Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise 2
Uploaded by
Jyo TamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 2
Uploaded by
Jyo TamCopyright:
Available Formats
Discriminant Analysis
Analysis Case Processing Summary Unweighted Cases Valid Excluded Missing or out-of-range group codes At least one missing discriminating variable Both missing or out-of-range group codes and at least one missing discriminating variable Total Total 0 20 .0 100.0 0 .0 0 .0 N 20 0 Percent 100.0 .0
Group Statistics Valid N (listwise) BRAND National Brand ANNUAL INCOME HOUSEHOLD SIZE Local Brand ANNUAL INCOME HOUSEHOLD SIZE Total ANNUAL INCOME HOUSEHOLD SIZE Unweighted 10 10 10 10 20 20 Weighted 10.000 10.000 10.000 10.000 20.000 20.000
Analysis 1
Summary of Canonical Discriminant Functions
Eigenvalues Functio n 1 Eigenvalue 1.113a % of Variance 100.0 Cumulative % 100.0 Canonical Correlation .726
a. First 1 canonical discriminant functions were used in the analysis.
Wilks' Lambda Test of Functio n(s) 1 Wilks' Lambda .473 Chi-square 12.721 df 2 Sig. .002
Standardized Canonical Discriminant Function Coefficients Function 1 ANNUAL INCOME HOUSEHOLD SIZE .722 -.490
Structure Matrix Function 1 ANNUAL INCOME HOUSEHOLD SIZE Pooled within-groups correlations between discriminating variables and standardized canonical discriminant functions Variables ordered by absolute size of correlation within function. .887 -.734
Canonical Discriminant Function Coefficients Function 1 ANNUAL INCOME HOUSEHOLD SIZE (Constant) Unstandardized coefficients .335 -.313 -4.545
Functions at Group Centroids Function BRAND National Brand Local Brand Unstandardized canonical discriminant functions evaluated at group means 1 1.001 -1.001
Classification Statistics
Classification Processing Summary Processed Excluded Missing or out-of-range group codes At least one missing discriminating variable Used in Output 20 0 20 0
Prior Probabilities for Groups BRAND Prior Cases Used in Analysis
Unweighted National Brand Local Brand Total .500 .500 1.000 10 10 20
Weighted 10.000 10.000 20.000
Classification Results
b,c
Predicted Group Membership BRAND Original Count National Brand Local Brand % National Brand Local Brand Cross-validated
a
National Brand 9 2 90.0 20.0 8 2 80.0 20.0
Local Brand 1 8 10.0 80.0 2 8 20.0 80.0
Total 10 10 100.0 100.0 10 10 100.0 100.0
Count
National Brand Local Brand
National Brand Local Brand
a. Cross validation is done only for those cases in the analysis. In cross validation, each case is classified by the functions derived from all cases other than that case. b. 85.0% of original grouped cases correctly classified. c. 80.0% of cross-validated grouped cases correctly classified.
Classification Results
b,c
Predicted Group Membership BRAND Original Count National Brand Local Brand % National Brand Local Brand Cross-validateda Count National Brand Local Brand % National Brand Local Brand National Brand 9 2 90.0 20.0 8 2 80.0 20.0 Local Brand 1 8 10.0 80.0 2 8 20.0 80.0 Total 10 10 100.0 100.0 10 10 100.0 100.0
a. Cross validation is done only for those cases in the analysis. In cross validation, each case is classified by the functions derived from all cases other than that case. b. 85.0% of original grouped cases correctly classified.
ANSWERS:
1) From the classification results table, we can say that discriminant function is able to classify 17 cases out of 20 or 85% of original grouped cases correctly and 16 cases out of 20 incase of cross validation or 80% of the cross validated grouped cases correctly.
2)
Wilks' lambda is the proportion of the total variance in the discriminant scores NOT explained by differences among the groups. From the wilks lemda table, we can say that discriminant function is statistically significant as the value of wilks lemda is equal to 0.473.ie less than 0.5 Also eigen value is equal to1.113 which is greater than 1 and canonical correlation is 0.726 which is also high. That means the discriminant function is significant.
3)
From both the standardised coefficient table and structure table, income is relatively better in discriminating b/w consumers for national and local brands.
4)
By looking at unstandardised coefficients table, we can find the value D; D= -4.545+0.335(annualincome) - 0.313(household size) If the value of D is close to 1.001 (group centroid table), then, the new customer will fall under national brand group and if the value of D is close to -1.001, then he will fll under local brand group.
You might also like
- Profit Driven Business Analytics: A Practitioner's Guide to Transforming Big Data into Added ValueFrom EverandProfit Driven Business Analytics: A Practitioner's Guide to Transforming Big Data into Added ValueNo ratings yet
- Name: Mohamed Abdulqadr Mohamed Section: Koe58 Course Code: Mgn909 Roll No: 22 REG NO: 11801223 Q1)Document7 pagesName: Mohamed Abdulqadr Mohamed Section: Koe58 Course Code: Mgn909 Roll No: 22 REG NO: 11801223 Q1)WIIL WAAALNo ratings yet
- F5 RevDocument69 pagesF5 Revpercy mapetereNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Attribute Measurement Systems AnalysisDocument15 pagesInstructions:: Attribute Measurement Systems AnalysiserayNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Attribute Measurement Systems AnalysisDocument15 pagesInstructions:: Attribute Measurement Systems AnalysisSead ZejnilovicNo ratings yet
- Exercises w3Document6 pagesExercises w3hqfNo ratings yet
- 1 - Clean - Edits - Stock Management (1336) 1Document12 pages1 - Clean - Edits - Stock Management (1336) 1ZED360 ON DEMANDNo ratings yet
- Revision 2Document37 pagesRevision 2percy mapetereNo ratings yet
- Airbnb SimulationDocument5 pagesAirbnb SimulationVianna NgNo ratings yet
- Calculate breakeven points, degrees of leverage, and optimal debt ratiosDocument2 pagesCalculate breakeven points, degrees of leverage, and optimal debt ratiosHuynh Thi Phuong ThuyNo ratings yet
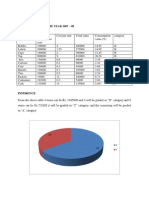
- Abc Analysis For The Year 2007 - 08: InferenceDocument7 pagesAbc Analysis For The Year 2007 - 08: Inferencesri5050No ratings yet
- CVP Analysis Chapter-10: Were $140,000, AL's Margin of Safety, in Units, WasDocument7 pagesCVP Analysis Chapter-10: Were $140,000, AL's Margin of Safety, in Units, Wasali hansiNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 4 Reportable SegmentsDocument7 pagesSeatwork 4 Reportable SegmentsMon RamNo ratings yet
- Revenue Test Value $3,275 Operating Profit Test Value $580 Identifiable Assets Test Value $6,750Document3 pagesRevenue Test Value $3,275 Operating Profit Test Value $580 Identifiable Assets Test Value $6,750anonimNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics Assignment AnalysisDocument9 pagesBusiness Statistics Assignment AnalysisAdy JohnstonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document7 pagesChapter 5Mohammad AnikNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 - Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument9 pagesChap 7 - Cost-Volume-Profit Analysislalith4uNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment For Acct For MGMTDocument4 pagesIndividual Assignment For Acct For MGMTSujib Barman88% (8)
- Inventory ManagementDocument43 pagesInventory Managementdharmendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Acn 3Document5 pagesAcn 3Navidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Piedmont Fasteners Break Even AnalysisDocument9 pagesPiedmont Fasteners Break Even AnalysisAi Lyn100% (1)
- Chapter3 - Solved AssignementDocument5 pagesChapter3 - Solved Assignementcumar maxamuud samatarNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square Analysis in MarketingDocument6 pagesChi-Square Analysis in MarketingNutukurthi Venkat RamjiNo ratings yet
- 320C10Document59 pages320C10Kara Mhisyella Assad100% (2)
- Bussiness Statistics: Group-6 Arshiya Singh Chahana JakharDocument18 pagesBussiness Statistics: Group-6 Arshiya Singh Chahana JakharMisha JaswalNo ratings yet
- Problems in Standard Deviation and EstimationDocument5 pagesProblems in Standard Deviation and EstimationsjaswanthNo ratings yet
- Course TitleDocument5 pagesCourse TitleSolomon G ShNo ratings yet
- Accounting for Managers: Calculating Break-Even PointsDocument123 pagesAccounting for Managers: Calculating Break-Even PointsAmanuel GirmaNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument5 pagesOutputSagar GawaliNo ratings yet
- Case Processing SummaryDocument4 pagesCase Processing SummaryMaheswaran RamalingamNo ratings yet
- QM 2Document38 pagesQM 2Devansh Jain100% (1)
- Bab X Biaya KualitasDocument18 pagesBab X Biaya KualitasRoys AhmadNo ratings yet
- Answer KeyDocument19 pagesAnswer KeyRenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Questions (2)Document4 pagesChapter 03 - Questions (2)gurnoorkaurgilllNo ratings yet
- Self-Test Solutions and Answers to Selected Even-Numbered ProblemsDocument26 pagesSelf-Test Solutions and Answers to Selected Even-Numbered ProblemsEllen WangNo ratings yet
- SINHGAD INSTITUTE BUSINESS STATISTICS EXAMDocument4 pagesSINHGAD INSTITUTE BUSINESS STATISTICS EXAMEun woo Lover N kdramaNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Kuis Akmen 2Document13 pagesKumpulan Kuis Akmen 2IstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 NotesDocument2 pagesExam 1 NotesBBYPENNYNo ratings yet
- Midterm - Ch. 10, 11Document14 pagesMidterm - Ch. 10, 11Cameron BelangerNo ratings yet
- 93% Score on Managerial Accounting QuizDocument6 pages93% Score on Managerial Accounting Quizgelsk50% (2)
- R34 Measures of LeverageDocument12 pagesR34 Measures of LeverageMoataz EmadNo ratings yet
- Iilustrate For Scale (COMPARATIVE VS. NON - Com)Document25 pagesIilustrate For Scale (COMPARATIVE VS. NON - Com)Thitima KongkunnavatNo ratings yet
- SABV Topic 2 QuestionsDocument3 pagesSABV Topic 2 QuestionsNgoc Hoang Ngan NgoNo ratings yet
- CMKT 300 2021 Module 4 Brand MetricsDocument28 pagesCMKT 300 2021 Module 4 Brand MetricsHồng KhanhNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4Document22 pagesWorksheet 4Vikrant bishtNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 Chapter 13A Sample QuestionsDocument4 pagesExam 4 Chapter 13A Sample QuestionsNirali PatelNo ratings yet
- Even-Numbered Problems Quality Cost SolutionsDocument26 pagesEven-Numbered Problems Quality Cost SolutionsAndrey HcivokramNo ratings yet
- Testing Techniques: Software Testing & Implementation Exercise SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesTesting Techniques: Software Testing & Implementation Exercise SOLUTIONFatima AsadNo ratings yet
- 1667750572final Assignment - ME06 BatchDocument8 pages1667750572final Assignment - ME06 BatchCalvin ManNo ratings yet
- OPN 501 Final Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesOPN 501 Final Exam QuestionsLydia PhilipNo ratings yet
- Pareto Chart TemplateDocument8 pagesPareto Chart Templatearifin2484No ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument7 pagesCVP AnalysisKat Lontok0% (1)
- Assignment For Session 11 - Channel Evaluation MeasuresDocument4 pagesAssignment For Session 11 - Channel Evaluation MeasuresSakshi KumariNo ratings yet
- FMAForecasting QDocument11 pagesFMAForecasting QAnisahMahmoodNo ratings yet
- CH 23 - Study QuestionsDocument5 pagesCH 23 - Study QuestionsKiranNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management and Environmental Management Applications in The Agricultural Production ProcessDocument6 pagesTotal Quality Management and Environmental Management Applications in The Agricultural Production ProcessKOPSIDAS ODYSSEASNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 1Document4 pagesAssignment 2 1Doinita ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Mahusay Acc3112 Major Output 1Document4 pagesMahusay Acc3112 Major Output 1Jeth MahusayNo ratings yet
- Advanced Portfolio Management: A Quant's Guide for Fundamental InvestorsFrom EverandAdvanced Portfolio Management: A Quant's Guide for Fundamental InvestorsNo ratings yet