100% found this document useful (1 vote)
308 views2 pagesRational and Irrational Numbers
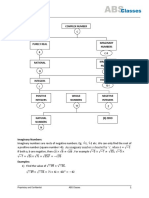
Rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction a/b where a and b are integers and b is not zero, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed in such a way and include non-terminating, non-repeating decimals. The set of real numbers includes both rational and irrational numbers, and surds are a specific type of irrational number related to roots. Key properties include that the sum or product of a rational and an irrational number is always irrational, and the negative of an irrational number remains irrational.
Uploaded by
Nikitha GCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
308 views2 pagesRational and Irrational Numbers
Rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction a/b where a and b are integers and b is not zero, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed in such a way and include non-terminating, non-repeating decimals. The set of real numbers includes both rational and irrational numbers, and surds are a specific type of irrational number related to roots. Key properties include that the sum or product of a rational and an irrational number is always irrational, and the negative of an irrational number remains irrational.
Uploaded by
Nikitha GCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd