Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class Notes-Types of Distribution Systems-ELEC 423-Spring 2012
Class Notes-Types of Distribution Systems-ELEC 423-Spring 2012
Uploaded by
Musa'bOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class Notes-Types of Distribution Systems-ELEC 423-Spring 2012
Class Notes-Types of Distribution Systems-ELEC 423-Spring 2012
Uploaded by
Musa'bCopyright:
Available Formats
ELEC 423 Powe Distribu 4 er ution Sys stem
Types of Distribution System s n ms
The fun nction of an electrical dis stribution syst tem is to del iver electrica energy from the transm al m mission substation or small ge ns enerating stat tion to each customer at su c uitable voltag The desig of a distrib ge. gn bution system is based on the loads that it supplies safely and with p permissible vo oltage regulat tion. The cho of oice a distribution system reflects a num r mber of factors such as ec conomic cons sideration, rel liability, flexi ibility and maint tenance. Since th project is connected wit the design of the power distribution system for industrial plan we he c th r n nt, have selec cted the most commonly used circuits for distributi t u ion. Many typ of arrang pes gement can us sually be classif fied as one of the followin basic type radial, pri f ng es: imary selectiv secondary selective, lo ve, y ooped primary and secondary network. A brief discus a y ssion of these basic circui arrangemen is given i the e it nts in following g.
2.5.1 Sim mple radial system s As show in fig. 2.2, there is only one primary feeder and one distributi transform [1]. The sy wn y y ion mer ystem has the lo owest investm ment and can be expanded easily. This system is co d ommonly used because it offers high reliability and saf flexible, st fe, table, and eas to operate and to maint sy tain. However the disadva r, antage of this sys stem is that th loss of cab primary supply or tran he ble, s nsformer will cut off the se ervice. In add dition, equipmen must shut down to reform routine mai nt d m intenance and serving. d
Fig.2.2: Si imple radial s system
2.5.2 Exp panded radial system Figure 2.3 shows an expanded rad system [1 This syste can be app 2 dial 1]. em plied to large loads by mea of ans of a radial primary distrib bution system to supply a number of u substation located nea the center o the m unit n ar pplying the lo through a radial secon oad ndary system A fault in o m. one-feeder results in loss o the of loads, sup load conn nected to that feeder only. The disadvan ntages of the system are th lack of co the ontinuity of se ervice and it is le flexible. ess
Fig.2.3: Exp panded radial system l
2.5.4 Primary loop system s p T me ntages Figure 2.5 shows a primary loop system [1]. This system o ffers the sam advantages and disadvan ry ystem. The failure of norm source o a primary cable fault can be isolated and f mal of as primar selective sy service re estored by se ectionalizing. However, finding a cab fault in the loop ma . f ble aybe difficult The t. quickest way to find a fault is to sec w ctionalize the loop and rec cluse, and may involve sev y veral re closin on ngs the fault. However, the system may be potential dangerous because the section may energized from e y lly s e ybe d both ends.
Fig.2.5: Primary Loop system
2.5.3 Primary selective syst tem h tion is connec cted to two s mary feeders through swit tching separate prim In this system each unit substat nt rce pon f source equipmen to provide a normal and alternate sour as shown in Fig. 2.4 up failure of the normal s the distrib bution transf former is sw witched to the alternate so e ource. Switc ching can be either manu or ual automatic but there wi be an interr c, ill ruption until load is transf ferred to the a alternate sourc ce.
mary selective system e Fig.2.4: Prim
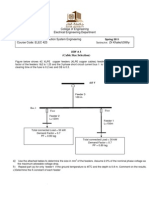
2.5.5 Sec condary selective syst tem s station are co onnected thro ough a norma ally open sec condary tie c circuit breake the er, If pairs of unit subs result is secondary sele ective system If the prima feeder or transformer fails the main secondary c m. ary n circuit breaker on the affecte transforme is opened and the tie circuit break closed an one transf o ed er ker nd former supplies the total load. Since the fa occur ele t . ault ectrical engine who will design this ty of distrib eer ype bution network should take care that both transformers can carry th total loads when fault is established We s c h s he s d. will study this case of distribution network sin Qatar Ga Company uses this typ in its indu y n nce as pe ustrial plants. Tw varieties of the seconda selective system [1] are shown in Fi 2.6. wo o ary s e ig.
Fi 2.6: Secon ig. ndary Selectiv Systems ve
Referenc ce [1] Reco ommended Practice for Electric Pow Distribut P E wer tion for Indu ustrial Plants IEEE Std 14 s, d 1-1969. [2] Desi of an Ele ign ectrical Distr ribution Syst tems for an I Industrial Pl lant, Final y project, EE year , Department, Qatar University, 20 U 007.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Harmonics in Power Distribution Networks!Document42 pagesHarmonics in Power Distribution Networks!Musa'b67% (6)
- Example-Design of Passive Harmonics FilterDocument2 pagesExample-Design of Passive Harmonics FilterMusa'b100% (2)
- High Dive SummaryDocument14 pagesHigh Dive Summarysoadquake98188% (8)
- Chapter #1 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument9 pagesChapter #1 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b100% (10)
- Chapter # 3 - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument11 pagesChapter # 3 - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b84% (19)
- Test Procedure - CT & PTDocument6 pagesTest Procedure - CT & PTmayur dhande100% (2)
- Chapter # 18 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument26 pagesChapter # 18 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'bNo ratings yet
- Sample Examination Fof Off-Grid Solar PV Technicians - Validated PDFDocument21 pagesSample Examination Fof Off-Grid Solar PV Technicians - Validated PDFAdewale BamgbadeNo ratings yet
- NPC Power System Protection PhilosophyDocument60 pagesNPC Power System Protection PhilosophySellappan Muthusamy100% (3)
- Chapter # 14 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument13 pagesChapter # 14 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b100% (3)
- Chap4-Insulation Coordination LatestDocument41 pagesChap4-Insulation Coordination LatestAhmed TayehNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 10 - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument19 pagesChapter # 10 - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b100% (1)
- Chapter #6, Engineering Economy, 7 TH Edition Leland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument12 pagesChapter #6, Engineering Economy, 7 TH Edition Leland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b100% (6)
- 20060317K Factor PDFDocument34 pages20060317K Factor PDFebrahimNo ratings yet
- Ohmic HeaterDocument28 pagesOhmic HeaterDeepankumar AthiyannanNo ratings yet
- UPDA Electrical Engineering Exam Questions 2015 Part 2 - December 2015- اختبار الهندسة الكهربائيةDocument8 pagesUPDA Electrical Engineering Exam Questions 2015 Part 2 - December 2015- اختبار الهندسة الكهربائيةMusa'b93% (15)
- Chapter # 15 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument13 pagesChapter # 15 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'b100% (1)
- Two Methods To Calculate PassDocument4 pagesTwo Methods To Calculate PassSurendar BandiNo ratings yet
- UPDA Electrical Engineering Exam Questions 2015 Part1 - December 2015- اختبار الهندسة الكهربائيةDocument2 pagesUPDA Electrical Engineering Exam Questions 2015 Part1 - December 2015- اختبار الهندسة الكهربائيةMusa'b86% (58)
- Project Management 1Document3 pagesProject Management 1Musa'b100% (1)
- Chapter #19 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument15 pagesChapter #19 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'bNo ratings yet
- Factors: How Time and Interest Affect Money: Solutions To End-Of-Chapter ProblemsDocument12 pagesFactors: How Time and Interest Affect Money: Solutions To End-Of-Chapter ProblemsMusa'b84% (19)
- Chapter # 12 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinDocument19 pagesChapter # 12 Solutions - Engineering Economy, 7 TH Editionleland Blank and Anthony TarquinMusa'bNo ratings yet
- Motor Characteristic CableDocument1 pageMotor Characteristic CableMusa'bNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ELEC 423 Power Distribution Spring 2012 MaleDocument4 pagesSyllabus ELEC 423 Power Distribution Spring 2012 MaleMusa'bNo ratings yet
- Term Project - 3Document2 pagesTerm Project - 3Musa'bNo ratings yet
- Term Project - 1Document3 pagesTerm Project - 1Musa'bNo ratings yet
- HW - 1-Elec 423-Spring 2012Document1 pageHW - 1-Elec 423-Spring 2012Musa'bNo ratings yet
- Elec 4 423 Powe Er Distribu Ution Sys Stem: Load CH Haracteri IsticsDocument4 pagesElec 4 423 Powe Er Distribu Ution Sys Stem: Load CH Haracteri Isticschampion2007No ratings yet
- HW - 5-Elec 423-Spring 2012Document2 pagesHW - 5-Elec 423-Spring 2012Musa'bNo ratings yet
- HW - 4-Elec 423-Spring 2012Document1 pageHW - 4-Elec 423-Spring 2012Musa'bNo ratings yet
- HW - 3-Elec 423-Spring 2012Document1 pageHW - 3-Elec 423-Spring 2012Musa'bNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3 Solve The Following Problems:: Problems 2.16, 2.17, and 2.1an D 2.23 in The Text BookDocument1 pageAssignment #3 Solve The Following Problems:: Problems 2.16, 2.17, and 2.1an D 2.23 in The Text BookMusa'bNo ratings yet
- Types of Distribution CablesDocument23 pagesTypes of Distribution CablesMusa'bNo ratings yet
- FILE0032Document85 pagesFILE0032MEOW41No ratings yet
- Second LawDocument19 pagesSecond Law215492No ratings yet
- EMI 04-09 Collected For Revision Practice MSDocument7 pagesEMI 04-09 Collected For Revision Practice MSmandoolalaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 ECE5018 TH VL2021220105372 Reference Material I 12-01-2022 MOSFET-Device-And-Circuit SimulationsDocument34 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 ECE5018 TH VL2021220105372 Reference Material I 12-01-2022 MOSFET-Device-And-Circuit SimulationsVibha M VNo ratings yet
- Problem 8.5-4. (2031510008-2031510045)Document9 pagesProblem 8.5-4. (2031510008-2031510045)Hendra StyawanNo ratings yet
- Single Phase TransformerDocument13 pagesSingle Phase TransformerIsuru Pasan DasanayakeNo ratings yet
- Hydro-Flo Technologies, Inc.: Call 630-762-0380 To Talk To A Hydro-Flo Application EngineerDocument12 pagesHydro-Flo Technologies, Inc.: Call 630-762-0380 To Talk To A Hydro-Flo Application EngineerrutujaNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document5 pagesLab 2Garrey BrionesNo ratings yet
- 40S 60S 80S 120 210S: Case DimensionsDocument2 pages40S 60S 80S 120 210S: Case DimensionsPasindu PriyankaraNo ratings yet
- Richard Fox Bachelor of Science in Education Middle School Teacher - The Baltimore County Public SchoolsDocument26 pagesRichard Fox Bachelor of Science in Education Middle School Teacher - The Baltimore County Public SchoolsBlog AsiaNo ratings yet
- Chen 801-T2Document27 pagesChen 801-T2hussainiNo ratings yet
- Practice Final 01Document7 pagesPractice Final 01hisuikameNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Power QualityDocument5 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Power QualityjausahaslkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 EnergyconDocument2 pagesChapter 10 EnergyconLuelsonCordovaDeclaradorNo ratings yet
- Natural Ventilation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesNatural Ventilation - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediadasaNo ratings yet
- Thermo Chapter1Document11 pagesThermo Chapter1Mon Jhio San JuanNo ratings yet
- Interruptor de Tanque Muerto 145 KV ABB PDFDocument10 pagesInterruptor de Tanque Muerto 145 KV ABB PDFOscar Omar QuintanillaNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument115 pagesStructure of AtomHarshtej Singh MakkarNo ratings yet
- Tle - ElectricalDocument220 pagesTle - ElectricalShiba ManisanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable EnergyDocument5 pagesSustainable EnergyMarkoNo ratings yet
- HCN Sla 00 Bac Ec 00 250-A GCB Factory Test ProcedureDocument13 pagesHCN Sla 00 Bac Ec 00 250-A GCB Factory Test ProcedureBuồnNgủNo ratings yet
- L-2 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 2Document6 pagesL-2 (DK) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel) 2GagneNo ratings yet
- ECEG2121-Worksheet I IDocument4 pagesECEG2121-Worksheet I IKenenisa J7No ratings yet