment - Interview Questions - ECE - 3JitheshNo ratings yet
- Optical Networks QBDocument6 pagesOptical Networks QBPreethi MuraliNo ratings yet
- DCCN Model Question-TheoryDocument13 pagesDCCN Model Question-TheoryChirag ParasharNo ratings yet
- Anna University EC2151 Electric Circuits and Electron Devices (Common To All Branches Under I & C Faculty) Semester: 2 Year: 1 StyrDocument5 pagesAnna University EC2151 Electric Circuits and Electron Devices (Common To All Branches Under I & C Faculty) Semester: 2 Year: 1 Styrsp_shailliNo ratings yet
- Kings: Question BankDocument11 pagesKings: Question BankpootommyNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Communications: 1. Network TheoryDocument7 pagesElectronics & Communications: 1. Network TheoryAneesh KurianNo ratings yet
- Dronacharya College of Engineering, GR - Noida.: Q6.Explain Bridges, Routers, Gateways and Different LevelDocument4 pagesDronacharya College of Engineering, GR - Noida.: Q6.Explain Bridges, Routers, Gateways and Different Levelshyamsagar15No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Questions and AnswersNavdeep AhlawatNo ratings yet
- DigitalDocument2 pagesDigitalVishwanath BrungiNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Analog Electronics, Power Systems, Electrical Machines, Electrical Measurements, and Power Electronics QuestionsDocument2 pagesDigital Electronics, Analog Electronics, Power Systems, Electrical Machines, Electrical Measurements, and Power Electronics QuestionsAkshat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Microprocessors FundamentalsDocument5 pagesElectronics and Microprocessors FundamentalsmythulasiNo ratings yet
- Isro, Barc Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesIsro, Barc Interview QuestionspuppykNo ratings yet
- PD QuesDocument32 pagesPD Quessunkara naga hari prasadNo ratings yet
- Question Bank PDCDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank PDCSanjay MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- OCEF ReviewsDocument2 pagesOCEF ReviewsIsuru KasthurirathneNo ratings yet
- Hve 216marksDocument6 pagesHve 216marksMani GaneshNo ratings yet
- EC6404-Linear Integrated Circuits Question BankDocument7 pagesEC6404-Linear Integrated Circuits Question BankkundaviNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design FundamentalsDocument10 pagesCMOS VLSI Design FundamentalsPranav sharmaNo ratings yet
- Kings: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDocument7 pagesKings: Department of Electronics and Communication Engineeringnishokvs16No ratings yet
- Advance Lab Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesAdvance Lab Viva QuestionsArunmozhi SinouvassaneNo ratings yet
- Drdo Interview QuestionsDocument209 pagesDrdo Interview QuestionsRamakrishna RajuNo ratings yet
- Ec2045 Satellite CommunicationDocument6 pagesEc2045 Satellite CommunicationSeekay Alais Karuppaiah CNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits Question BankDocument11 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits Question Bankkalyan thallapaneniNo ratings yet
- EE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankDocument11 pagesEE2203-Electronic Device and Circuits Question BankAnbarasan Annamalai100% (1)
- EeeDocument3 pagesEeeAditya VyasNo ratings yet
- Ec2403 Microwave Question BankDocument6 pagesEc2403 Microwave Question BankNasrin Rafee50% (2)
- Question Bank For Eletronic Design PracticesDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank For Eletronic Design PracticesabcdNo ratings yet
- EE1152- Circuits & ElectronicsDocument5 pagesEE1152- Circuits & ElectronicsSaranya PrabhuNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks PDFDocument5 pages2 Marks PDFBala913No ratings yet
- Mech-I-Basic Electronics Engg AssignmentDocument6 pagesMech-I-Basic Electronics Engg AssignmentArunNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Microprocessor and Microcontroller 37. What Is Power Electronics ?Document12 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Microprocessor and Microcontroller 37. What Is Power Electronics ?perakkaNo ratings yet
- Assignment SSED 2022Document2 pagesAssignment SSED 2022prashantsheetalNo ratings yet
- Design A Decade Counter.: What Is VHDL?Document2 pagesDesign A Decade Counter.: What Is VHDL?shockwaveNo ratings yet
- Me2255 Electronics and Microprocessor Anna University Question BankDocument6 pagesMe2255 Electronics and Microprocessor Anna University Question BankMayakannan RNo ratings yet
- ECA Lab QuestionsDocument11 pagesECA Lab QuestionsRaj Kumar0% (1)
- Ec 3 Lab Viva QuestionsDocument4 pagesEc 3 Lab Viva QuestionsDeepti Chandrasekharan0% (1)
- EC6801 Question Bank on Wireless CommunicationDocument10 pagesEC6801 Question Bank on Wireless CommunicationEASACOLLEGENo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Wireless CommunicationDocument10 pagesQuestion Bank For Wireless CommunicationPRIYA RAJI100% (2)
- EC6801 IT Wireless CommunicationDocument10 pagesEC6801 IT Wireless CommunicationAnbu ArasanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank MECH1Document5 pagesQuestion Bank MECH1Rameez FaroukNo ratings yet
- ECE Question Bank for IV Semester covering PDEs, Z-Transforms, Communication SystemsDocument8 pagesECE Question Bank for IV Semester covering PDEs, Z-Transforms, Communication SystemssgdhruvNo ratings yet
- Raisoni College CMOS VLSI Design Question BankDocument7 pagesRaisoni College CMOS VLSI Design Question BankRaja Khurram ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Cseitquestions - Blogspot.In Cseitquestions - Blogs Pot - in Cseitquestions - Blogspot.InDocument23 pagesCseitquestions - Blogspot.In Cseitquestions - Blogs Pot - in Cseitquestions - Blogspot.IndeepikaNo ratings yet
- S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science and EngineeringDocument7 pagesS.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology Department of Computer Science and Engineeringਹਰਪਿ੍ਤ ਸਿੰਘNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document2 pagesAssignment 4baalaajeeNo ratings yet
- I-Parcel User GuideDocument57 pagesI-Parcel User GuideBrian GrayNo ratings yet
- Synopsis: A Study On Customer Satisfaction AT Nerolac Paints LTD., KadapaDocument5 pagesSynopsis: A Study On Customer Satisfaction AT Nerolac Paints LTD., KadapaAnu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Company Profi Le: IHC HytopDocument13 pagesCompany Profi Le: IHC HytopHanzil HakeemNo ratings yet
- Sampling Fundamentals ModifiedDocument45 pagesSampling Fundamentals ModifiedArjun KhoslaNo ratings yet
- EE3331C Feedback Control Systems L1: Overview: Arthur TAYDocument28 pagesEE3331C Feedback Control Systems L1: Overview: Arthur TAYpremsanjith subramani0% (1)
- 63db2cf62042802 Budget Eco SurveyDocument125 pages63db2cf62042802 Budget Eco SurveyNehaNo ratings yet
- James Ashmore - Curriculum VitaeDocument2 pagesJames Ashmore - Curriculum VitaeJames AshmoreNo ratings yet
- Company's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)Document23 pagesCompany's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)ashairways100% (2)
- Philippines Taxation Scope and ReformsDocument4 pagesPhilippines Taxation Scope and ReformsAngie Olpos Boreros BaritugoNo ratings yet
- Market Participants in Securities MarketDocument11 pagesMarket Participants in Securities MarketSandra PhilipNo ratings yet
- Product Data: Airstream™ 42BHC, BVC System Fan CoilsDocument40 pagesProduct Data: Airstream™ 42BHC, BVC System Fan CoilsMaxmore KarumamupiyoNo ratings yet
- Sierra Wireless AirPrimeDocument2 pagesSierra Wireless AirPrimeAminullah -No ratings yet
- Jodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentDocument17 pagesJodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentWMBF NewsNo ratings yet
- ApudDocument53 pagesApudlatifahNo ratings yet
- 2014 March CaravanDocument48 pages2014 March CaravanbahiashrineNo ratings yet
- ProkonDocument57 pagesProkonSelvasatha0% (1)
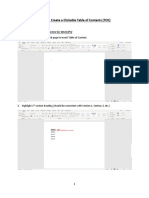
- How To: Create A Clickable Table of Contents (TOC)Document10 pagesHow To: Create A Clickable Table of Contents (TOC)Xuan Mai Nguyen ThiNo ratings yet
- Nuxeo Platform 5.6 UserGuideDocument255 pagesNuxeo Platform 5.6 UserGuidePatrick McCourtNo ratings yet
- Siyaram S AR 18-19 With Notice CompressedDocument128 pagesSiyaram S AR 18-19 With Notice Compressedkhushboo rajputNo ratings yet
- Easyjet Group6Document11 pagesEasyjet Group6Rishabh RakhechaNo ratings yet
- (Jf613e) CVT Renault-Nissan PDFDocument4 pages(Jf613e) CVT Renault-Nissan PDFJhoanny RodríguezNo ratings yet
- PHASE 2 - Chapter 6 Object ModellingDocument28 pagesPHASE 2 - Chapter 6 Object Modellingscm39No ratings yet