Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Section 2c
Uploaded by
drsohaire0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
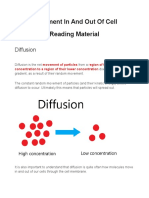
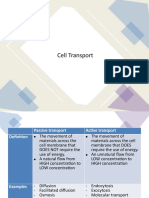
14 views9 pagesDiffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached. It occurs through random particle movement, such as when smell molecules from an air freshener spread through the air until the concentration is equal everywhere. Active transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient by selectively pumping chemicals across cell membranes. Osmosis is the movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high concentration until equilibrium is reached, such as when water enters plant cells placed in water to gain turgor pressure until the cell wall prevents further expansion.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached. It occurs through random particle movement, such as when smell molecules from an air freshener spread through the air until the concentration is equal everywhere. Active transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient by selectively pumping chemicals across cell membranes. Osmosis is the movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high concentration until equilibrium is reached, such as when water enters plant cells placed in water to gain turgor pressure until the cell wall prevents further expansion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views9 pagesSection 2c
Uploaded by
drsohaireDiffusion is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached. It occurs through random particle movement, such as when smell molecules from an air freshener spread through the air until the concentration is equal everywhere. Active transport requires energy to move substances against their concentration gradient by selectively pumping chemicals across cell membranes. Osmosis is the movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high concentration until equilibrium is reached, such as when water enters plant cells placed in water to gain turgor pressure until the cell wall prevents further expansion.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
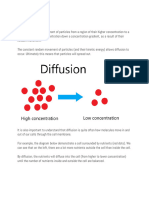
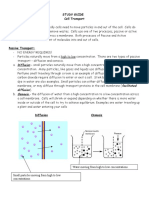
Definition: Diffusion
Movement of particles from a high
concentration to a low concentration until
equilibrium is reached.
What does this actually mean?
Imagine a solid air freshener. Inside the air
freshener, there is a very high concentration of
the molecule that makes the smell. When the air
freshener opens it allows the particles out.
Gradually in their random movement they begin
to spread out. The smell moves into the air
where there was previously no smell. The
particles move from areas where there were lots
of them to areas where there were few. This will
continue until the number of particles is the
same everywhere. This is equilibrium.
Active Transport
• There are times when cells need to move
chemicals across the cell membrane against the
concentration gradient (i.e. from a low
concentration to a high concentration). This
requires energy, as the chemicals need to be
pumped across the cell membrane.
• The cells of the small intestine absorb some food
particles by active transport.
• Substances are selectively transported. The cell
can choose which chemicals are pumped into or
out of the cell. For example, nerve cells actively
pump potassium inside the cell while pumping
sodium out of the cell.
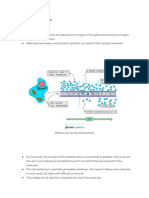
• Definition:
Osmosis
• movement of water from a weak solution to a more
concentrated one through a semi-permeable until
equilibrium is reached.
• What does this mean?
• A weak solution is one which has few substances
dissolved in it. Pure water is obviously as weak as a
solution gets. Water moves from a weak solution to
more concentrated one. A semi-permeable membrane
separates the two solutions. This prevents the dissolved
solutions from mixing, so only the water can move. This
will continue until the solutions on either side of the
membrane are the same concentration.
• E.g. imagine a plant cell in water. The cytoplasm is a
concentrated solution and so water will enter the cell by
osmosis. This will make the cell swell up as its volume
increases. This continues until the cell wall prevents the
cell from expanding more. This state is called tugor and
• If red blood cells were placed in water they
would take in water by osmosis, swelling up
until they burst.
• The reverse will happen if the cells were
placed in a solution that was more
concentrated than the cytoplasm. Water
would leave the cell by osmosis and enter the
surrounding more concentrated solution. This
means that the cell contents would become
smaller as it loses liquid.
• When this happens to a plant cell the cell
membrane pulls away from the cell wall. This
causes the plant cell to lose its support. This
You might also like
- General Freight Trucking Business PlanDocument37 pagesGeneral Freight Trucking Business Planlorenneth67% (3)
- SHEPPARD Kenworth Medium Duty HD94 ALTERNATE Steering-Gear Bleed Procedure 2Document3 pagesSHEPPARD Kenworth Medium Duty HD94 ALTERNATE Steering-Gear Bleed Procedure 2Mas Inyeccion ElectronicaNo ratings yet
- Dubai Design CriteriaDocument36 pagesDubai Design CriteriaFranjo JohaNo ratings yet
- CVD SD Wan Design 2018octDocument31 pagesCVD SD Wan Design 2018octWebguru77No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter 3: Movement in & Out of CellsNabil Ahmed100% (1)
- Underground Coal Mining Methods - A ReviewDocument19 pagesUnderground Coal Mining Methods - A ReviewAryan AnandNo ratings yet
- Toyota Motor Manufacturing OM Group 8Document17 pagesToyota Motor Manufacturing OM Group 8Angshuman Sarkar50% (2)
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationLee KaiYangNo ratings yet
- IATA AirportDevelopmentReferenceManual Original PDFDocument732 pagesIATA AirportDevelopmentReferenceManual Original PDFraul11838028No ratings yet
- 3 - Movement in and Out of CellsDocument22 pages3 - Movement in and Out of CellsRashed Nada100% (1)
- Autonomous Cars (Lidar) Training ManualDocument89 pagesAutonomous Cars (Lidar) Training Manualjonte kimondio100% (1)
- Autonomous VehiclesDocument30 pagesAutonomous VehiclesAnil RV50% (4)
- Air Cargo Tracking SysteDocument25 pagesAir Cargo Tracking SysteGurkirat Singh SandhuNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellDocument6 pagesMovement in and Out of CellMahamudul HassanNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells 1Document10 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells 1saadNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cellsf8sdh6xvzyNo ratings yet
- Movement in and OutDocument35 pagesMovement in and OutzefanyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsDocument10 pagesChapter - 3diffusion in Living OrganismsBoney StephenNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport NotesDocument10 pagesCell Transport NotesReyad BarbarNo ratings yet
- Bio CH 3Document15 pagesBio CH 3SourabhiNo ratings yet
- MOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportDocument4 pagesMOvement in and Out of Cells - Osmosis & Active TransportTshepo O MotsemmeNo ratings yet
- 3.movement in & Out of Cells PDFDocument3 pages3.movement in & Out of Cells PDFAntrika YadavNo ratings yet
- Bio 100 - 2Document19 pagesBio 100 - 2Duain Areed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument3 pagesDiffusion and Osmosisshaniah100% (1)
- In and Out of CellsDocument3 pagesIn and Out of CellsA personNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument10 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsMoni VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Movement Into & Out of CellDocument27 pagesCh-3 Movement Into & Out of CellHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Cell Content 2Document34 pagesOsmosis and Cell Content 2Ñïà ǸìæNo ratings yet
- 3 Diffusion & OsmosisDocument27 pages3 Diffusion & OsmosisnasserkhanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis AND Active TransportScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- 04 NotesDocument6 pages04 NotesAirus SamaNo ratings yet
- Bio NotasDocument34 pagesBio NotasDhuhaa YusufNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2. Transport Across The Cell MembraneDocument48 pagesUNIT 2. Transport Across The Cell Membranemunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument31 pagesCell TransportjhabNo ratings yet
- Notes Movement in & Out of CellsDocument6 pagesNotes Movement in & Out of CellsddddddffdfdfNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument23 pagesCell Transport7104No ratings yet
- Movement Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMovement Across The Cell MembraneUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- 3.5.) Cellular Transport Processes (BIO40)Document17 pages3.5.) Cellular Transport Processes (BIO40)Mary Ferl Jasmin LupagueNo ratings yet
- CH 7.3 Cell TransportDocument19 pagesCH 7.3 Cell TransportRoen Grace Lapuz CalivosoNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationmefunNo ratings yet
- Osmosis, Diffusion PresentationDocument19 pagesOsmosis, Diffusion PresentationRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level Biology (5090) : Movement Into and Out of CellsDocument55 pagesCambridge O Level Biology (5090) : Movement Into and Out of CellsMoinuddin SummitNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport SystemDocument12 pagesCell Transport SystemHarold MangaNo ratings yet
- Movement of Particles NoteDocument2 pagesMovement of Particles NoteSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and OsmosisDocument2 pagesDiffusion and OsmosisMera FunportalNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis and Active TransportDocument18 pagesDiffusion Osmosis and Active TransportThompson Ta Ta JevonNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument3 pagesUntitled Documenttoro toroNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Across The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesDiffusion Across The Cell Membranetoro toroNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument40 pagesMovement in and Out of CellslubaajamesNo ratings yet
- Kaumaram Sushila International Residential School Grade:-9 IGCSE Sub: - Biology CHAPTER: - UNIT 3 NotesDocument10 pagesKaumaram Sushila International Residential School Grade:-9 IGCSE Sub: - Biology CHAPTER: - UNIT 3 NotesAkil BabujiNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Movement in and Out of The CellDocument10 pagesCH 3 Movement in and Out of The CellAmal HassanNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Powerpoint NotesDocument33 pagesCell Transport Powerpoint Notesapi-644325383No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Section 1-1Document31 pagesChapter 1 Section 1-1Akar AliNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport and HomeostasisDocument2 pagesCell Transport and Homeostasishomamunfat100% (1)
- Study Guide Cell TransportDocument2 pagesStudy Guide Cell TransportBobNo ratings yet
- Movement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Document12 pagesMovement Into and Out of Cells Objectives:3.1Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearDocument13 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion - 2nd YearFrancisco Samarco100% (1)
- Biologia - Cell Transport Reading and QuestionsDocument9 pagesBiologia - Cell Transport Reading and QuestionsMARLEN AVELLANEDANo ratings yet
- Water RelationDocument62 pagesWater RelationBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventDocument3 pagesOsmosis: Osmosis Is The Spontaneous Net Movement of SolventCHIEF VISHAAL 45No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument12 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsSamaira JainNo ratings yet
- Movement of Molecules Notes (Year 10 Biology)Document16 pagesMovement of Molecules Notes (Year 10 Biology)Janki patelNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutDocument3 pagesOsmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutizzahNo ratings yet
- Ch3 OL RevisionDocument11 pagesCh3 OL Revisionzuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of Cells NotesDocument9 pagesMovement in and Out of Cells Notesmanarehab35No ratings yet
- Biochem Laboratory Activity 2Document4 pagesBiochem Laboratory Activity 2Kristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Diffusion: Diffusion in Living OrganismsDocument12 pages3.1 Diffusion: Diffusion in Living OrganismsX GamerNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Powerpoint NotesDocument33 pagesCell Transport Powerpoint Notesapi-644325383No ratings yet
- Movement of SubstancesDocument25 pagesMovement of Substancesapi-305909325No ratings yet
- Tailfin 2022 Aeropack InstructionsDocument13 pagesTailfin 2022 Aeropack InstructionsIwak LemuNo ratings yet
- Bavarian Times Magazine - Edition 02 - May 2013Document68 pagesBavarian Times Magazine - Edition 02 - May 2013Bavarian Times MagazineNo ratings yet
- Commercial Law Case DigestDocument21 pagesCommercial Law Case DigestpacburroNo ratings yet
- RTD A Line Saturday Westbound ScheduleDocument2 pagesRTD A Line Saturday Westbound ScheduleRyan O'CoffeyNo ratings yet
- Yulu - Smart Shared Bicycles - TeaserDocument1 pageYulu - Smart Shared Bicycles - TeaserNi007ckNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Abdullah Mohammad IshfaqueDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Abdullah Mohammad IshfaqueAbdullah EhaanNo ratings yet
- Isuzu Q Series QKR55E, QKR55F, QKR55H, QKR77E, QKR77F, QKR77H Manual PDFDocument200 pagesIsuzu Q Series QKR55E, QKR55F, QKR55H, QKR77E, QKR77F, QKR77H Manual PDFMarce CristaldoNo ratings yet
- Tsymbal Umd 0117N 11885Document87 pagesTsymbal Umd 0117N 11885sofiakamranNo ratings yet
- HandbookDocument3 pagesHandbookbfoo_6No ratings yet
- RegsssDocument44 pagesRegsssPrerak Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- GeswarlalDocument6 pagesGeswarlalriteshNo ratings yet
- Codes StandardsDocument3 pagesCodes Standardsakshaf10No ratings yet
- Final Website News Flash 12-2021Document2 pagesFinal Website News Flash 12-2021api-583715685No ratings yet
- LCS at Litbang MoT - VfinalDocument33 pagesLCS at Litbang MoT - VfinalNurMazhariyaUlmiNo ratings yet
- CS100 - District1 - Sta Elena Marikina - Dimaano-A53Document21 pagesCS100 - District1 - Sta Elena Marikina - Dimaano-A53FELICITY MONTEFALCONo ratings yet
- OPNAV 3120.32C, Standard Organization and Regulations Manual of The U.S. NavyDocument23 pagesOPNAV 3120.32C, Standard Organization and Regulations Manual of The U.S. NavyLaurenz LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Return TicketDocument3 pagesReturn TicketSURAJ ROYNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Trial Kolej Tunku Kursiah PDFDocument6 pagesAnswer Scheme Trial Kolej Tunku Kursiah PDFNor Kamarul AshikinNo ratings yet
- Department Orders SummaryDocument15 pagesDepartment Orders SummaryLowie Torres TonioNo ratings yet