Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DC Motor
Uploaded by
SarahWaheedahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DC Motor
Uploaded by
SarahWaheedahCopyright:
Available Formats
SMJE 2103
DC Motors
DC Motor
Discussion topics:
1. Basic structure
2. Field circuit connections
3. Equivalent circuit
4. Induced torque
5. Terminal characteristics
6. Speed
DC Motor
- basic structure -
DC Motor
- field circuit connections -
shunt compound
Separate excitation
series
DC Motor
- equivalent circuit -
DC Motor
- equivalent circuit (separate)-
Separate
power supply
for field circuit
DC Motor
- equivalent circuit (shunt)-
Power supply for
field circuit
directly from
terminal
DC Motor
- equivalent circuit (series)-
DC Motor
- equivalent circuit (compound)-
long-shunt connection
DC Motor
- equivalent circuit (compound)-
Short-shunt connection
DC Motor
- induced torque (series)-
As the load increases, its flux increases and
proportional to armature current.
So, the motor decreases in speed.
A series dc motor has sharply drooping
torque-speed characteristic.
The application requiring very high torque,
such starter motor in cars, elevator motor etc.
DC Motor
- induced torque (compound)-
It has a component of flux in constant.
Also, another component in proportional to its
armature current.
So, higher starting torque than a shunt and
lower than a series motors.
DC Motor
- induced torque (compound)-
DC Motor
- terminal characteristics (separate/shunt)-
A plot of the machines output quantities
between torque and speed.
Load increase, load torque
load
will exceed
induced torque
ind
, the motor will start slow
down.
Internal generated voltage drops,
Armature current will increase,
Induced torque increases and equal to load
torque,
DC Motor
- terminal characteristics (separate/shunt)-
DC Motor
- terminal characteristics (separate/shunt)-
DC Motor
- terminal characteristics (series)-
DC Motor
- terminal characteristics (series)-
DC Motor
- terminal characteristics (compound)-
DC Motor
- speed (shunt) -
Two common methods:
1. Adjusting the filed resistance R
F
, then field
flux.
2. Adjusting the terminal voltage applied to the
armature.
Less common method:
1. Inserting a resistor in series with the
armature circuit.
DC Motor
- speed (shunt) -
R
F
changing
Voltage changing
DC Motor
- speed (shunt) -
DC Motor
- speed (series) -
The way how to change the speed of dc
motor.
By changing the terminal voltage of the motor.
If terminal voltage is increased, the speed will
increase for any given torque.
DC Motor
- speed (compound) -
Same as for a shunt motor
You might also like
- AC MotorsDocument52 pagesAC Motorsjennybunnyomg50% (6)
- EM ch-9 DC MOTORS AND GENERATORSDocument65 pagesEM ch-9 DC MOTORS AND GENERATORSmuhammad.anas2007No ratings yet
- DC MOTORS AND GENERATORS: TERMINAL CHARACTERISTICS AND SPEED CONTROLDocument15 pagesDC MOTORS AND GENERATORS: TERMINAL CHARACTERISTICS AND SPEED CONTROLptarwatkar123No ratings yet
- "DC Motors": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument23 pages"DC Motors": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion One: Chapter NineDocument15 pagesEnergy Conversion One: Chapter NineSneh Deep SKNo ratings yet
- Lab 3b PPT - Series MotorDocument23 pagesLab 3b PPT - Series MotorLiaqat AliNo ratings yet
- DC DrivesDocument38 pagesDC DrivesMariaNo ratings yet
- Compound MotorDocument17 pagesCompound MotorZeroziah NazatoNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - DC Motors PDFDocument22 pagesGroup 6 - DC Motors PDFRashen DilNo ratings yet
- SPE 2321 Lecture 3 & 4 and 5Document75 pagesSPE 2321 Lecture 3 & 4 and 5Martinez MutaiNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument25 pagesDC MotorDeandre LaingNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 BedcDocument61 pagesUnit 2 BedcASHISHNo ratings yet
- EM CH-4-5-6 Ac MachinesDocument80 pagesEM CH-4-5-6 Ac Machinesmuhammad.anas2007No ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument80 pagesDC MotorsRaja Desingu100% (1)
- Hev M2Document18 pagesHev M2Anandhu ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 DC MachinesDocument82 pagesChapter 4 DC MachinesShikoyeniNo ratings yet
- The Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsDocument6 pagesThe Advantages and Hazards of DC MotorsGalco IndustrialNo ratings yet
- DC MotorsDocument42 pagesDC MotorsArabella SanchezNo ratings yet
- "Series DC Motor/ Motor Efficiency": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsDocument12 pages"Series DC Motor/ Motor Efficiency": AV-222 Electromechanical SystemsSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Guide Electrical Motors 40 CharactersDocument20 pagesGuide Electrical Motors 40 Charactersrksamy0102No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Drive ChaacteristicsDocument26 pagesUnit Ii Drive Chaacteristicssaravanakmar vNo ratings yet
- Types of MotorsDocument12 pagesTypes of MotorsMatin Inamdar100% (1)
- Energy Savings in Air Compressors - by Incorporation of VFDDocument32 pagesEnergy Savings in Air Compressors - by Incorporation of VFDnikut_0777No ratings yet
- DC Motor Drives: Speed Control and Transient AnalysisDocument38 pagesDC Motor Drives: Speed Control and Transient Analysisblaze emberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document18 pagesChapter 5AndrewHaweNo ratings yet
- IDS NewDocument128 pagesIDS NewShahbaz Ali100% (1)
- Week 10Document24 pagesWeek 10M. HamzaNo ratings yet
- Ayush Kashyav Professional PracticeDocument21 pagesAyush Kashyav Professional PracticeDEZ Automation And ControlNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 SSDDocument85 pagesUnit - 2 SSDAkshat SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Separately Excited DC Motor ExplainedDocument3 pagesSeparately Excited DC Motor ExplainedMaitri ShahNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Block DiagramDocument29 pages1.3 Block DiagramAlphaBravoNo ratings yet
- DC Machine Fundamental ExplainedDocument31 pagesDC Machine Fundamental Explainedahtisham shahNo ratings yet
- Servo-Motor: Batch 7: Mouli R N Nagaaswin N Naveen K Nilesh Ram Praveen K Nirmal Kumar SDocument27 pagesServo-Motor: Batch 7: Mouli R N Nagaaswin N Naveen K Nilesh Ram Praveen K Nirmal Kumar SThameem AbbasNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed System Modeling (Final Report)Document41 pagesDC Motor Speed System Modeling (Final Report)Khubaib Ahmed80% (5)
- MoappDocument5 pagesMoappluanleNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of DC Series MotorDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of DC Series MotorMohammed AlhakeemiNo ratings yet
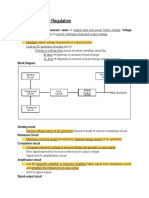
- Module 11: Voltage RegulatorsDocument4 pagesModule 11: Voltage RegulatorsChristian AganoNo ratings yet
- EE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocument10 pagesEE 306 - Electrical Engineering LaboratoryMohammed KhouliNo ratings yet
- DC Motor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesDC Motor - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008No ratings yet
- Guerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)Document22 pagesGuerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)John Nichol GuerraNo ratings yet
- AGK - Electrics 16 DC Motors 16 S2Document16 pagesAGK - Electrics 16 DC Motors 16 S2Cemalettin öztoprakNo ratings yet
- Electric Motors: - Classification / TypesDocument24 pagesElectric Motors: - Classification / TypesBholendra ShakarNo ratings yet
- DC Motors Introduction, Equivalent Circuit, TypesDocument25 pagesDC Motors Introduction, Equivalent Circuit, Typesmuhammadarsalank01No ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Machines - Three-Phase Induction MotorsDocument20 pagesElectrical Power and Machines - Three-Phase Induction MotorsDhanis Paramaguru100% (1)
- Types of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesDocument77 pagesTypes of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesJyothish VijayNo ratings yet
- Features of Rotating MachinesDocument17 pagesFeatures of Rotating MachinesAngelu TarvenaNo ratings yet
- Sigma Institute of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Bakrol, VadodaraDocument52 pagesSigma Institute of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Bakrol, VadodaraBhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- DC Motors and Generators Chapter # 9Document13 pagesDC Motors and Generators Chapter # 9SamiNo ratings yet
- Chaapter 5 DC MotorDocument43 pagesChaapter 5 DC MotorvipularunpatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument40 pagesChapter 4 PDFbroNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Paper PresentationDocument11 pagesElectrical Machines Paper PresentationsweetupriyaNo ratings yet
- EE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsDocument10 pagesEE 448 Laboratory Experiment 4 Introduction To DC MotorsjegjegtNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseFrom EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseNo ratings yet
- Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkFrom EverandAdvanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB / SimulinkNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Solution of Exercise 12Document1 pageSolution of Exercise 12SarahWaheedahNo ratings yet
- Discrete Time Signals and SystemsDocument58 pagesDiscrete Time Signals and SystemsSarahWaheedahNo ratings yet
- Week11 Exercise SolutionDocument2 pagesWeek11 Exercise SolutionSarahWaheedahNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Exercises Week13Document2 pagesSolutions of Exercises Week13SarahWaheedahNo ratings yet
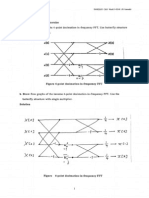
- Discrete Fourier TransformDocument9 pagesDiscrete Fourier TransformSarahWaheedahNo ratings yet
- Power QualityDocument28 pagesPower QualitySarahWaheedahNo ratings yet
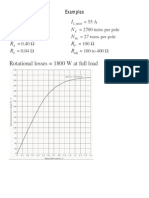
- Examples of DC MotorDocument7 pagesExamples of DC MotorSarahWaheedahNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current Type 1Document19 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current Type 1RandomNo ratings yet
- 3.07 Moments and LeversDocument33 pages3.07 Moments and LeversMohab MqattashNo ratings yet
- Activity01 (1) CarreonDocument14 pagesActivity01 (1) CarreonHaja Kiev Erenz CarreonNo ratings yet
- Brake Torque Application DataDocument0 pagesBrake Torque Application Dataellie210879No ratings yet
- Cam and ValveDocument13 pagesCam and ValveTi PiccoliNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Physics Part 1 2023Document3 pagesPre Board Physics Part 1 2023Kamran AliNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Moment of InertiaDocument12 pagesEquivalent Moment of InertiaYasiru KaluarachchiNo ratings yet
- Physics XIDocument124 pagesPhysics XIQulb e AbbasNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine and Governor (SimPowerSystems)Document5 pagesSteam Turbine and Governor (SimPowerSystems)hitmancuteadNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument2 pagesAnalysisJosef CatiggayNo ratings yet
- Design calculation-G.M.maitraDocument15 pagesDesign calculation-G.M.maitraAnuj ShahNo ratings yet
- Lab #7 - Joint Kinetics and Internal Forces: PurposeDocument12 pagesLab #7 - Joint Kinetics and Internal Forces: PurposeChristian VitaliNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Mshimizu WebDocument156 pagesCatalogo Mshimizu WebMauro S CabralNo ratings yet
- Servomotors NX Series: Technical Manual PVD 3663Document92 pagesServomotors NX Series: Technical Manual PVD 3663قناتيNo ratings yet
- A Text Book of Physics (C.R. Dasgupta) (Z-Library)Document760 pagesA Text Book of Physics (C.R. Dasgupta) (Z-Library)toffee9soumavaNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Testing of I.C.EnginesDocument18 pagesMeasurements and Testing of I.C.EnginespriyankarNo ratings yet
- Rotation of A Rigid Body (8 Hours)Document21 pagesRotation of A Rigid Body (8 Hours)Nur Farhana SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- A Compact Rotary Series Elastic Actuator For HumanDocument11 pagesA Compact Rotary Series Elastic Actuator For HumanJhon Michel Diaz LozanoNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope Theory of MachinesDocument33 pagesGyroscope Theory of Machinesadel audayNo ratings yet
- Physics - Syllabus PDFDocument67 pagesPhysics - Syllabus PDFPugazh ArasuNo ratings yet
- Additional Numericals in Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesAdditional Numericals in Fluid MechanicsTshiring RaiNo ratings yet
- BR Cat VF-W STD Eng r07 1Document268 pagesBR Cat VF-W STD Eng r07 1Brian LeslieNo ratings yet
- Asae S296Document5 pagesAsae S296Ricardo GarciaNo ratings yet
- NC JaganDocument494 pagesNC JaganSean Zimmerman100% (3)
- E-Series Torque Multiplier Instruction SheetDocument76 pagesE-Series Torque Multiplier Instruction SheetMAMI RAKOTOMAHANINANo ratings yet
- Understanding Moment of Force and EquilibriumDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Moment of Force and EquilibriumProteep MitraNo ratings yet
- pDRIVE Basic MXDocument33 pagespDRIVE Basic MXThang VuNo ratings yet
- The Problems2Document2 pagesThe Problems2angelNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force HandoutDocument28 pagesAP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force HandoutmoonidiveNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HoursDocument9 pagesMechanics Ii Time Allowed: 2 HourssubipuruNo ratings yet