0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views21 pagesStray Current
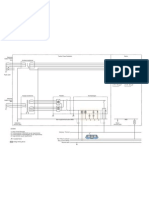
Stray current refers to electrical current that flows through unintended paths, particularly in rail systems where it can cause corrosion of metal structures due to chemical reactions. To mitigate stray current effects, measures such as decreasing rail circuit resistance, increasing rail-to-earth resistance, and limiting rail potential are recommended. Insulation materials and proper installation techniques are essential to protect against stray current corrosion in infrastructure like MRT Line-6.
Uploaded by
Shahriyar Kabir RistaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views21 pagesStray Current
Stray current refers to electrical current that flows through unintended paths, particularly in rail systems where it can cause corrosion of metal structures due to chemical reactions. To mitigate stray current effects, measures such as decreasing rail circuit resistance, increasing rail-to-earth resistance, and limiting rail potential are recommended. Insulation materials and proper installation techniques are essential to protect against stray current corrosion in infrastructure like MRT Line-6.
Uploaded by
Shahriyar Kabir RistaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd