0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views9 pagesCyber Physical Systems
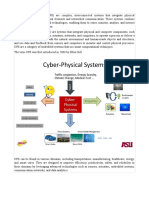
Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) integrate physical processes with computing and communication technologies, playing a crucial role in various sectors, including the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT). The architecture of CPS has evolved from a three-layer to a five-layer structure, enhancing capabilities in data processing and service delivery. CPS applications span multiple fields such as intelligent transportation, agriculture, and mobile education, with significant potential for improving efficiency and innovation in smart cities and manufacturing.
Uploaded by
kreilamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views9 pagesCyber Physical Systems
Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) integrate physical processes with computing and communication technologies, playing a crucial role in various sectors, including the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT). The architecture of CPS has evolved from a three-layer to a five-layer structure, enhancing capabilities in data processing and service delivery. CPS applications span multiple fields such as intelligent transportation, agriculture, and mobile education, with significant potential for improving efficiency and innovation in smart cities and manufacturing.
Uploaded by
kreilamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9