Pimpri Chinchwad Education Trust’s
Pimpri Chinchwad College of Engineering
Fluid Mechanics
IE2 Assignment: Orifice meter
Orifice Advantages of Orifice Meter
An orifice is a small opening or hole through which
Cost-Effective: Orifice meters are relatively inexpensive
fluid flows. Orifices are commonly used in pipes,
compared to other flow measurement devices.
tanks, and other fluid systems for various purposes.
Simple Design: They have a simple construction, making
By measuring the pressure difference across the
them easy to install and maintain.
orifice, the flow rate of the fluid can be determined.
Wide Applicability: Orifice meters can be used for a wide
Orifice meters are widely employed in various
range of fluid types and flow rates, making them versatile in
industries for monitoring and controlling fluid flow
various industrial applications.
processes due to their simplicity, reliability, and cost-
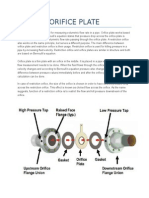
effectiveness. Fig.1: Tank with an orifice Fig.2: Orifice plate
Equation & Calculation Limitations of Orifice Meter
Construction
Pressure Loss: Orifice meters induce pressure loss due to
An orifice meter typically consists of: The equation commonly used to calculate the flow rate Q through an orifice meter is
the constriction caused by the orifice plate, leading to energy
A pipe with an orifice plate installed perpendicular to derived from Bernoulli's equation and is known as the Orifice Equation. It is given by:
losses in the system. Accuracy Dependency: Accuracy is
the flow. The orifice plate has a precisely machined
affected by factors such as changes in fluid properties and
hole. Upstream and downstream pressure taps for
flow conditions, requiring careful calibration and
measuring pressure difference. Pressure gauges or
where: Q= Flow rate through the orifice (m³/s) maintenance. Limited Turndown Ratio: Orifice meters have
transmitters connected to the taps for pressure
a limited turndown ratio, which may restrict their
measurement. Optionally, a differential pressure Cd= Discharge coefficient (dimensionless), which accounts for the efficiency of the
effectiveness in applications with widely varying flow rates.
transmitter to calculate flow rate based on pressure orifice plate and is typically between 0.6 to 0.8 for sharp-edged orifices.
difference. A= Cross-sectional area of the orifice (m²)
g= Acceleration due to gravity (m/s²) Conclusion
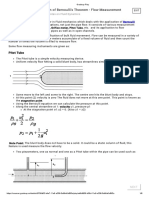
Working Principle
The orifice meter works on the principle of Bernoulli's h= Pressure differential across the orifice (m), calculated as h = (h1 – h2), where h1 and In conclusion, the orifice meter stands as a pivotal tool in fluid
equation. As fluid flows through the orifice, there is a h1 are the pressures measured upstream and downstream of the orifice respectively. mechanics, facilitating precise measurement and control of
decrease in pressure due to the constriction caused The area A of the orifice can be calculated using the formula for the area of a circle: fluid flow rates in various industrial settings. Its cost-
by the orifice plate. The pressure drop across the effectiveness, simple design, and wide applicability
orifice is proportional to the square of the fluid underscore its significance in diverse industries such as oil
where: d = Diameter of the orifice (m) and gas, water treatment, and chemical processing.
velocity. This pressure difference is measured using
Substituting the expression for A into the Orifice Equation, we get: However, despite its advantages, the orifice meter is not
press
u r e t a p s lo c a t e d u p s t r e a m a nd downstream of
the or ifice, and it is used to calculate the flow rate of without limitations, as it introduces pressure loss, requires
calibration for accuracy, and exhibits a limited turndown ratio.
the fluid passing through the pipe.
TYMEA047 MAYUR DHORE