HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
CHAPTER 2
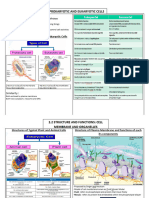
Structure of Cell
The cell defined as the unit of structure and function in animals and
plants.
A human body consists of about 100 trillions of cells.
Cells are two types:
A. Prokaryotic Cell: These cells do not have a well-developed
nucleus though they have some other organelles present as in the
prokaryotic cell. e.g. Archebacteria
B. Eukaryotic Cell: These cells have a well-developed nucleus and
other organelles present as in the eukaryotic cell. e.g. Human, Plants.
COMPONENTS OF THE CELL
The major components of the cell are-
(1) Cell membrane, (2) Cytoplasm, and (3) Nucleus.
1. Cell Membrane:
�Cell Membrane is thin elastic and has highly complex structure
composed of proteins and lipids. It is a semi – permeable membrane,
containing ‘pores’ that allow the passage of water, oxygen, co2 &
some solutes in and out of the cell and plays a vital role in
maintaining the balance of the cell.
2. Cytoplasm:
It is the region lying between the cell membrane and nucleus. The
cytoplasm contain Cell organ like – Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi
bodies, Mitochondria, Lysosomes.
A. Mitochondria:
It is largest cytoplasmic organelles and energy house of the cell. It is
also known as Power house of the cell.
Structure:
Length- 5-12µm. Diameter- 0.5-1µm
Filamentous or globular or Rod in shape. It consists of oxidative
enzymes which convert chemical energy of the nutrients into form of
A.T.P. and this energy is available for cellular activity. Mitochondria
supply 95% of cell energy and so called power house of the cell.
Components of Mitochondria:
1. Outer Membrane, 2. Inner Membrane, 3. Intermediate Space, 4.
Cristae, 5. Matrix.
The membranes are made up of phospholipids and proteins.
�Function:
Power generating units of the cells.
Important to maintain proper concentration of calcium ions within the
various compartments of the cell.
Energy transduction through respiration
B. Endoplasmic reticulum:
Network of tubular and flat vesicular structures in the cytoplasm.
Endoplasmic Reticulum is two type:
1. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: - Smooth Endoplasmic
Reticulum without the presence of ribosomes. They found Lipid
2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: - Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
with the presence of ribosomes. They found Protein
Function:
Synthesis of proteins.
Protein segregation.
Unsaturation of fatty acid.
Muscle contraction.
C. Lysosomes:
�These are the irregular structures surrounded by the unit membrane.
More acidic than rest of the cytoplasm and external bacteria as well as
worn out cell components are digested in them.
Function:
Acts as a form of digestive system of the cell, because enzymes
present in it can digest essentially all macromolecules.
Engulf exogenous substances e.g. bacteria.
When a cell dies, lysosomal enzymes causes autolysis of the cell
that’s why lysosomes are called as Suicidal Bags.
D. Golgi Bodies:
Golgi Bodies is a collection of membrane enclosed sacs composed of
four or more stacked layers of thin, flat enclosed vessels lying near
the side of the nucleus.
3. Nucleus:
A nucleus is defined as a double- membrane eukaryotic cell organelle
that contains the genetic material.
Structure of Nucleus:
Typically, it is the most evident organelle in the cell.
The nucleus is completely bound by membranes.
A nuclear membrane is a selectively permeable membrane.
�The nucleus contains a dense network of fine fibrous called
chromatin.
Chromatin is made up of DNA and nuclear proteins.
Functions:
1. The nucleus is the most important organelle of the cell which
controls all the metabolic functions of the cell hence it is called the
brain of the cell.
2. It plays a central role in cellular reproduction.
3. It also controls the chemical activities of the cell for the
development and growth of the cell.
4. It controls the heredity characteristics of an organism.
Plastids:
Plastids are double membrane-bound structures present in plants and
other eukaryotes involved in the synthesis and storage of food.
Types:
1. Chromoplast:
These can be usually found in flowering plants, ageing leaves and
fruits. Chloroplasts convert into chromoplasts. Chromoplasts have
carotenoid pigments that allow different colours that you see in leaves
and fruits.
�2. Chloroplast:
They are green coloured plastids, which comprise green-coloured
pigments within the plant cell and are called chlorophyll.
3. Leucoplasts:
They are colourless plastids and are mainly used for the storage of
starch, lipids and proteins within the plant cell.