0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views72 pages6e Iecd3
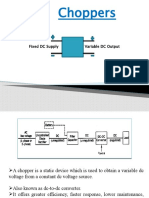
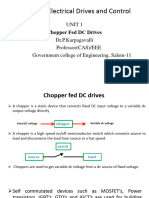
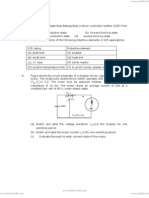
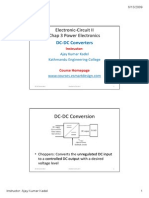
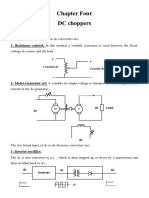
The document discusses various types of inverters, including single-phase and three-phase inverters, and their classifications based on output, input source, commutation methods, and connections. It also covers the operation of choppers, dual converters, and cycloconverters, highlighting their applications in adjustable speed drives, induction heating, and power supplies. Key concepts such as feedback diodes, series inverters, and frequency control methods are explained.
Uploaded by
nishunishant1903Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views72 pages6e Iecd3
The document discusses various types of inverters, including single-phase and three-phase inverters, and their classifications based on output, input source, commutation methods, and connections. It also covers the operation of choppers, dual converters, and cycloconverters, highlighting their applications in adjustable speed drives, induction heating, and power supplies. Key concepts such as feedback diodes, series inverters, and frequency control methods are explained.
Uploaded by
nishunishant1903Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd