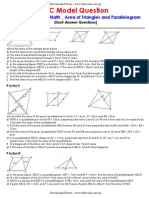
Type 5: length and area ratio of (similar) triangles
[DSE 2012 II (17)]
17. In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. E and F are points lying on AB and CD respectively. AD
produced and EF produced meet at G. It is given that DF:FC = 3:4 and AD:DG = 1:1. If the
area of DFG is 3 cm2, then the area of the parallelogram ABCD is
A. 12 cm2.
B. 14 cm2.
C. 18 cm2.
D. 21 cm2.
[DSE 2013 II (18)]
18. In the figure, ABCD is a trapezium with AD//BC and AD:BC = 2:3. Let E be the mid-point of BC,
AC and DE intersect at F. If the area of CEF is 36 cm2,then the area of the trapezium ABCD is
A. 216 cm2 .
B. 264 cm2 .
C. 280 cm2 .
D. 320 cm2 .
[DSE 2014 II (17)]
17. In the figure, B is a point lying on AC such that AB:BC = 3:2. It is given that AE // BD. If the area of
BCD and the area of CDE are 4 cm2 and 8 cm2 respectively, then the area of the trapezium ABDE is
A. 18 cm2
B. 21 cm2
C. 27 cm2
D. 33 cm2
�[DSE 2015 II (17)]
17. In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. E is a point lying on CD such that DE : EC = 2 : 3 . AD
produced and BE produced meet at F while AE produced and BC produced meet at G . If the area of
ΔDEF is 8 cm2 , then the area of ΔCEG is
A. 12 cm2 .
B. 18 cm2 .
C. 20 cm2 .
D. 27 cm2 .
[DSE 2016 II (20)]
20. In the figure, ABCD , CDEF and EFGH are squares. AG cuts CD and EF at P and Q respectively.
Find the ratio of the area of quadrilateral DEQP to the area of quadrilateral ABCP.
A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 3
C. 3 : 5
D. 4 : 9
[DSE 2017 II (16)]
16. In the figure, ABCD and BEDF are parallelograms. E is a point lying on BC such that
BE : EC 2 : 3 . AC cuts BF and DE at G and H respectively. If the area of ABG is 135 cm 2 ,
then the area of the quadrilateral DFGH is
A. 60 cm2 .
B. 81 cm 2 .
C. 90 cm2 .
D. 144 cm2 .
�[DSE 2018 II (16)]
16. In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. E is a point lying on BC such that BE : EC 5:3 . AE and
BD intersect at the point F . If the area of ABF is 120 cm2 , then the area of the quadrilateral CDFE
is
A. 237 cm2 .
B. 307 cm2 .
C. 312 cm2 .
D. 429 cm2 .
[DSE 2019 II (16)]
16. In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram and AEFG is a square. It is given that BE : EF : FC 2: 7 :3 .
BD cuts AE and FG at the points X and Y respectively. If the area of ABX is 24 cm2 , then the
area of the quadrilateral CDYF is
A. 54 cm2 .
B. 77 cm2 .
C. 81 cm2 .
D. 87 cm2 .
[DSE 2020 II (17)]
17. In the figure, P and Q are points lying on OR while U and T are points lying on OS such that
OP PQ QR and PU //QT //RS . The ratio of the
area of the trapezium PQTU to the area of the
trapezium QRST is
A. 1:2 .
B. 2:3 .
C. 3:5 .
D. 4:9 .
�[DSE 2020 II (18)]
18. In the figure, ABCD is a parallelogram. Let E be a point lying on AD such that AE : ED 2: 5 . CB is
produced to the point F such that BF DE . Denote the point of intersection of AB and EF by G . It
is given that BD and CG intersect at
the point H . If the area of AEG is
48 cm2 , then the area of CDH is
A. 98 cm2 .
B. 343 cm2 .
C. 420 cm2 .
D. 588 cm2 .
[DSE 2022 II (17)]
17. In the figure, M and N are points lying on PQ and PR respectively such that PM : MQ 5 : 6 and
QN : NR 3 : 4 . If the area of the quadrilateral MNRP
is 59 cm2, then the area of ∆MNQ is
A. 17 cm2.
B. 18 cm2.
C. 19 cm2.
D. 20 cm2.
[DSE 2023 II (17)]
17. In the figure, PQRS is a parallelogram. Let X be a point lying on PQ . Denote the point of intersection
of PR and SX by Y . If the area of PXY and the area of the quadrilateral QRYX are 32 cm2 and 58 cm2
respectively, then the area of RSY is
A. 40 cm2 .
B. 50 cm2 .
C. 58 cm2 .
D. 72 cm2 .