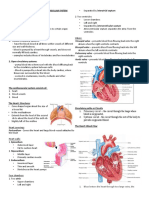
Heart
Tuesday, July 11, 2023 12:49 AM
Working principle
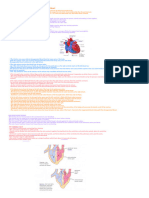
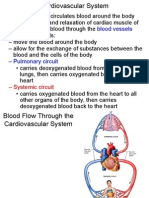
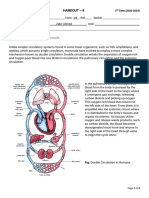
There are 2 large veins called superior and inferior vena cava. The superior vena cava carries
deoxygenated blood form the upper part of the body towards the heard. The inferior vena cava carries
deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body towards the heart. The inferior and superior vena
cava's fuses together to form the larges vein in the body called vena cava. The large volume of
deoxygenated blood travels to the heart through the vena cava. The end of the vena cava which is
joined to the right atrium of the heart has a semi lunar valve. The atria of the heart relaxes causing for
the blood in the vena cava to force open the semi lunar valve and flow into the right ventricle. The blood
fills the right atrium. Once the right atrium is fully filled with blood the semi lunar valve closes
preventing backflow of the blood from the right aria to back to the vena cava. Once the vena cava is fully
filled the cardiac muscles of the atria contracts reducing the volume of the atrium increasing the
pressure of the blood. The pressure produced from the blood forces open the tricuspid valve and flows
into the right ventricle of the heart. Once the ventricle of the heart is fully filled with blood the tricuspid
valve closes preventing the backflow of the blood form the right ventricle to the right atrium of the
heart. Then the cardiac muscles of the right ventricle contracts producing enough pressure for the blood
to be pumped into the pulmonary artery. The semilunar valve of the pulmonary artery is forced open as
the blood is pumped into it through the right ventricle. Once the ventricles relaxes the semi lunar valve
of the pulmonary artery closes preventing backflow of blood back int the right ventricle. The
deoxygenated blood travels into the lungs. In the lungs the blood gets oxygenated. Once the blood is
oxygenated the oxygenated blood flows into the left atrium of the heart through the pulmonary vein.
The blood passing through the pulmonary vein forces open the semi lunar valve located at the end of
the pulmonary vein and flows into the relaxed left atrium. The left atrium fully fills with blood. Once the
left atrium is filled with blood the semi lunar value of the pulmonary vein closes up preventing backflow
of the blood from the left ventricle back to the pulmonary vein. The left ventricle cardiac muscles
contracts producing enough pressure for the blood to force open the bicuspid valve and flow into the
left ventricle. One the blood fully fills up the left ventricle the bicuspid valve closes preventing backflow
of blood back into the left atrium. The left ventricle's cardiac muscles contract with high force producing
enough pressure for the blood to be pumped into the aorta at high speed and pressure. Once the blood
is pumped into the aorta the semi lunar vale of the aorta closes preventing backflow of blood back to
the heart. There are chords called tendonous chords or tendinea code that attaches to the
atrioventricular valves and makes sure they are not turned upside down by the pressure caused.
Thickness
There aria's thickness is much less when compared with the ventricles thickness. The reason is because
they only needs to contract a little and produce small amount of force and produce less pressure as the
blood need to travel a shorter distance. When we compare the ventricles with each other the left
ventricle is much thicker than the right ventricle. So as the right ventricle is less thicker produces small
force and blood is pumped to the pulmonary artery at less pressure so blood travels much slowly. This is
an advantage as blood travels slowly gives more opportunity for gas exchange and makes sure that the
blood do not damage the smooth endothelial cell layer in the capillaries present around the alveoli and
also the distance the blood needs to travel is shorter. While the left ventricle is much thicker with large
amounts of cardiac muscles present because should produce enough force to pump the blood into the
aorta at high pressure so the blood will be circulated throughout the body at high speed as the distance
the blood needs to travel is larger.
Cardiac cycles
Atrial systole
Contraction of the atria. The semi lunar valves closed , the atrioventricular valves opens , atria contracts
unit -1 Page 1
�Contraction of the atria. The semi lunar valves closed , the atrioventricular valves opens , atria contracts
and ventricles relaxes
Ventricular systole
Contraction of the ventricles. The atrioventricular valves closed , semi lunar valves opens at the end, the
ventricles contracted and atria relaxed.
Full cardiac diastole
The state where both the atria and the ventricles are relaxed. The atrioventricular valves closed but
slightly open allowing small amount of blood to leak through. The semi lunar valves closed.
Heartbeat
Consists of two sounds called "lub" and "dub". Both these sounds are produced during the ventricular
systole and diastole. First "lub" sound is produced during ventricular systole when the blood is forced
upon the atrioventricular valves then the second sound "dub" occurs during ventricular systole where
the ventricle relaxes and the backflow of blood hits the closed semi lunar valves of pulmonary artery and
the aorta.
unit -1 Page 2