Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isometric Drawing1
Uploaded by
prasaad08Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Isometric Drawing1
Uploaded by
prasaad08Copyright:
Available Formats
The University of Gaziantep
Faculty of Engineering
ME 101
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS
Isometric Drawing
Dr. Ouzhan YILMAZ (Assist.Prof.) Mechanical Engineering Department Room: 319 oyilmaz@gantep.edu.tr http://www.gantep.edu.tr/~oyilmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Introduction and Objectives
This lecture introduces the concept of Isometric projection and Isometric drawing of an object. Followings will be highlighted to be able to explain the Isometric drawing: Axonometric projection Isometric projection Isometric drawing Isometric and non-isometric lines (Boxing and offset methods) Angles in isometric drawing Curves in isometric drawing Circles in isometric drawing (Four center ellipse) Isometric circle arcs Students are required to understand the fundamentals of isometric drawing and the technical and practical details while drawing of an object.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Axonometric Projection
Is a parallel projection technique used to create a pictorial drawing of an object by rotating the object on an axis relative a projection or picture plane. Axonometric projection is one of the four principal projection techniques: multiview, axonometric, oblique and Line of sight
A C B D C Parallel & normal to picture plane A B D
perspective
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Axonometric Projection
In Multi views and axonometric projections, the lines of sight are perpendicular to the plane of projection; therefore, both are considered orthographic projections
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Axonometric Projection
Type of axonometric drawing
a
Axonometric axis
c
1. Isometric
All angles are equal.
A
A C
B B a D D
Axonometric axis
c
2. Dimetric
Two angles are equal.
Axonometric axis
c
3. Trimetric
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
None of angles are
equal.
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric Projection
Rotate 45 about vertical axis Tilt forward (35o16)
An isometric projection is a true representation of the isometric view of an object.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
All edges foreshorten about 0.8 time.
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric Drawing
Isometric drawing is a drawing drawn on an isometric axes using full scale. Isometric drawings are almost always preferred over isometric projection for engineering drawings, because they are easier to produce
Isometric projection
(True projection)
Isometric drawing
(Full scale)
Forshorten
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Full scale
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric Axes
An isometric drawing is an axonometric pictorial drawing for which the angle between each axis equals 120 degrees and the scale used is full scale
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Positions of Isometric axes
Isometric axes can be arbitrarily positioned to create different views of a single object.
Regular isometric
Reverse axis isometric
Long axis isometric
View point is looking down on the top of the object.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
View point is looking up on the bottom of the object.
View point is looking from the right (or left) of the object.
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Selection of Isometric axes
View (a) is preferred as it reveals more detail than the others
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric and Non-isometric lines & planes
In an isometric drawing, true length distances can only be measured along isometric lines, that is, lines that run parallel to any of the isometric axes. Any line that does not run parallel to an isometric axis is called a non-isometric line Non-isometric lines include inclined and oblique lines and can not be measured directly. Instead they must be created by locating two end points.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric and Non-isometric lines & planes
The three faces of the isometric cube are isometric planes, because they are parallel to the isometric surfaces formed by any two adjacent isometric axes. Planes that are not parallel to any isometric plane are called nonisometric planes
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric and Non-isometric lines & planes
True-length distances are shown along isometric lines.
Isometric line is the line that run parallel to any of the
isometric axes. Isometric lines
Nonisometric lines
Isometric axes
Isometric planes
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric drawing
The Boxing-in Method for Creating Isometric Drawings The four basic steps for creating an isometric drawing are: 1. Determine the isometric viewpoint that clearly depicts the features of the object, then draw the isometric axes which will produce that view-point. 2. Construct isometric planes, using the overall width (W), height (H), and depth (D) of the object, such that the object will be totally enclosed in a box. 3. Locate details on the isometric planes. 4. Darken all visible lines, and eliminate hidden lines unless absolutely necessary to describe the object.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric sketching from multi-view drawing
Front View
Regular H
Top Front
W
Side
D
Top View
W
Side View
D
Reverse
Front
Side
Bottom
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric drawing
STEPS 1. Positioning object. 2. Select isometric axis.
3. Sketch enclosing box.
4. Add details. 5. Darken visible lines.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric drawing
STEPS 1. Positioning object. 2. Select isometric axis. 3. Sketch enclosing box. 4. Add details. 5. Darken visible lines. Note In isometric sketch/drawing), hidden lines are omitted unless they are absolutely necessary to completely describe the object.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric drawing: object has inclined surfaces
D
Nonisometric line
y H y
x x
Front View
W
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric drawing: object has inclined surfaces
x
C B A x B C A y x
y C
Nonisometric line
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Isometric drawing
x
Regular
y B
C E D A B
Front View
C A
D F
Reverse
E
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Drawing of Circle and Arcs
In isometric drawing, a circle appears as an ellipse.
Sketching Steps
1. Locate the centre of an ellipse.
2. Construct an isometric square. 3. Sketch arcs that connect the
tangent points.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Drawing of Circle and Arcs
Four-centre method is usually used when drawn an isometric ellipse with drawing instrument. Sketching Steps
1. Locate the centre of an ellipse. 2. Construct an isometric square.
3. Construct a perpendicular
bisector from each tangent point.
4. Locate the four centres. 5. Draw the arcs with these centres
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
and tangent to isometric square.
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Drawing of Circle and Arcs
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Drawing of Circle and Arcs
Half circle
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Quarter circle
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Drawing of Irregular curves in Isometric drawing
Steps
1. Construct points along the
curve in multiview drawing.
2. Locate these points in the
isometric view. 3. Sketch the connecting lines.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Hidden lines in Isometric drawing
In isometric drawings, hidden lines are omitted unless they are absolutely necessary to completely describe the object. Most isometric drawings will not have hidden lines.
To avoid using hidden lines, choose the most descriptive viewpoint. However, if an isometric viewpoint cannot be found that clearly depicts all the major features, hidden lines may be used.
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
Isometric Drawing
ME 101
Center lines in Isometric drawing
Centerlines are drawn only for showing symmetry or for dimensioning. Normally, centerlines are not shown, because many isometric drawings are used to communicate to nontechnical people and not for engineering purposes
Dr. Ouzhan Ylmaz
You might also like
- Basics of MetrologyDocument37 pagesBasics of Metrologymanoj kumar GNo ratings yet
- NAL Manual New Automatic Spray System (12.04.2019)Document32 pagesNAL Manual New Automatic Spray System (12.04.2019)sunil0% (1)
- Advanced Metrology Infrastructure and Inspection Capability To Analyze Sub 20nm Defects-Kfir - Dotan - AMATDocument27 pagesAdvanced Metrology Infrastructure and Inspection Capability To Analyze Sub 20nm Defects-Kfir - Dotan - AMATHamid HamidNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Six Sigma Methodology ManufacturingDocument21 pagesCase Study in Six Sigma Methodology ManufacturingNemanja ĆulibrkNo ratings yet
- Basic Metrology Practices TAYLOR HOBSONDocument70 pagesBasic Metrology Practices TAYLOR HOBSONss2mrattri100% (2)
- Conflict ManagementDocument7 pagesConflict ManagementMichelle Jácome FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength of Concrete Cubes Procedure and SpecificationDocument3 pagesCompressive Strength of Concrete Cubes Procedure and SpecificationSHOAIBNo ratings yet
- Project Life Cycle & Project Management Process Groups: Information Systems DepartmentDocument63 pagesProject Life Cycle & Project Management Process Groups: Information Systems DepartmentAjmal EnsanahNo ratings yet
- Go No Go GaugesDocument1 pageGo No Go Gaugesspj99696649148No ratings yet
- Flow Chart For SubsidyDocument1 pageFlow Chart For SubsidyAvinash MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Management Du Systeme D'Information: Communication Basis Meetings Management Project Reviews Reporting CapitalisationDocument19 pagesManagement Du Systeme D'Information: Communication Basis Meetings Management Project Reviews Reporting CapitalisationSơn Thủy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Adp Project ReportDocument14 pagesAdp Project ReportHamza SandhuNo ratings yet
- Simple Business Plan Outline-01Document33 pagesSimple Business Plan Outline-01vrgurijalaNo ratings yet
- Metrology Laboratory WorkDocument9 pagesMetrology Laboratory WorkAmod PantheeNo ratings yet
- Use of Chemical Characterization to Assess Medical Device EquivalencyDocument23 pagesUse of Chemical Characterization to Assess Medical Device EquivalencySathesh Kumar AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- Reverse Engineering Project - Carleton University - 2009Document8 pagesReverse Engineering Project - Carleton University - 2009Noshin NugawelaNo ratings yet
- Comply with e-signature laws using Adobe SignDocument5 pagesComply with e-signature laws using Adobe SignClaudiaFerriNo ratings yet
- Surface Hardness and Compressive Strength of ConcreteDocument20 pagesSurface Hardness and Compressive Strength of ConcreteAmer FarkhanNo ratings yet
- Failure Studies in Materials - ch8Document47 pagesFailure Studies in Materials - ch8tamailhamNo ratings yet
- Polymer Procession Term Test-1Document90 pagesPolymer Procession Term Test-1সাইদুর রহমানNo ratings yet
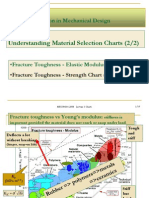
- Caceres-L3 Understanding Materials Selection ChartsDocument23 pagesCaceres-L3 Understanding Materials Selection ChartsUngku Mohd RafiqNo ratings yet
- International Diving Institute Civil SuitDocument28 pagesInternational Diving Institute Civil SuitLester MurphySrNo ratings yet
- IAFMD9 Issue 309062017Document31 pagesIAFMD9 Issue 309062017bzivkovic100% (1)
- Design For SustainabilityDocument16 pagesDesign For SustainabilityGuangbeng LeeNo ratings yet
- Jigs and Fixture PDFDocument5 pagesJigs and Fixture PDFAbdul Gani100% (1)
- Quality Management Lean Tools and TechniquesDocument19 pagesQuality Management Lean Tools and TechniquesAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Mechanics of Materials Equations SummaryDocument5 pagesFundamental Mechanics of Materials Equations SummaryWong Jian MingNo ratings yet
- FSC Interpretations Chain of Custody 2021.07.05Document49 pagesFSC Interpretations Chain of Custody 2021.07.05Budi Suryo UntoroNo ratings yet
- Measurement and InspectionDocument33 pagesMeasurement and InspectionSri RNo ratings yet
- Calculating Plastic Component Shrinkage and DistortionDocument4 pagesCalculating Plastic Component Shrinkage and DistortionRajendra Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Routine Press Maintenance Routine Press Maintenance Routine Press Maintenance Routine Press MaintenanceDocument42 pagesRoutine Press Maintenance Routine Press Maintenance Routine Press Maintenance Routine Press MaintenanceMorshedNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Project Report PreparationDocument16 pagesGuidelines For Project Report PreparationHari DasNo ratings yet
- Eva Film Inter Layer For Laminated GlassDocument7 pagesEva Film Inter Layer For Laminated GlassPeter LinNo ratings yet
- Glass MechanicsDocument18 pagesGlass MechanicsSudhakar KrishnamurthyNo ratings yet
- Properties of Polymer ConcreteDocument35 pagesProperties of Polymer ConcreteKannan Kandappan100% (1)
- US Legal Binding Document for ASTM A572 Steel StandardDocument5 pagesUS Legal Binding Document for ASTM A572 Steel Standardeko.kusgmail.comNo ratings yet
- FSC-DIR-40-004 en CoC Certification 2015-12-09Document20 pagesFSC-DIR-40-004 en CoC Certification 2015-12-09Daniel BogleaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6Document3 pagesExperiment 6Subhasis BiswalNo ratings yet
- Quality Control of Tempered Glass Panels With PhotoelasticityDocument8 pagesQuality Control of Tempered Glass Panels With PhotoelasticityMohamedNo ratings yet
- Waterproofing, Insulation Materials and OpeningsDocument37 pagesWaterproofing, Insulation Materials and OpeningspalaganasNo ratings yet
- Windows and Laminated Glass TL ValuesDocument119 pagesWindows and Laminated Glass TL ValuescataninoNo ratings yet
- Metals Extrusion and Drawing Processes ExplainedDocument26 pagesMetals Extrusion and Drawing Processes ExplainedArvind BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Problem Definition Customer NeedsDocument51 pagesProblem Definition Customer Needslente_weyNo ratings yet
- CRM - Profiting From Understanding Customer Needs PresentationDocument12 pagesCRM - Profiting From Understanding Customer Needs PresentationSachin GargNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON: ComparatorsDocument25 pagesPresentation ON: Comparatorsaneesh19inNo ratings yet
- Robust Design of Plastic ProductsDocument11 pagesRobust Design of Plastic Productsiganu76No ratings yet
- Creating and Leading Effective TeamsDocument6 pagesCreating and Leading Effective TeamsMathew KilonzoNo ratings yet
- Rationel Design Drawings and Structural CalculationsDocument8 pagesRationel Design Drawings and Structural CalculationsAmro Ahmad AliNo ratings yet
- Niyama Criteria Niyama Criteria Niyama CriteriaDocument18 pagesNiyama Criteria Niyama Criteria Niyama CriteriaVarthini RajaNo ratings yet
- Bitumen ReportDocument1 pageBitumen ReportRevItUp BenNo ratings yet
- PPE Regulation EU & UK Medical Device DirectivesDocument37 pagesPPE Regulation EU & UK Medical Device DirectivesKarthi Thiyagarajan0% (1)
- How Voids Form in Thick Plastic PartsDocument4 pagesHow Voids Form in Thick Plastic PartsRavindra ErabattiNo ratings yet
- FSC STD 40 004 - V3 0 - EN Chain of Custody CertificationDocument36 pagesFSC STD 40 004 - V3 0 - EN Chain of Custody CertificationDaniel ModicaNo ratings yet
- The Aluminum Beverage CanDocument7 pagesThe Aluminum Beverage CanDennys Quimi BorborNo ratings yet
- Material SelectionDocument60 pagesMaterial SelectionKhoa Nguyễn AnhNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Design of Moulds Molding PartsDocument8 pagesUnit-V Design of Moulds Molding Partsyuvaraj4509No ratings yet
- Iso 3Document27 pagesIso 3nandhuNo ratings yet
- Isometric DrawingDocument27 pagesIsometric DrawingTsiry Tsilavo100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing=IsometricDocument16 pagesEngineering Drawing=Isometricpanashezhou321No ratings yet
- Isometric and Oblique Drawing TechniquesDocument28 pagesIsometric and Oblique Drawing Techniqueshisham_eyesNo ratings yet
- HMT Mod 5 NotesDocument66 pagesHMT Mod 5 Notesprasaad08No ratings yet
- GearsDocument44 pagesGearsprasaad08No ratings yet
- Iron-Carbon DiagramDocument11 pagesIron-Carbon DiagramrampradNo ratings yet
- Question Bank III B.Tech-II Sem Design of Machine Members-Ii Unit - I A Design of Curved Beams Short Answer QuestionsDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank III B.Tech-II Sem Design of Machine Members-Ii Unit - I A Design of Curved Beams Short Answer Questionsprasaad08No ratings yet
- Connecting RodDocument29 pagesConnecting Rodprasaad08No ratings yet
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotesprasaad08No ratings yet
- 10th Maths em 24-Jul-2016 21-44-08 - WatermarkedDocument1 page10th Maths em 24-Jul-2016 21-44-08 - Watermarkedprasaad08No ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On The Combustion and Emission Characteristics of A Diesel EngineFuelled With Used Cooking Oil Methyl Esterand Its Diesel BlendsDocument7 pagesExperimental Studies On The Combustion and Emission Characteristics of A Diesel EngineFuelled With Used Cooking Oil Methyl Esterand Its Diesel Blendsprasaad08No ratings yet
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument1 page9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- IJEE 11 v4n5Document12 pagesIJEE 11 v4n5prasaad08No ratings yet
- 9A01303 SurveyingDocument4 pages9A01303 Surveyingprasaad08No ratings yet
- FIE FormDocument10 pagesFIE Formprasaad08No ratings yet
- ES 2 MarksDocument17 pagesES 2 Marksprasaad08No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SurveyingDocument611 pagesFundamentals of Surveyingrvkumar361969091% (58)
- Nanotechnology: Course: B.E & B.Tech Subject: APPLIED CHEMISTRY Unit: VDocument10 pagesNanotechnology: Course: B.E & B.Tech Subject: APPLIED CHEMISTRY Unit: Vprasaad08No ratings yet
- After Gate Guide 2015Document100 pagesAfter Gate Guide 2015JaydeepRanipaNo ratings yet
- Energies: Emission Characteristics of A CI Engine Running With A Range of Biodiesel FeedstocksDocument17 pagesEnergies: Emission Characteristics of A CI Engine Running With A Range of Biodiesel FeedstocksArul JONo ratings yet
- Aluminium: A Large Aluminium Billet From Which Wrought Products Will Be ProducedDocument38 pagesAluminium: A Large Aluminium Billet From Which Wrought Products Will Be Producedprasaad08No ratings yet
- M.Tech - F Semester Regulor Exqminotions April 20t5: TimetobleDocument1 pageM.Tech - F Semester Regulor Exqminotions April 20t5: Timetobleprasaad08No ratings yet
- Design of Machine Members-IIDocument8 pagesDesign of Machine Members-IIprasaad08No ratings yet
- Cad Cam Viva QueDocument5 pagesCad Cam Viva QueJeeva KarunyaNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Viva QueDocument5 pagesCad Cam Viva QueJeeva KarunyaNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2Document34 pagesProduction Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2prasaad08No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document6 pagesLecture 1prasaad08No ratings yet
- YVC RaoDocument98 pagesYVC Raoprasaad08No ratings yet
- DV03PUB1 Study GuideDocument5 pagesDV03PUB1 Study Guideprasaad08No ratings yet
- NMDC Et AdvertisementDocument8 pagesNMDC Et AdvertisementbecbellaryNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2Document34 pagesProduction Engineering Syllabus (1) - 2prasaad08No ratings yet
- Jntua B.tech Eee r13 SyllabusDocument116 pagesJntua B.tech Eee r13 Syllabusprasaad08No ratings yet
- R09 B.Tech III Year I Semester Machine Elements ExamDocument1 pageR09 B.Tech III Year I Semester Machine Elements Examprasaad08No ratings yet
- Bitsler Double BTC ScriptDocument50 pagesBitsler Double BTC ScriptAwais AliNo ratings yet
- Excel Formulas in HindiDocument10 pagesExcel Formulas in HindiMahor Pramod100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Oblique DrawingsDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Oblique DrawingsNur Hafizah RazaliNo ratings yet
- 24 CM Diagram Accurately Drawn: 1 The Diagram Shows Rectangle ABCD NOTDocument3 pages24 CM Diagram Accurately Drawn: 1 The Diagram Shows Rectangle ABCD NOTahmadyusufhz3No ratings yet
- HTML Codes - Table of Ascii Characters and SymbolsDocument7 pagesHTML Codes - Table of Ascii Characters and SymbolsAbhishek MalwankarNo ratings yet
- LevellingDocument32 pagesLevellingEmaNo ratings yet
- Latitude Pre-Test - Answer Key PDFDocument5 pagesLatitude Pre-Test - Answer Key PDFIrene MartinNo ratings yet
- Steval Ids001v2 SchematicDocument4 pagesSteval Ids001v2 SchematicDian Eko KuncoroNo ratings yet
- 06 Multiview Projection Drawing Part 1Document46 pages06 Multiview Projection Drawing Part 1Lakshwanath JaganathNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of EdgewoodDocument1 pageTopographic Map of EdgewoodHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Formatting TextDocument45 pagesFormatting TextLokithNo ratings yet
- Asus g750jh Repair Guide SCHDocument5 pagesAsus g750jh Repair Guide SCHGabriel DrideanuNo ratings yet
- Type Family: Garamond: Italic Fonts, Which Are Based On Cursive Writing, Have Forms Distinct From RomanDocument1 pageType Family: Garamond: Italic Fonts, Which Are Based On Cursive Writing, Have Forms Distinct From Romanapi-25990764No ratings yet
- Garmin GPS 128 1998Document74 pagesGarmin GPS 128 1998Eric EasonNo ratings yet
- Vvairios Diagramas de CajasDocument51 pagesVvairios Diagramas de CajasIbrain Moran100% (1)
- Rangka Kursus (Course Outline)Document2 pagesRangka Kursus (Course Outline)navri_nalhadNo ratings yet
- Catalogue and Indexes of San Charts and Other Hydrographic PublicationsDocument27 pagesCatalogue and Indexes of San Charts and Other Hydrographic PublicationsCodruţ ErașcuNo ratings yet
- Latitude, Longitude, and Great Circle DistancesDocument4 pagesLatitude, Longitude, and Great Circle DistancesTaz NazNo ratings yet
- Gale's Table by Suman JyotiDocument2 pagesGale's Table by Suman JyotiSuman JyotiNo ratings yet
- Flooding Carindale South Flood Flag MapDocument1 pageFlooding Carindale South Flood Flag MapNgaire TaylorNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of OlneyDocument1 pageTopographic Map of OlneyHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Sunlight StyleGuide DataViz PDFDocument13 pagesSunlight StyleGuide DataViz PDFSai Kiran AdepuNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2Robert M. MaluyaNo ratings yet
- Perspective Drawing GuideDocument28 pagesPerspective Drawing GuideAthenapixieNo ratings yet
- Cad and Drafting ManualDocument47 pagesCad and Drafting ManualHumble SNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Survey ReportsDocument9 pagesTransmission Line Survey ReportsGhayas Ud-din DarNo ratings yet
- Topographic Map of Higgins SouthDocument1 pageTopographic Map of Higgins SouthHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Map - Region of Timor LesteDocument1 pageMap - Region of Timor Lestecartographica100% (1)
- Visual Identity Guidelines: November 2016Document21 pagesVisual Identity Guidelines: November 2016w marko100% (1)
- Geodetic Engineer Certificate Form Ge0313 PDFDocument1 pageGeodetic Engineer Certificate Form Ge0313 PDFHomer CasauayNo ratings yet