A SEMINAR ON MATERIAL SELECTION PRESENTED BY MD SHAHID & MD FASI UR RAHMAN
OVERVIEW
Materials Selection Why Materials Selection ??? Product Analysis
Product function and interdependent
Design limiting material properties Stress strain diagram for material
Fundamental properties
Classification of materials Flow chart of material selection
Ashby chart
Examples LEAF SPRINGS, HELMET,
VACCUM CLEANER, DRINKS CONTAINER
�Materials Selection
Material selection is a step in the process of designing any physical object. In the context of Product Design, the main goal of material selection is to minimize cost while meeting product performance goals
The designer of any product must get involved with
material selection.
Only occasionally will the exact grade of material be
specified by the customer.
Even then the designer must understand the material
to be able to design the product.
��IN ORDER TO STAY COMPETITIVE IN TODAYS MARKETPLACE, A COMPANY MUST UNDERSTAND ITS CUSTOMERS' WANTS AND NEEDS AND DESIGN PROCESSES TO MEET THEIR EXPECTATIONS AND REQUIREMENTS.
�Decisions, decisions!
So many materials, so much information.
How do we decide? How do we begin to choose?
First we need to look at the function of the product product analysis
�Product Analysis
Just what it says analyse the product!
What does it do? How does it do it? Where does it do it? Who uses it? What should it cost?
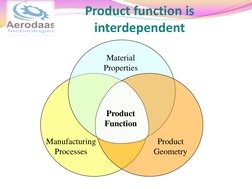
�Product function is interdependent
Material Properties
Product Function
Manufacturing Processes
Product Geometry
�Material properties
Mechanical properties quantities that characterize the behavior of a material in response to external, or applied forces
Physical properties quantities that characterize the behavior of a material in response to physical phenomena other than mechanical forces (e.g. such as heat, electricity, radiation)
��Mechanical properties
stress
F/A
A
ductile ?
S ut
Sy
L L
brittle
elastic plastic
strain
L L L
stiffness ?
Strength = stress at failure = (failure)
�Mechanical properties
�Fundamental properties
Characteristic Strength Elastic strength Stiffness Ductility Hardness Corrosion resistance Behavior strong, weak elastic then plastic flexible, rigid draws, forms easily resists surface indentation resists chemicals, oxidation Property ultimate strength yield strength modulus of elasticity % elongation, % area reduction Brinell No. galvanic series Units MPa (ksi) MPa (ksi) MPa (Mpsi) dimensionless MPa (ksi) activity number
�Fundamental properties
Characteristic Fatigue resistance Conductivity (heat, electric) Creep resistance Impact resistance Density (mass) Density (weight) Temperature tolerance Behavior endures many load cycles Property endurance limit thermal conductivity electrical conductivity creep strength Charpy energy mass density weight density melting point Units MPa (Mpsi) (Btu/hr) / (F-ft), Mhos MPa (ksi) N-m, (ft-lbs) kg/m3, (slugs/ft3) N/m3, (lbs/ft3) degrees C, F
conducts, insulates
time dependent stretching shock, impact loads heavy, light softens, or melts easily
�Property profiles by family
�Material families / subfamilies
Materials
Metals Ferrous
Plastics Thermoplastics Thermosets Elastomers
Ceramics
Composites
Family (Ashby)
Non-ferrous
Sub-family
�Material sub-families / classes
Materials
Metals Ferrous Cast iron Carbon steel Alloy steel Stainless steel
Family Sub-family
Classes
�Metals
Metals
Ferrous cast iron carbon steel alloy steel stainless steel
Non-ferrous aluminum brass bronze copper lead magnesium nickel tin titanium tungsten zinc
�Polymers
Polymers
Natural and synthetic rubbers
Thermoplastics
ABS acetal acrylic nylon polycarbonate polyethylene polypropylene polystyrene vinyl
Thermosets alkyd epoxy melamine phenolic polyester urethane
Elastomers butyl fluorocarbon neoprene nitrile polysulfide rubber silicone
�Materials selection
prospective materials and processes
functional? manufacturable?
screening
rejected materials and processes
feasible materials and processes
relative performance?
rating
best material(s) and processes
�Screening: How do we choose a material?
Product function depends upon
material, manufacturing process, geometry
We have to consider all three
Do we select a few feasible materials first then select the specific mfg process?
or
Do we select a few feasible mfg processes then select the specific material?
�Screening: Materials first approach
Application Information
1. Applied loads magnitude cyclic nature (steady, fatigue) rate (slow, impact) duration (creep) 2. Ambient conditions temperature moisture sunlight chemical liquids/vapors 3. Safety 4. Cost
�Screening: Manufacturing process first approach
Part Information
1. 2. 3.
Production volume Part size (overall) Shape capability (features) boss holes undercuts (internal/external) uniform walls cross sections (uniform /regular) rotational symmetry captured cavities
�ASHBY CHART
How can we use it?
��EXAMPLE 1
�Given conditions
�Result
�EXAMPLE 2
�����EXAMPLE 3
��Drink Container