Name / Mohamed fouad ahmed roshdy
Report Title: the Electrodynamometer:
Introduction:
An electrodynamometer is an electrical measuring instrument
used to measure current, voltage, and power in both alternating
current (AC) and direct current (DC) systems. It is widely used
in laboratories for precise measurement and calibration. The
electrodynamometer operates based on the mechanical force
between two current-carrying coils.
2. Principle of Operation
The electrodynamometer functions on the principle of
interaction between magnetic fields. When electric current
flows through the fixed and moving coils, it generates magnetic
fields. The interaction between these magnetic fields produces a
torque that is proportional to the product of the currents in both
coils. This torque causes the moving coil to rotate, and the
resulting deflection of a pointer indicates the measurement.
Mathematical Expression:
For a wattmeter configuration:
T∝Ifixed⋅Imoving⋅cos(ϕ)T \propto I_{\text{fixed}} \cdot
I_{\text{moving}} \cdot \cos(\phi)T∝Ifixed⋅Imoving⋅cos(ϕ)
Where:
TTT = Deflecting torque
� III = Current through the coils
ϕ\phiϕ = Phase angle between voltage and current (in AC)
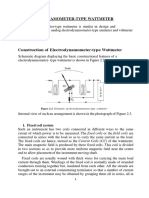
3. Construction
An electrodynamometer consists of the following main
components:
Fixed Coils: Two fixed coils are connected in series and
carry the load current. These generate a magnetic field.
Moving Coil: Mounted between the fixed coils and
connected to the voltage circuit. It is attached to a
spindle with a pointer.
Control Springs: Provide restoring torque and carry
current to and from the moving coil.
Damping System: Often air damping is used to prevent
oscillations.
Pointer and Scale: The pointer moves over a calibrated
scale to indicate the measured value
4. Working
The current in the fixed coils generates a magnetic field.
When the moving coil carries current, it interacts with the
magnetic field of the fixed coils. The resultant torque causes
the coil (and the pointer) to deflect. The amount of deflection
is proportional to the electrical quantity being measured
(voltage, current, or power), depending on the configuration
of the instrument.
In a voltmeter, the moving coil is connected in parallel
with the load.
In an ammeter, the fixed coil is connected in series with
the circuit.
� In a wattmeter, one coil acts as a current coil (series),
and the other as a potential coil (parallel).
5. Types of Electrodynamometers
1. Electrodynamometer Ammeter – Measures current.
2. Electrodynamometer Voltmeter – Measures voltage.
3. Electrodynamometer Wattmeter – Measures electric
power (most common application).
6. Applications
Accurate power measurement in AC and DC systems.
Used in calibration laboratories for standard
measurements.
Measurement of voltage and current where high
precision is required.
Used in research and educational laboratories.
7. Advantages
Can be used with both AC and DC.
High accuracy in power measurements.
Stable and reliable under controlled conditions.
Suitable for use as standard measuring instruments.
8. Disadvantages
Costly and not suitable for portable applications.
Delicate construction; sensitive to mechanical shock.
Affected by temperature changes and external magnetic
fields.
Non-uniform scale, especially at the lower end of the
range.
�9. Conclusion
The electrodynamometer is a fundamental instrument in
electrical measurement technology, especially valued for its
accuracy in measuring power in AC and DC systems. Despite
its limitations in portability and cost, it remains a critical
tool in labs and calibration settings due to its precision and
dual-current applicability.
10. References
A. K. Sawhney, A Course in Electrical and Electronic
Measurements and Instrumentation, Dhanpat Rai & Co.,
Latest Edition
E. W. Golding and F. C. Widdis, Electrical Measurements
and Measuring Instruments, Reem Publications.
R. K. Rajput, Electrical and Electronic Measurement and
Instrumentation, S. Chand Publishing.
H. S. Kalsi, Electronic Instrumentation, Tata McGraw-Hill
Education.
B. L. Theraja and A. K. Theraja, A Textbook of Electrical
Technology – Volume I, S. Chand & Co.