0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views3 pagesGen Chem 2
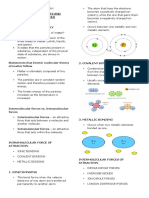
The document covers the Kinetic Molecular Model, which explains the behavior of matter in different states (solid, liquid, gas) based on particle motion and intermolecular forces. It details various types of intermolecular forces such as dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonds, and London dispersion forces, and outlines the properties of solids and liquids. Additionally, it discusses the characteristics of crystalline and amorphous solids, including their structures and types.
Uploaded by
Dhea DunqueCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views3 pagesGen Chem 2
The document covers the Kinetic Molecular Model, which explains the behavior of matter in different states (solid, liquid, gas) based on particle motion and intermolecular forces. It details various types of intermolecular forces such as dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonds, and London dispersion forces, and outlines the properties of solids and liquids. Additionally, it discusses the characteristics of crystalline and amorphous solids, including their structures and types.
Uploaded by
Dhea DunqueCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3