Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2011 3 Second Exam CE482
Uploaded by
Essam AbourasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2011 3 Second Exam CE482
Uploaded by
Essam AbourasCopyright:
Available Formats
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Total 25 25 25 25 100 CE 482 Second Exam. Second Semester 2010-11 Q.
1 A CE 482 student, working on the vertical and horizontal alignment design problem using a map with scale 1 meter : 300 meters. The student is checking the vertical gradient (grade) between two points A and B. The student notes that the elevations of point A is 312 meters and the elevation of point B is 328 meters. He also found that the distances between the two points on the map is 70 cm (centimeters). Determine the following: a) The slope from A to B in units of meter/meter is __________________.
b)
The change in the vertical elevation from A to B is ____________ meter per station of horizontal distance.
c)
If the student desires to plot circular curve with a 220 meter radius on the map with the scale mentioned above, the radius of the curve required, to the nearest centimeter is ____________________.
1/4
2/4
Q.2 Briefly answer the following questions: aWhich is longer decision sight distance or stopping sight distance?
b-
What does a superelevation rate of 4% mean? What is the maximum rate you would select for used in Jeddah?
c-
Explain the concept of driver expectancy. What happens when it is violated?
d)
List three types of Intersesctions
e-
What would be the stopping sight distance on a downgrade of 10%?
3/4
4/4
Q.3 (A) Calculate the stooping sight distance over the crest curve of a 450 m vertical curve with a plus grade of 5.6 percent and minus grade of 3.2 percent using the assumption on the text..
(B) In part (A) if the height of the object sighted increases to 0.6 m and the height of the average driver decreases to 0.90 m calculates the available sight distance.
(C) Calculate the stopping distance if the design seeped of the highway is 90 kmp.
5/4
(D) Check that the available stopping sight distance provided by this curve for the condition in part B is adequate.
6/4
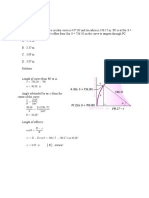
STA 47+000.00 ELV. 400 m G1 PVC
PVI P PVT G2
STA 47+400.00 ELV. 408 m Road A
Q-4 In an alignment design problem of a new highway, a student is laying out the vertical tangents over road A. The back tangent g1 is 4.00 percent and the forward tangent g2 is -2.00 percent. The satiation of the PVC is 47+000.00, and the vertical elevation of the PVC is 400.00 m. Road A crosses under the vertical curve of the new highway at station 47+400.00. The elevation of point P on the new highway on this vertical curve cannot be any lower then 408.00 m in order to provide sufficient clearance for special vehicles under the new highway for road A. See sketch above. a) Find the maximum length of the vertical curve that will pass through point P and satisfy the above condition. what will happen to the elevation of point P if we increase the length of the curves which found in part (a )
b)
7/4
Q.3
(25 points)
A). Calculate the stooping sight distance over the crest curve of a 450 m vertical curve with a plus grade of 5.6 percent and minus grade of 3.2 percent using the assumption on the text. Note that the formula given was for English measurement so convert before using the formula. SULUTION Assume S < L
L=
AS 2 100( 2h 1 + 2h2 ) 2 8.8 * S 2 100( 2 *1.07 + 2 * 0.15 ) 2
450 =
=143.77 144 m
Since S< L The assumption holds.
B). In part A if the height of the object sighted increases to 0.6 m and the height of the average driver decreases to 0.9 0 m calculates the available sight distance.
450 =
8.8 * S 2 100( 2 * 0.9 + 2 * 0.6 ) 2
S = 174.28 = 174 m
Since S< L The assumption holds. C) Calculate the stopping distance if the design seeped of the highway is 90 kmp. Assume friction factor =0.3 Stopping Distance = Traveling Distance + Breaking Distance = tv +V2/ (254f) Stopping Distance = 90 kmph (1000/3600) *2.5 + (90)2 / (254*0.3) Stopping Distance = 62.5 + 106.3 = 168 m B) Check that the available stopping sight distance provided by this curve for the condition in part B is adequate. Since Sight Distance on the curve > Stopping distance then it is OK
8/4
You might also like
- Transpo Sample ProblemsDocument18 pagesTranspo Sample ProblemsHeiro Keystrife100% (1)
- High WayDocument4 pagesHigh WayAnilkmar P MNo ratings yet
- CN106 Engineering Surveying: Semester 2 Examinations 2005-2006Document8 pagesCN106 Engineering Surveying: Semester 2 Examinations 2005-2006H S Vishwanath ShastryNo ratings yet
- 9 Setting OutDocument4 pages9 Setting OutElisha ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Vertical Curve WorksheetDocument5 pagesVertical Curve WorksheetmollalignmNo ratings yet
- Parabolic CurveDocument16 pagesParabolic CurveharabassNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 S2017Document2 pagesProblem Set 2 S2017Wael ElDessoukiNo ratings yet
- Parabolic CurveDocument16 pagesParabolic CurveAnonymous KUNMyMBEENo ratings yet
- Problem Set (GD)Document4 pagesProblem Set (GD)yadoleNo ratings yet
- 2004 Ex 1Document12 pages2004 Ex 1hoormohameed2019No ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Horizontal AlignmentDocument2 pagesSheet 2 Horizontal AlignmentAhmwd MohammedNo ratings yet
- University of NairobiDocument3 pagesUniversity of NairobijavoNo ratings yet
- Project For Module 2 - Problem Set With SolutionDocument22 pagesProject For Module 2 - Problem Set With SolutionNara JoNo ratings yet
- Given Road Alignment.: (20 Marks)Document1 pageGiven Road Alignment.: (20 Marks)robert theNo ratings yet
- HW Engineering I Solution To The Workout ProblemsDocument19 pagesHW Engineering I Solution To The Workout ProblemsNahom EshNo ratings yet
- Assign ProbDocument11 pagesAssign ProbHazel CordanoNo ratings yet
- Highway I AssignmentDocument4 pagesHighway I Assignmentjos0% (1)
- Assignment 3 2023Document9 pagesAssignment 3 2023justinkarlpolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 2023Document2 pagesAssignment 3 2023justinkarlpolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Simplecurves Jamie&bowDocument3 pagesSimplecurves Jamie&bowJamie Amanda FaderonNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument10 pagesProblemsJune CostalesNo ratings yet
- Simple Curve SamplesDocument21 pagesSimple Curve SamplesNicko Mendoza50% (2)
- C1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1Document2 pagesC1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1bhkedarNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Instructionsvarunsingh214761No ratings yet
- Ce 404-Sec11Document20 pagesCe 404-Sec11Yasser AlghrafyNo ratings yet
- Assignment Highway Engg For 2013Document5 pagesAssignment Highway Engg For 2013amareNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 SolutionsDocument3 pagesAssignment 5 SolutionsTino SciortinoNo ratings yet
- JH Academy Notes ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERINGDocument53 pagesJH Academy Notes ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERINGKarnalPreeth100% (2)
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument8 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- Station 0+00 0+50 1+00 1+50 2+00 2+50 3+00 3+50 4+00 4+50 5+00 Cumulative Volume Cu.m 10000 12500 14500 13500 10000 7000 6000 10000 12000 13000 14000Document2 pagesStation 0+00 0+50 1+00 1+50 2+00 2+50 3+00 3+50 4+00 4+50 5+00 Cumulative Volume Cu.m 10000 12500 14500 13500 10000 7000 6000 10000 12000 13000 14000helen haileselassieNo ratings yet
- Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument34 pagesSurveying and Transportation EngineeringRimar LiguanNo ratings yet
- Homework # 3: Ce416: Geometric Design of HighwaysDocument1 pageHomework # 3: Ce416: Geometric Design of HighwaysnasserNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8: Geometric Design and Turning Maneuvers: Problem 1Document2 pagesAssignment 8: Geometric Design and Turning Maneuvers: Problem 1mehdiNo ratings yet
- rr220106 Surveying IIDocument8 pagesrr220106 Surveying IISRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Worked Example On The Design of RampDocument4 pagesWorked Example On The Design of RampEbisa Adamu100% (1)
- BasicSurveying ExamforPracticeDocument6 pagesBasicSurveying ExamforPracticewinArunkumarNo ratings yet
- 11ap T1 Sec BDocument3 pages11ap T1 Sec Bmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Transportation Engg 1Document58 pagesTransportation Engg 1Praveen M balaramNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument8 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Advanced SurveyingDocument5 pagesSample Question Paper Advanced Surveyingchinmoy palNo ratings yet
- Test On Transportation EngineeringDocument10 pagesTest On Transportation Engineeringjhacademyhyd50% (2)
- Geometric Design of Highways - Part 1Document14 pagesGeometric Design of Highways - Part 1Ronnel BernabeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1112Document9 pagesEngineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1112Amirul AizatNo ratings yet
- C1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1Document2 pagesC1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1bhkedarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam: Solutions and Answers HereDocument2 pagesFinal Exam: Solutions and Answers HereMeyhNo ratings yet
- AE May 2015 98 Civ B7Document4 pagesAE May 2015 98 Civ B7tirockiNo ratings yet
- Cive1107 2003 1Document5 pagesCive1107 2003 1Bhunjun VandanaNo ratings yet
- HW Engineering I Work Out ProblemsDocument4 pagesHW Engineering I Work Out ProblemsHaile GuebreMariam100% (1)
- Model Answer: SolutionDocument5 pagesModel Answer: SolutionnasserNo ratings yet
- Oct 2010Document3 pagesOct 2010Azrul AzizNo ratings yet
- 87BDocument5 pages87BJamie Schultz100% (1)
- Advanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandAdvanced AutoCAD® 2017: Exercise WorkbookRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Image, Video and 3D Data Registration: Medical, Satellite and Video Processing Applications with Quality MetricsFrom EverandImage, Video and 3D Data Registration: Medical, Satellite and Video Processing Applications with Quality MetricsNo ratings yet
- Opposite Integers1Document2 pagesOpposite Integers1Hapsari C. Hanandya NannaNo ratings yet
- 312 Full-3Document8 pages312 Full-3Le TrungNo ratings yet
- The Awakening Study Guide AnswersDocument24 pagesThe Awakening Study Guide AnswersAli RidhaNo ratings yet
- Crushing and Screening Equipment Handbook (Low Res)Document46 pagesCrushing and Screening Equipment Handbook (Low Res)Jayesh NairNo ratings yet
- Please Get Rid of That SmellDocument4 pagesPlease Get Rid of That Smellmcant1980No ratings yet
- Phonological Translation in Translation Texts Download TableDocument1 pagePhonological Translation in Translation Texts Download Tablelinl04023No ratings yet
- GRFU Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument9 pagesGRFU Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDJamal HagiNo ratings yet
- 7th NisssDocument9 pages7th NisssVedang PandeyNo ratings yet
- Final CDP MuzaffarpurDocument224 pagesFinal CDP MuzaffarpurVivek Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Why Are You Applying For Financial AidDocument2 pagesWhy Are You Applying For Financial AidqwertyNo ratings yet
- Borland C++Document3 pagesBorland C++Sanjay SethNo ratings yet
- The Journal of The Acoustical Society of AmericaDocument12 pagesThe Journal of The Acoustical Society of Americadr01dNo ratings yet
- IASDocument3 pagesIASankit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Course Reader For Chapter IiiDocument33 pagesCourse Reader For Chapter Iiipau baniagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-02 Data Collection and Analysis STATDocument12 pagesLesson 1-02 Data Collection and Analysis STATallan.manaloto23No ratings yet
- заданиеDocument13 pagesзаданиеЦените МоментыNo ratings yet
- 15 TribonDocument10 pages15 Tribonlequanghung98No ratings yet
- Enhancement of Agricultural Stakeholders by Using Android ApplicationDocument5 pagesEnhancement of Agricultural Stakeholders by Using Android ApplicationVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- Oberon: Oberon G28, Excellent Operating Under Shock Loading and Unusually Severe Load Service ConditionsDocument2 pagesOberon: Oberon G28, Excellent Operating Under Shock Loading and Unusually Severe Load Service ConditionsRafael BalloriNo ratings yet
- Green Bill: Easypa Y Scan & PayDocument4 pagesGreen Bill: Easypa Y Scan & Paymohamed elmakhzniNo ratings yet
- An Isolated Bridge Boost Converter With Active Soft SwitchingDocument8 pagesAn Isolated Bridge Boost Converter With Active Soft SwitchingJie99No ratings yet
- HOSTILE - Colony Module Schematics (Updated)Document18 pagesHOSTILE - Colony Module Schematics (Updated)Oleksandr TrifanNo ratings yet
- Chart-5050 by Songram BMA 54thDocument4 pagesChart-5050 by Songram BMA 54thMd. Noor HasanNo ratings yet
- Punjab Medical Faculty Registration Form: Personal DetailsDocument2 pagesPunjab Medical Faculty Registration Form: Personal DetailsAamir Khan PtiNo ratings yet
- Department of Human Services: Course Information Course DescriptionDocument9 pagesDepartment of Human Services: Course Information Course DescriptionS ElburnNo ratings yet
- Understanding M-Values PDFDocument9 pagesUnderstanding M-Values PDFrolandoNo ratings yet
- PDF Kajaria Report Final - CompressDocument40 pagesPDF Kajaria Report Final - CompressMd Borhan Uddin 2035097660No ratings yet
- New NCERTDocument3 pagesNew NCERTajmalhusain1082007No ratings yet
- Urban Worksheet - StudentDocument29 pagesUrban Worksheet - StudentChris WongNo ratings yet
- 8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved QuestionsDocument3 pages8th Chemical Effects of Electric Current Solved QuestionsGururaj KulkarniNo ratings yet