0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesLMU Study Plan
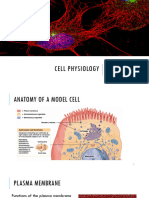
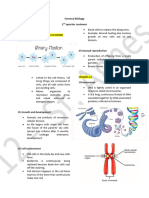
The document outlines a detailed study plan covering various topics in biology from April 4 to April 24, including metabolism, cell membrane structure, and molecular biology techniques. It includes specific dates for focused lectures on topics such as protein structure, DNA replication, and cancer biology, as well as mock tests for exam preparation. Additionally, it provides flashcard questions and answers on cell membrane structure and transport mechanisms.
Uploaded by
sriswathivg10Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesLMU Study Plan
The document outlines a detailed study plan covering various topics in biology from April 4 to April 24, including metabolism, cell membrane structure, and molecular biology techniques. It includes specific dates for focused lectures on topics such as protein structure, DNA replication, and cancer biology, as well as mock tests for exam preparation. Additionally, it provides flashcard questions and answers on cell membrane structure and transport mechanisms.
Uploaded by
sriswathivg10Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd