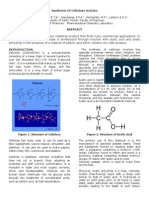
Material Science Ok
Uploaded by
Puwa CalvinMaterial Science Ok
Uploaded by
Puwa CalvinCourse
Code Course Title Credit Value Status L T P Total
Material Science
ECE
1101 2 C 25 5 0 30
Course Description:
This course explores the fundamentals of material science, focusing on the relationships
between material structure, processing, properties, and performance. Students will investigate
metals, ceramics, polymers, composites, and emerging materials, emphasizing their
applications in engineering and technology. Topics include atomic bonding, crystal
structures, mechanical/thermal/electrical properties, material characterization, and sustainable
design. Through labs and case studies, students gain hands-on experience in analyzing real-
world material challenges, such as aerospace components and biodegradable polymers.
Learning Outcomes:
By the end of the course, students will be able to:
1. Classify materials into categories (metals, ceramics, polymers, composites) and
describe their defining characteristics.
2. Explain how atomic structure, bonding, and defects influence material
properties.
3. Analyze phase diagrams and processing techniques (e.g., heat treatment,
casting) to predict material behavior.
4. Evaluate materials for engineering applications using structure-property-
performance relationships.
5. Demonstrate proficiency in characterization tools (microscopy, spectroscopy,
tensile testing).
6. Discuss ethical, environmental, and economic impacts of material selection and
sustainability.
Course Objectives:
1. Provide a foundational understanding of material science principles, including
atomic structure and bonding.
2. Enable students to apply material selection criteria to solve engineering
problems.
3. Develop practical skills through labs on metallography, heat treatment, and
mechanical testing.
4. Foster critical thinking for optimizing material performance and sustainability.
5. Highlight ethical considerations in resource use and environmental impact.
Course Content:
1) Fundamentals
- Introduction to material science, classification, and applications.
- Atomic structure, bonding (ionic, covalent, metallic), and crystallography (BCC,
FCC, HCP).
- Crystal defects (vacancies, dislocations) and microstructure-property
relationships.
2) Material Types & Processing
- Metals/Alloys: Phase diagrams, solidification, heat treatment (quenching,
annealing).
- Ceramics: Brittle fracture, thermal/electrical insulation applications.
- Polymers: Polymerization, thermoplastics vs. thermosets, viscoelasticity.
- Composites: Fiber-reinforced materials, rule of mixtures.
3) Material Properties
- Mechanical: Stress-strain curves, hardness, fatigue, fracture mechanics.
- Electrical/Thermal: Conductivity, semiconductors, superconductors, insulation.
- Optical/Magnetic: Refractive index, ferromagnetism, applications in devices.
3) Characterization & Selection
- Microscopy (SEM, TEM), spectroscopy (XRD, EDS), thermal analysis (DSC,
TGA).
- Material selection strategies (Ashby charts, cost-performance trade-offs).
4) Sustainability & Emerging Materials
- Life-cycle analysis, recycling, and green materials (biodegradable polymers).
- Nanomaterials, biomaterials, smart materials (shape-memory alloys).
5) Applications & Review
- Case study presentations (e.g., aerospace materials, electronic devices).
- Final project: Material selection for a real-world problem (e.g., medical
implants).
- 6) Labs: Metallography, tensile testing, heat treatment of steel, polymer
synthesis.