0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views2 pagesDOM Assignment
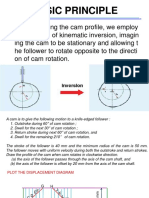
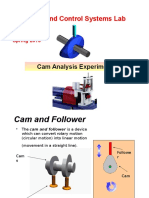
The document outlines a set of questions related to the dynamics of machines, specifically focusing on the analysis of various cam profiles and their interactions with roller and flat-faced followers. It includes derivations for displacement, velocity, and acceleration, as well as calculations for principal dimensions, accelerations, and forces involved in different cam mechanisms. The questions cover both theoretical derivations and practical applications in mechanical engineering contexts.
Uploaded by
Syed TauqueerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
62 views2 pagesDOM Assignment
The document outlines a set of questions related to the dynamics of machines, specifically focusing on the analysis of various cam profiles and their interactions with roller and flat-faced followers. It includes derivations for displacement, velocity, and acceleration, as well as calculations for principal dimensions, accelerations, and forces involved in different cam mechanisms. The questions cover both theoretical derivations and practical applications in mechanical engineering contexts.
Uploaded by
Syed TauqueerCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd