Name: ___________________________________________ Date: _________________________ Class: _______________
Past Paper Questions: Perpendicular Bisectors
6
1 The curve y = 9 − and the line y + x = 8 intersect at two points. Find
x
(i) the coordinates of the two points, [4]
(ii) the equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the two points. [4]
9709/01/M/J/04
�2
y
C
x
O
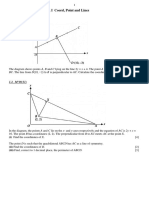
D (10, –3)
The diagram shows points A, B and C lying on the line 2y = x + 4. The point A lies on the y-axis
and AB = BC. The line from D (10, −3) to B is perpendicular to AC. Calculate the coordinates of B
and C. [7]
9709/01/M/J/09
�3
y
B (15, 22)
x
O
A (3, –2)
The diagram shows a triangle ABC in which A is (3, −2) and B is (15, 22). The gradients of AB, AC
and BC are 2m, −2m and m respectively, where m is a positive constant.
(i) Find the gradient of AB and deduce the value of m. [2]
(ii) Find the coordinates of C. [4]
The perpendicular bisector of AB meets BC at D.
(iii) Find the coordinates of D. [4]
9709/11/M/J/10
�4 y
C (5, 4)
A
(–1, 2)
x
O
The diagram shows a rhombus ABCD in which the point A is (−1, 2), the point C is (5, 4) and the
point B lies on the y-axis. Find
(i) the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AC, [3]
(ii) the coordinates of B and D, [3]
(iii) the area of the rhombus. [3]
9709/13/M/J/10
�5 The coordinates of A are (−3, 2) and the coordinates of C are (5, 6). The mid-point of AC is M and
the perpendicular bisector of AC cuts the x-axis at B.
(i) Find the equation of MB and the coordinates of B. [5]
(ii) Show that AB is perpendicular to BC. [2]
(iii) Given that ABCD is a square, find the coordinates of D and the length of AD. [2]
9709/11/M/J/12
�6 The point A has coordinates (−1, −5) and the point B has coordinates (7, 1). The perpendicular
bisector of AB meets the x-axis at C and the y-axis at D. Calculate the length of CD. [6]
9709/12/M/J/12
�7 The point R is the reflection of the point −1, 3� in the line 3y + 2x = 33. Find by calculation the
coordinates of R. [7]
9709/12/M/J/13
�8 Find the coordinates of the point at which the perpendicular bisector of the line joining 2, 7� to
10, 3� meets the x-axis. [5]
9709/12/M/J/14
�9 The point C lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the points A 4, 6� and B 10, 2�.
C also lies on the line parallel to AB through 3, 11�.
(i) Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB. [4]
(ii) Calculate the coordinates of C. [3]
9709/12/M/J/15
�10 Three points have coordinates A 0, 7�, B 8, 3� and C 3k, k�. Find the value of the constant k for
which
(i) C lies on the line that passes through A and B, [4]
(ii) C lies on the perpendicular bisector of AB. [4]
9709/12/M/J/16
�11 The point A has coordinates −2, 6�. The equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line AB is
2y = 3x + 5.
(i) Find the equation of AB. [3]
(ii) Find the coordinates of B. [3]
9709/12/M/J/17
�12 Points A and B have coordinates h, h� and 4h + 6, 5h� respectively. The equation of the perpendicular
bisector of AB is 3x + 2y = k. Find the values of the constants h and k. [7]
9709/12/M/J/18
�13 The coordinates of points A and B are −3k − 1, k + 3� and k + 3, 3k + 5� respectively, where k is a
constant (k ≠ −1).
(i) Find and simplify the gradient of AB, showing that it is independent of k. [2]
(ii) Find and simplify the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB. [5]
9709/13/M/J/18
�14 Three points have coordinates A (2, 6), B (8, 10) and C (6, 0). The perpendicular bisector of AB
meets the line BC at D. Find
(i) the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB in the form ax + by = c, [4]
(ii) the coordinates of D. [4]
9709/01/O/N/05
�15 The point A has coordinates −1, 6� and the point B has coordinates 7, 2�.
(i) Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB, giving your answer in the form y = mx + c.
[4]
(ii) A point C on the perpendicular bisector has coordinates p, q�. The distance OC is 2 units, where
O is the origin. Write down two equations involving p and q and hence find the coordinates of
the possible positions of C. [5]
9709/11/O/N/13
�16 Points A, B and C have coordinates A −3, 7�, B 5, 1� and C −1, k�, where k is a constant.
(i) Given that AB = BC, calculate the possible values of k. [3]
The perpendicular bisector of AB intersects the x-axis at D.
(ii) Calculate the coordinates of D. [5]
9709/12/O/N/15
�17 The points A 1, 1� and B 5, 9� lie on the curve 6y = 5x2 − 18x + 19.
(i) Show that the equation of the perpendicular bisector of AB is 2y = 13 − x. [4]
The perpendicular bisector of AB meets the curve at C and D.
O@ A
p
(ii) Find, by calculation, the distance CD, giving your answer in the form , where p and q are
q
integers. [5]
9709/11/O/N/17
� 12
18 The equation of a curve is y = 2x + and the equation of a line is y + x = k, where k is a constant.
x
(i) Find the set of values of k for which the line does not meet the curve. [3]
In the case where k = 15, the curve intersects the line at points A and B.
(ii) Find the coordinates of A and B. [3]
(iii) Find the equation of the perpendicular bisector of the line joining A and B. [3]
9709/12/O/N/18