Solid Modeling
Regularized Boolean Operations
Prepared by :- Hitesh H. Parmar [ MEFGI 1st PG-CE ] Contact :- Hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com
�Topics that we will cover today.
Representation of Solid Model.
Definition of Solid Model Boolean set Operation
Ordinary Boolean Operation on Solids Regularized Boolean Operation on Solids Examples
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
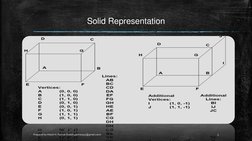
�Solid Representation
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
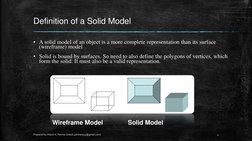
�Definition of a Solid Model
A solid model of an object is a more complete representation than its surface (wireframe) model
Solid is bound by surfaces. So need to also define the polygons of vertices, which form the solid. It must also be a valid representation.
Wireframe Model
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
Solid Model
4
�Ordinary Boolean Operation on Solids
One of the most popular methods for combining objects is by Boolean set operations, such as union, difference, and intersection Applying an ordinary Boolean set operation to two solid objects, however, does not necessarily yield a solid object. For example, the ordinary Boolean intersections of the cubes in Fig. 12.3(a) through (e) are a solid, a plane, a line, a point, and the null object, respectively.
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
�Ordinary Boolean Set Operations on Solid Objects
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
�Ordinary Boolean Set Operations on Solid Objects
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
�Ordinary Boolean Set Operations on Solid Objects
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
�Regularized Boolean Operation on Solids
Rather than using the ordinary Boolean set operators, we will instead use the regularized Boolean set operators, denoted *, *, and *, and defined such that operations on solids always yield solids. For example, the regularized Boolean intersection of the objects shown in Fig. 12.3 is the same as their ordinary Boolean intersection in cases (a) and (e), but is empty in (b) through (d).
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
�Regularized Boolean Set Operations
Using regularized boolean operators: All 3 intersections = NULL Effectively, we throw away any results from an operation that is of lower dimensionality than the original solids.
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
10
�Regularized Boolean Set Operations
boundary / interior points :
points whose distance from the object and the objects complement is zero / other points
closed set
a set contains all its boundary points
open set
a set contains none of its boundary points
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
11
�Regularized Boolean Set Operations
Closure :
the union of a set with the set of its boundary points is a closed set
Boundary :
the set of closed sets boundary points
Interior :
the complement of the boundary with respect to the object
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
12
�Regularized Boolean Set Operations
regularization :
the closure of a sets interior points
regularized Boolean set operator :
A op* B= closure (interior (A op B)) only produce the regular set when applied to regular sets
Object
Closure
Interior
Regularized Object
13
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
�Ordinary & Regularized Boolean Set Operations
[ O1]
[ Example 1 ]
[ O2] [ O2]
[ O1]
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
14
�Ordinary Boolean Set Operations
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
[ Example 2 ]
15
�Regularized Boolean Set Operations
[ Example 3 ]
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
16
� Regularized Boolean Operations
Source : University of Manitoba
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com) 17
�Thanks
Prepared by Hitesh H. Parmar (hitesh.parmar915@gmail.com)
18
![Solid Modeling
Regularized Boolean Operations
Prepared by :- Hitesh H. Parmar [ MEFGI 1st PG-CE ]
Contact](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/141/178751875/1.jpeg)