0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views3 pagesScience Module Force and Motion
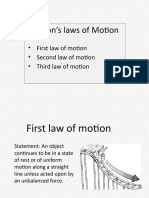
The Science Module on Force and Motion introduces students to fundamental concepts such as force, motion, and Newton's Laws of Motion. Learners will engage in discussions and experiments to understand how forces affect motion, with objectives including defining force, explaining Newton's laws, and solving related problems. Activities include hands-on experiments like the Balloon Rocket and assessments to reinforce understanding of the material.
Uploaded by
francescheelcCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
75 views3 pagesScience Module Force and Motion
The Science Module on Force and Motion introduces students to fundamental concepts such as force, motion, and Newton's Laws of Motion. Learners will engage in discussions and experiments to understand how forces affect motion, with objectives including defining force, explaining Newton's laws, and solving related problems. Activities include hands-on experiments like the Balloon Rocket and assessments to reinforce understanding of the material.
Uploaded by
francescheelcCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd