Professional Documents
Culture Documents
VA Theory
Uploaded by
Elka Sushea IICopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
VA Theory
Uploaded by
Elka Sushea IICopyright:
Available Formats
Voltammetry
Voltammetry
An Introduction in Theory
Metrohm Ltd. CH-9100 Herisau Switzerland
Overview
Voltammetry
What is Voltammetry? Electrode Types Voltammetric Techniques Measurement Modes Calibration Techniques Advantages of Voltammetry Summary
Voltammetry
Voltammetry
Voltammetry = Volt-Am(pero)-Metry Voltage ramp applied to electrode Current measured
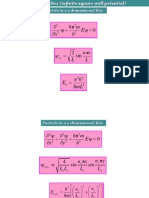
I = f(U)
Method first described 1922 by Heyrovsky
Instrumentation in voltammetry
Voltammetry
Me+
746
e-
Me0
Voltage Source (Potentiostat)
polarographic cell
Principle of voltammetry
Voltammetry
Pb ions are reduced and dissolved in mercury
+
Pb2+ Pb2+ Pb2+ Pb2+ Pb2+ Pb2+ Pb2+
Pb2+
Pb2+ Pb2+ Pb2+ +2ePb0 Pb2+ Pb2+ Pb2+
Pb2+
Pb2+
Pb2+
Principle of voltammetry
Voltammetry
resulting curve
I
quantitative information
U qualitative information
Principle of voltammetry
Voltammetry
U Pb I Cd
potential increased current measured metal ions are reduced and dissolved in mercury.
time
Reduction to metal (amalgam formation)
Electrodes
Voltammetry
1 1 1
Working Electrode Reference Electrode Auxiliary Electrode
Reference electrode
Voltammetry
provides stable reference potential
Ag/AgCl/KCl 3 mol/L
Double junction system with exchangeable electrolyte
Auxiliary electrode
Voltammetry
Current flows between working and auxiliary electrode Two types available:
Platinum (Pt) Glassy Carbon (GC)
Depending on application !
Working Electrodes
Voltammetry
MME
Multi Mode Electrode
RDE
Rotating Disc Electrode
GC, Au, Ag Pt, UT SMDE DME HMDE
MME
Voltammetry
Multi Mode Electrode
mercury needle tapper
capillary
Hg drop
Multi Mode Electrode
Voltammetry
DME
Needle
SMDE
HMDE
Tapper
Capillary
Hg drop
New Drop
Stable surface
One drop !
Droplife
Choice of the working electrode
Voltammetry
Depends on the concentration of the analyte DME SMDE HMDE & RDE
Traces
ppm
Low ppm
ppb
ppt
Which working electrode ?
Voltammetry
Standard electrode: MME Organics: DME or SMDE Metal Traces: HMDE Special applications: RDE Gold electrode: Hg, As UT* with Hg film: Cd, Pb, Cu UT* Hg free: Cr, W, Ni
* UT: Ultra Trace Graphite Electrode
Which working electrode ?
Voltammetry
Potential ranges of different electrode types
Oxidation of electrode
Mercury Glassy Carbon
Gold
H+ + e-
Platinum Potential (V) -1.2 -1.0 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2
Voltammetric Techniques
Voltammetry
Polarography
uses the dropping mercury electrode (DME, SMDE)
(Stripping) Voltammetry
uses a stationary electrode (HMDE, RDE)
Voltammetric Analysis
Voltammetry
Polarography
Pb2+
Pb0
direct reduction or oxidation at the electrode limited sensitivity universal technique
Voltammetric Techniques
Voltammetry
Polarography
Stripping Voltammetry
U
U Pb I Cd
Pb I Cd
time
Electrolysis time
Reduction to metal (amalgam formation)
Reduction to metal (amalgam formation)
Oxidation to ion (determination)
Voltammetric Analysis
Voltammetry
Anodic Stripping Voltammetry (ASV) 2 steps
1. deposition (metal reduction) Cd2+ Cd0(Hg) 2. determination (Stripping) Cd0(Hg) Cd2+
2 steps
CSV
Voltammetric Analysis
Voltammetry
Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetry (AdSV)
1. deposition (adsorption) Ni2+(DMG-)2
Ni2+(DMG-)2ads
2. determination (Stripping) Ni2+(DMG-)2ads Ni2+ +
2 DMGred
DMG: Dimethylglyoxime, complexing agent
Stripping Voltammetry
Voltammetry
Properties
2 step measurement electrochemical deposition (enrichment) determination (stripping step) high sensitivity for trace analysis (down to ppt range) mainly for metal analysis.
PSA
Measurement Modes
Voltammetry
= modulation of potential ramp
Purpose:
Increasing sensitvity decreasing background signals Increasing selectivity separation of faradayic and capacitive current
Direct Current: DC
Voltammetry
potential ramp
U
resulting curve
time
voltage step
wave height
drop time time
half wave potential
Differential Pulse: DP
Voltammetry
potential modulation
resulting curve
I
U pulse amplitude drop time voltage step time
peak height peak potential
DC and DP
Voltammetry
I
quantitative information
U I
quantitative information
U qualitative information
U
Modes
Electrolyte in VA
Voltammetry
Correct electrolyte is most important :
see Application Bulletins
Purpose of the electrolyte:
Increases the conductivity Adjusts the pH Complexes the analyte Increase selectivity (masking of interfering elements)
Electrolyte in VA
Voltammetry
Peak potentials of different metals depending on the electrolyte
NH4Ac/HAc NH3/NH4Cl Mn Mn Co
Co
Ni Zn
Cd Cd CdPb
Pb Pb Cu Hg
Cu
Hg
Hg Hg Hg
Zn Co Ni Zn
Na tartrate Potential (V)
CuHg 0
-1.6 -1.4 -1.2 -1.0 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2
0.2 0.4 0.6
Concentration evaluation
Voltammetry
Peak evaluation Calibration
standard addition external calibration (calibration curve)
Peak evaluation
Voltammetry
height
Peak maximum Basepoints Baseline Peak height Peak area
basepoints
baseline
Calibration Curve
Voltammetry
Voltammograms of standards
Calibration Curve
peak height
conc c1 c2 c3
Sample with Cal. Curve
Voltammetry
Voltammograms of sample
Calibration Curve
peak height
conc c sample
Standard Addition
Voltammetry
Voltammograms additions
Standard Addition Curve
peak height
conc -cS Add1 Add2
sample
E
Sum
Calibration Techniques
Voltammetry
External Calibration
Measure standard solutions Calculate calibration curve measure sample
Standard Addition
measure sample measure additions to sample solution
Voltammetry
Why Voltammetry?
Advantages of Voltammetry
Voltammetry
No problem with high salt concentrations Speciation possible: e.g. Cr3+ - Cr6+ free / complexed metal Low detection limits: sub-ppb Capital outlay: Low price Low running costs: only N2
Advantages of Voltammetry
Voltammetry
No extensive laboratory infrastructure Versatility: inorganics and organics Anions Official methods (DIN,ISO,USP, ASTM, etc.) Alternative and complementary method to AAS/ICP
Advantages of Voltammetry
Voltammetry
Simultaneous Determination of Metals: up to 4 metals in one run Automation: 80 Samples plus all buffers and standards Calibration in every run: Variable Standard Addition if required.
Summary
Voltammetry
Most important points
What you should know about VA !
Voltammetry
VA: Voltam[pero]metry
I = f(U) AE: Pt, GC RE: Ag/AgCl/KCl 3 mol/L WE: MME (DME, SMDE, HMDE) or RDE DC, DP, AC1/AC2, SQW, CV, PSA
Electrodes:
Measurement Modes:
What you should know about VA !
Voltammetry
Methods
Polarography: "Liquid" electrode (DME, SMDE) Stripping Voltammetry (HMDE, RDE): Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetry Allows signal enhancement Increase selectivity Allows masking of elements
Electrolyte (buffer)
What you should know about VA !
Voltammetry
Concentration Evaluation:
Peak evaluation Calibration Standard Addition Technique Calibration Curve Technique
Advantages of Voltammetry
You might also like
- Cyclic VoltammetryDocument10 pagesCyclic VoltammetryAlacránAlemánNo ratings yet
- Differential Thermal Analysis and Differential Scanning CalorimetryDocument12 pagesDifferential Thermal Analysis and Differential Scanning CalorimetryZahir Rayhan Jhon100% (1)
- Essays on Analytical Chemistry: In Memory of Professor Anders RingbomFrom EverandEssays on Analytical Chemistry: In Memory of Professor Anders RingbomErkki WänninenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electrochemistry 16thDocument95 pagesChapter 1 Electrochemistry 16thTravis McmillanNo ratings yet
- ChE391 LabManual F15Document67 pagesChE391 LabManual F1588l8No ratings yet
- Atkins Chapter07.Lect02Document11 pagesAtkins Chapter07.Lect02Qisthy Hanifati HazrinaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry of Zirconium and Hafnium: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandAnalytical Chemistry of Zirconium and Hafnium: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Part Two Electrochemical Methods: Dr. Professor: Zhang, Chengxiao E-Mail: Tel: 85307567Document36 pagesPart Two Electrochemical Methods: Dr. Professor: Zhang, Chengxiao E-Mail: Tel: 85307567Mwezi JulesNo ratings yet
- CatalysisDocument54 pagesCatalysisRajatSonkarNo ratings yet
- Grofcsik Andras-Physical Chemistry - 1Document195 pagesGrofcsik Andras-Physical Chemistry - 1György SzidóniaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Numbers: Chemistry For The Gifted and Talented 61Document14 pagesOxidation Numbers: Chemistry For The Gifted and Talented 61EricNo ratings yet
- Polymers Homework1 1Document4 pagesPolymers Homework1 1mike100% (1)
- Practical Analytical 1 ,,chemistryDocument45 pagesPractical Analytical 1 ,,chemistryFadlin AdimNo ratings yet
- S For The Mon Ught TH T HoDocument110 pagesS For The Mon Ught TH T Hoysreddy8No ratings yet
- Mod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesDocument2 pagesMod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesdufraiscNo ratings yet
- Rates and EquilibriaDocument15 pagesRates and EquilibriaThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Tunneling & Harmonic OscillatorDocument33 pagesQuantum Mechanics Tunneling & Harmonic Oscillatorvivek patelNo ratings yet
- CHEM 3440: Thermal MethodsDocument7 pagesCHEM 3440: Thermal Methodstieuca08No ratings yet
- Bs and M.SC - Applied Chemistry PDFDocument4 pagesBs and M.SC - Applied Chemistry PDFZaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- CP 5 - Investigating The Rates of Hydrolysis of HalogenoalkanesDocument2 pagesCP 5 - Investigating The Rates of Hydrolysis of HalogenoalkanesPOPNo ratings yet
- Chemistry II EM Basic Learning MaterialDocument40 pagesChemistry II EM Basic Learning MaterialMAHINDRA BALLANo ratings yet
- Aliphatic Organic SynthesisDocument30 pagesAliphatic Organic SynthesisrationalwikiNo ratings yet
- Overview On Fuel CellsDocument6 pagesOverview On Fuel CellsCarol BrigagãoNo ratings yet
- 3-2 MSDocument60 pages3-2 MSputriNo ratings yet
- Section 3 EnergeticsDocument47 pagesSection 3 Energeticsapi-3734333No ratings yet
- 016610024Document8 pages016610024Saleh BreakerboyNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry 2 Week 1Document46 pagesPhysical Chemistry 2 Week 1Sarah AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Ap Lab Manual 2 - Gravimetric Analysis of A Metal CarbonateDocument4 pagesAp Lab Manual 2 - Gravimetric Analysis of A Metal CarbonateJacob StephansNo ratings yet
- Science 3 (Chemistry) Lab Manual 2018Document76 pagesScience 3 (Chemistry) Lab Manual 2018José VidalNo ratings yet
- Gcse Science - Chemistry 1Document40 pagesGcse Science - Chemistry 1api-320022467No ratings yet
- Gattermann - Laboratory Methods of Organic ChemistryDocument449 pagesGattermann - Laboratory Methods of Organic ChemistryGaurav DharNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals TestDocument12 pagesTransition Metals Testpaulcampbell37No ratings yet
- Voltammetric TechniquesDocument21 pagesVoltammetric TechniquesruteshvsNo ratings yet
- SALTDocument22 pagesSALTparitoshNo ratings yet
- Review of A-Level Chemistry Content: David Read & Charles Harrison August 2010Document39 pagesReview of A-Level Chemistry Content: David Read & Charles Harrison August 2010krisnuNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions - Chapter 15Document6 pagesSample Questions - Chapter 15Rasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Titration (Chemistry Experiment Report)Document7 pagesTitration (Chemistry Experiment Report)JasgeoNo ratings yet
- PPP Enthalpy ChangesDocument39 pagesPPP Enthalpy ChangesHenryLim9100% (1)
- Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology: Glassware: A Statistical StudyDocument8 pagesKwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology: Glassware: A Statistical StudyJIEHASMARTNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal ComplexesDocument103 pagesTransition Metal Complexesidownloadbooksforstu100% (1)
- Inorganic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualDocument16 pagesInorganic Chemistry: Laboratory ManualAhmed ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFDocument3 pagesGravimetric Analysis of Iron PDFEmrico Luiz PerezNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument140 pagesPolymersNitin Nishant100% (2)
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) : Mr. Sagar Kishor SavaleDocument27 pagesDifferential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) : Mr. Sagar Kishor SavaleDivya Tripathy100% (1)
- Gravimetric Analysis and Precipitation EquilibriaDocument55 pagesGravimetric Analysis and Precipitation EquilibriaasdfNo ratings yet
- 15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsDocument16 pages15.2 Born-Haber Cycle: 15.2.2 Explain How The Relative Sizes and The Charges of IonsGiselle PeachNo ratings yet
- Gravimetric Analysis Very GoodDocument24 pagesGravimetric Analysis Very Gooddhungelsubhash8154No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH08 D and F Block Elements 02Document8 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH08 D and F Block Elements 02srivathson7No ratings yet
- MSCCH03 PDFDocument466 pagesMSCCH03 PDFEmman Ann100% (1)
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5Document386 pagesEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5AbdulRahman Mustafa100% (1)
- Isotopic Dilution MethodDocument3 pagesIsotopic Dilution MethodZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of UnknownDocument10 pagesQualitative Analysis of UnknownJulie Edington100% (1)
- HPLC Detectors: Adapted From: HPLC For Pharmaceutical Scientists by Y.Kazakevich and R. LobruttoDocument7 pagesHPLC Detectors: Adapted From: HPLC For Pharmaceutical Scientists by Y.Kazakevich and R. LobruttogunaseelandNo ratings yet
- Conductometric MeasurementsDocument34 pagesConductometric Measurementsmonika vermaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Manganese in Steel by Flame Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument7 pagesDetermination of Manganese in Steel by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrossexycassie100% (1)
- AC 101 Unit 1 Titrimetric AnalysisDocument90 pagesAC 101 Unit 1 Titrimetric AnalysisRishabh Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Upload 67Document1 pageUpload 67Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 23Document1 pageUpload 23Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 48Document1 pageUpload 48Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 49Document1 pageUpload 49Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 2Document1 pageUpload 2Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 1Document1 pageUpload 1Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 5Document1 pageUpload 5Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Sample Preparation For Voltammetry: Metrohm Ltd. CH-9100 Herisau SwitzerlandDocument21 pagesSample Preparation For Voltammetry: Metrohm Ltd. CH-9100 Herisau SwitzerlandElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 4Document1 pageUpload 4Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Upload 2Document1 pageUpload 2Elka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Slide Uv VisDocument54 pagesSlide Uv VisElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Sample Preparation For Voltammetry: Metrohm Ltd. CH-9100 Herisau SwitzerlandDocument21 pagesSample Preparation For Voltammetry: Metrohm Ltd. CH-9100 Herisau SwitzerlandElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- VA InstrumentsDocument25 pagesVA InstrumentsElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- VA TheoryDocument42 pagesVA TheoryElka Sushea II100% (1)
- Slide ElectronalitikDocument21 pagesSlide ElectronalitikElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Linier RegresiDocument4 pagesLinier RegresiElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Food Additives: Integrated Science IIDocument21 pagesFood Additives: Integrated Science IIElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- 0712 GaDocument12 pages0712 GaElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Slide MSDocument66 pagesSlide MSRia Sita AriskaNo ratings yet
- Linier RegresiDocument4 pagesLinier RegresiElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Industry BDDocument8 pagesIndustry BDLabib AhsanNo ratings yet
- Repete Corporation TrainingDocument11 pagesRepete Corporation TrainingKomang PutraNo ratings yet
- MV Motor Publication Jan 2012Document16 pagesMV Motor Publication Jan 2012safinditNo ratings yet
- HW-7. Transient Heat Conduction PDFDocument1 pageHW-7. Transient Heat Conduction PDFSafaa Hameed Al NaseryNo ratings yet
- CV Chandra Salim, M.TDocument4 pagesCV Chandra Salim, M.TChandra SalimNo ratings yet
- Capability Maturity Model (CMM) : Purpose: To Assess and Help Improve Process in Software Development OrganizationsDocument45 pagesCapability Maturity Model (CMM) : Purpose: To Assess and Help Improve Process in Software Development Organizationsbooster6699No ratings yet
- Lios AdminDocument71 pagesLios AdminGiang Nguyen VanNo ratings yet
- 00 LSPU Stage 2 Audit Report 2018 PDFDocument21 pages00 LSPU Stage 2 Audit Report 2018 PDFRolando Cruzada Jr.No ratings yet
- 221 Cardiolife Defibrillator Lab5Document3 pages221 Cardiolife Defibrillator Lab5Salah ElbadawyNo ratings yet
- R6013e MVTRDocument6 pagesR6013e MVTRlucnhamdaidon8426No ratings yet
- Ad Js Injection - JsDocument2 pagesAd Js Injection - JsWalison SilvaNo ratings yet
- 2004 Viking-Excalibur ManualDocument45 pages2004 Viking-Excalibur ManualjackNo ratings yet
- Nanotransistor A Botton UP ViewDocument8 pagesNanotransistor A Botton UP ViewDerlone AraújoNo ratings yet
- Joint Forces Extrication KitsDocument2 pagesJoint Forces Extrication KitssolsysNo ratings yet
- Implementation of The Modified Compression Field TheoryDocument33 pagesImplementation of The Modified Compression Field TheoryDang Bao TranNo ratings yet
- 17.02.SI.0009. Princess Etab Ben Jalawi A'al Saud Villa 1Document2 pages17.02.SI.0009. Princess Etab Ben Jalawi A'al Saud Villa 1Arafat BauntoNo ratings yet
- API 5L-Annex KDocument5 pagesAPI 5L-Annex KHareendran AkmNo ratings yet
- Ligoo Manual and DiagramDocument54 pagesLigoo Manual and DiagramAngelito Ramos100% (1)
- Fixed Fire Fighting in Road Tunnels Current Practices and RecommandationsDocument86 pagesFixed Fire Fighting in Road Tunnels Current Practices and RecommandationsMoonRiMouNo ratings yet
- IT AssignmentDocument3 pagesIT AssignmentKanthi Rekha VardhiNo ratings yet
- Siemens ET200M Systems ManualDocument240 pagesSiemens ET200M Systems ManualAndrey ZimnitskiyNo ratings yet
- Stanika Rajya SthapanaDocument7 pagesStanika Rajya SthapanaSravani KalaburigiNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Requirements For High Rise Building 15 M in Height or AboveDocument40 pagesFire Protection Requirements For High Rise Building 15 M in Height or AboveNishant Sharma100% (1)
- Eurocode 3 PDF FreeDocument2 pagesEurocode 3 PDF FreeBret0% (1)
- Fault Tolerant Control of A Quadrotor UAV Using Sliding Mode ControlDocument6 pagesFault Tolerant Control of A Quadrotor UAV Using Sliding Mode ControladilsondissoNo ratings yet
- CS401 Final Term Solved Paperz MAGA Files All Paperz in ONe FileDocument47 pagesCS401 Final Term Solved Paperz MAGA Files All Paperz in ONe FileUmair Masood100% (3)
- E-LIBRARY RULES - Home-BasedDocument5 pagesE-LIBRARY RULES - Home-BasedBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Accessories For Copper Communication Networks: CatalogDocument88 pagesAccessories For Copper Communication Networks: CatalogefecastNo ratings yet
- Consumer Guide DOEDocument35 pagesConsumer Guide DOEYanoNo ratings yet
- Manual Multimetro HPDocument2 pagesManual Multimetro HPMauricioNo ratings yet
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)