0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesHow to Graph a Parabola Explained
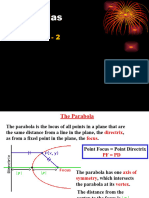
A parabola is a symmetrical curve formed by the intersection of a cone and a plane, characterized by its focus, directrix, and vertex. The standard equations for vertical and horizontal parabolas are y = a(x - h)² + k and x = a(y - k)² + h, respectively, where (h, k) is the vertex. To graph a parabola, identify the vertex, find the axis of symmetry, plot points, and sketch the curve while maintaining symmetry.
Uploaded by
johnlester.duarte1120Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesHow to Graph a Parabola Explained
A parabola is a symmetrical curve formed by the intersection of a cone and a plane, characterized by its focus, directrix, and vertex. The standard equations for vertical and horizontal parabolas are y = a(x - h)² + k and x = a(y - k)² + h, respectively, where (h, k) is the vertex. To graph a parabola, identify the vertex, find the axis of symmetry, plot points, and sketch the curve while maintaining symmetry.
Uploaded by
johnlester.duarte1120Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd