0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesComprehensive Math Dictionary Terms
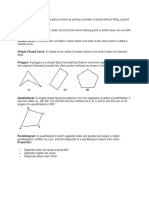
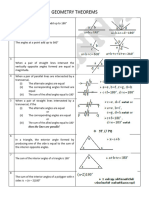
The document is a comprehensive math dictionary that defines key mathematical terms and concepts across four quarters. It includes definitions for terms related to algebra, geometry, and trigonometry, such as binomials, quadratic equations, and the Pythagorean theorem. Each section is organized by quarter, providing a structured overview of essential mathematical vocabulary and theorems.
Uploaded by
johnraydaniele12Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesComprehensive Math Dictionary Terms
The document is a comprehensive math dictionary that defines key mathematical terms and concepts across four quarters. It includes definitions for terms related to algebra, geometry, and trigonometry, such as binomials, quadratic equations, and the Pythagorean theorem. Each section is organized by quarter, providing a structured overview of essential mathematical vocabulary and theorems.
Uploaded by
johnraydaniele12Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd