Professional Documents
Culture Documents
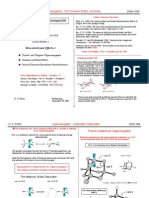
How Does This Center Control The Direction of Attack at The Trigonal Carbon?
Uploaded by
Ravichandran MohanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Does This Center Control The Direction of Attack at The Trigonal Carbon?
Uploaded by
Ravichandran MohanCopyright:
Available Formats
Crams Rule
C X
*
diastereomeric
faces
X = C, O, N
stereogenic
center
How does this center control
The direction of attack at
The trigonal carbon?
R
M
S
L
O
L
R N u
O H
M
S
L
N u R
O H
M
S
Nu:
Less steric effects
Major product
Nu:
Minor product
O
M S
R
L
R
M
S
L
O
L
M
S
R
O
L
S
M
R
O
This is the important
interaction that must be
minimized. Thus, in this
approach the carbonyl
substituent plays the major
role.
Favored Conformer
for Attack
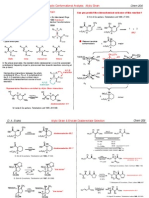
The interpretation of Felkin and Anh
Brgi-Dunitz
trajectory
109
Obtuse attack trajectory
minimizes unfavorable
interactions between these
orbitals
C O
R
M
L
S
s
p *
N u
Houk computational view:
The obtuse angle of attack supports the nonpassive role of the
R-group in ketones. Not only will there be steric interactions
between the S or M groups and the R-group, but also interactions
with the incoming nucleophile due to the attack trajectory. In this
model one would predict an increase of stereodifferentiation as the
size of R increases. This has been found experimentally
O
O
R R
Preferred conformation.
Less interaction between
the small group and the
R-group. Note that this
model "feels" the influence
of increasing size of R.
In this coformer, an
increased interaction
is seen between the
medium group and R.
Also, there is more
interaction with the
nucleophile.
A useful orbital approach by Cieplak
,
suggests that the nucleophile
will attack the carbonyl anti to the best donor ligand.
A.S. Cieplak, B.D. Yait and C.R. Johnson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., (1989), 111, 8447
A.S. Cieplak, J. Am. Chem. Soc., (1981), 103, 4548.
D o n o r
O
s
*
of nucleophile
Carbon
donor
s -bond
Nu:
E
Cases for Modification of the Models
Compare the "normal" situation with the influence of
a sterically bulky Lewis acid
L
S
M
O
H
O
H
S
M
L
Lewis acid
Nu:
As the bulk of the
Lewis acid increases
Lewis acid
:Nu
This gives the
Cram product
This gives the
"anti-Cram" product
Dipolar Model
often described as the Cornforth model
R'
R
H
Cl
R"M
R'
R
H
Cl
OH
R" O
Preferred direction
of attack.
favored conformer
S
X
L
O
R
X
L
S
O
R
Chelation Control
See: M.T. Reetz, Acc. Chem. Res., (1993), 26, 462.
R
L
S
H e t
O
M
Preferred
direction
of attack
Het = heteroatom
M = metal
L
S
H e t
O
R
M
O
Ti
O
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
H
Me
R
Ph
O
S
O
S
Me
Me
Me
Me
Me
Me
Ph
Ph
O
O
Mg
Me
I
MeMgI H
3
O
+
Predict a product from the following
reaction
A potentially useful extension of Cram's rule is the asymmetric
induction provided by a remote ester (Prelog's rule):
R
O
L
O
O
S
M
R'MgX
Why would you think this might not provide as
important directing influences?
Explain the following trends observed by Midland and coworkers
M.M. Midland and Y.C. Kwon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1983), 105, 3725.
H
M e
O
M e
H
M e
M e
O H
H
H
M e
M e
H
O H
H
H
H
N a B H
4
S i a
2
B H
G
G
5
:
1
1
:
10
Ratio
You might also like
- Chemistry - Harvard's Advanced Organic Chemistry 2003Document717 pagesChemistry - Harvard's Advanced Organic Chemistry 2003ramik100% (23)
- Naming and Drawing Alkenes Worksheet and KeyDocument6 pagesNaming and Drawing Alkenes Worksheet and Keyhaniiman100% (1)
- Asymmetric SynthesisDocument55 pagesAsymmetric Synthesisevsgoud_goud0% (1)
- Stereochemistry MSCDocument29 pagesStereochemistry MSCBapu Thorat50% (2)
- Hyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. EvansDocument12 pagesHyperconjugation, The Anomeric Effect, and More: Chem 206 D. A. Evansomkar9996767No ratings yet
- Learning Spanish EbookDocument23 pagesLearning Spanish EbookDonnette Davis100% (10)
- OC Stereoisomerism EDocument60 pagesOC Stereoisomerism EJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- D. A. Evans and F. Michael - An Introduction To Frontier Molecular Orbital Theory-1Document8 pagesD. A. Evans and F. Michael - An Introduction To Frontier Molecular Orbital Theory-1Nuansak3No ratings yet
- NMR HandoutDocument23 pagesNMR HandoutVirendra Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Cram's RuleDocument13 pagesCram's RulePablo Romo ValdesNo ratings yet
- Cram's RuleDocument13 pagesCram's Rulemanurihimalsha0% (1)
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Fang GaoNo ratings yet
- Allylic StrainDocument18 pagesAllylic StrainRahn NaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture 8 PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Agostic Bani Seminar2Document47 pagesAgostic Bani Seminar2Arif SajjadNo ratings yet
- Thermal Dissociation and Recombination of Polyatomic MoleculesDocument14 pagesThermal Dissociation and Recombination of Polyatomic Moleculescoolatuber1No ratings yet
- Hyper ConjugationDocument29 pagesHyper ConjugationDargorlethNo ratings yet
- Detonation DiffractionDocument8 pagesDetonation Diffractioninvscd123No ratings yet
- Theory and Application Voltammetry Measurement of Electrode Reaction KineticsDocument5 pagesTheory and Application Voltammetry Measurement of Electrode Reaction KineticsJubin KumarNo ratings yet
- Teoria y Aplicacion de A CiclicaDocument5 pagesTeoria y Aplicacion de A CiclicaMAVERICK_HUNTER1234936No ratings yet
- Some Properties and Trends of EnthalpiesDocument8 pagesSome Properties and Trends of EnthalpiesangelNo ratings yet
- W. MCF - L/Rlt/Se (Received June 1St. 1965)Document8 pagesW. MCF - L/Rlt/Se (Received June 1St. 1965)Shailendra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Molecular OrbitalsDocument123 pagesMolecular Orbitalsel ioiosxdxdxdxzdNo ratings yet
- The Principle of Least Nuclear Motion ExplainedDocument61 pagesThe Principle of Least Nuclear Motion ExplainedBiswarup DasNo ratings yet
- Frick Chemical Laboratory contribution on dipole momentsDocument14 pagesFrick Chemical Laboratory contribution on dipole momentsAnonymous FigYuONxuuNo ratings yet
- Mona SCH YfytitycDocument7 pagesMona SCH YfytitycJeevananthan S P KannanNo ratings yet
- Laurence E. Fried and Gregory S. Ezra - Generalized Algebraic Quantization: Corrections To Arbitrary Order in Planck's ConstantDocument11 pagesLaurence E. Fried and Gregory S. Ezra - Generalized Algebraic Quantization: Corrections To Arbitrary Order in Planck's ConstantOmasazzNo ratings yet
- Li6 N Alpha TriitumDocument2 pagesLi6 N Alpha TriitumPanchapakesan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 06 Conformational Anal 3Document13 pages06 Conformational Anal 3eraborNo ratings yet
- Stereoisomerization and Homolytic Decomposition of Cis and Trans Bridgehead Diazenes1 2Document10 pagesStereoisomerization and Homolytic Decomposition of Cis and Trans Bridgehead Diazenes1 2Nabil KhalidNo ratings yet
- Critical Behavior of Repulsively Interacting Particles Adsorbed On Disordered Triangular LatticesDocument7 pagesCritical Behavior of Repulsively Interacting Particles Adsorbed On Disordered Triangular LatticesMarcelo PerarnauNo ratings yet
- 05 Conformational Anal 2Document11 pages05 Conformational Anal 2Swati GautamNo ratings yet
- Thompson PDFDocument50 pagesThompson PDFYudi FernandezNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NMR NotesDocument160 pagesOrganic Chemistry NMR NotesMaximilian Müller100% (1)
- Lorentz and CPT Violation in The Neutrino SectorDocument4 pagesLorentz and CPT Violation in The Neutrino SectornayantharaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Isotope Effect in Organic ChemistryDocument28 pagesKinetic Isotope Effect in Organic ChemistryMaximiliano DelahigueraNo ratings yet
- Design of Chimes To Produce Consonant, Non-Harmonic Scales: Arthur GrettonDocument6 pagesDesign of Chimes To Produce Consonant, Non-Harmonic Scales: Arthur GrettonMJSwayNo ratings yet
- 5P Stereochemistry Part 5 1Document18 pages5P Stereochemistry Part 5 1Shivaneshwari ArumugamNo ratings yet
- NSB Round 3Document10 pagesNSB Round 3Xyril GalendezNo ratings yet
- Resonance in FormamideDocument7 pagesResonance in FormamideRodrigo YepsenNo ratings yet
- BGK Collision ModelDocument15 pagesBGK Collision ModelVineeth MaxxNo ratings yet
- Observation of Multiple Thresholds in The Cavity QED MicrolaserDocument4 pagesObservation of Multiple Thresholds in The Cavity QED MicrolasercfangyenNo ratings yet
- M Topics: Chapters 5-9 ReviewDocument10 pagesM Topics: Chapters 5-9 Reviewbluemoon4777No ratings yet
- Chapter04 OxidationdDocument46 pagesChapter04 OxidationdWilliam H. BasingerNo ratings yet
- Silicon Etching With KOHDocument9 pagesSilicon Etching With KOHTito Winnerson SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Chem 481 C 14Document6 pagesChem 481 C 14Bayram KarahanNo ratings yet
- S Trogat Z 1991 StabilityDocument23 pagesS Trogat Z 1991 StabilitypastafarianboyNo ratings yet
- Theories of Chemical KineticsDocument9 pagesTheories of Chemical KineticsJazzel Queny ZalduaNo ratings yet
- Lotte Holmegaard Et Al - Control of Rotational Wave-Packet Dynamics in Asymmetric Top MoleculesDocument4 pagesLotte Holmegaard Et Al - Control of Rotational Wave-Packet Dynamics in Asymmetric Top MoleculesMddl2aNo ratings yet
- Eric O. Morano and Joseph E. Shepherd - Effect of Reaction Periodicity On Detonation PropagationDocument4 pagesEric O. Morano and Joseph E. Shepherd - Effect of Reaction Periodicity On Detonation PropagationNikeShoxxxNo ratings yet
- Numerical Study of The Detonation Wave Structure in Et Hylene-Oxygen MixturesDocument7 pagesNumerical Study of The Detonation Wave Structure in Et Hylene-Oxygen MixturesBananaliksNo ratings yet
- 257 289Document33 pages257 289Sveti JeronimNo ratings yet
- Quantifying Chaos in Lorenz 63 ModelDocument9 pagesQuantifying Chaos in Lorenz 63 ModelVAIBHAV ahirNo ratings yet
- NMR Lecture 4 Chemical ShiftDocument15 pagesNMR Lecture 4 Chemical ShiftAnselmo Mtz GagosNo ratings yet
- Energy States of MoleculesDocument12 pagesEnergy States of MoleculesBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- Use of Isotopes For Studying Reaction Mechanisms: - JU-n-e-1-9-9-7 - 4-7Document7 pagesUse of Isotopes For Studying Reaction Mechanisms: - JU-n-e-1-9-9-7 - 4-7Ab AbNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesOrganic ChemistrySundaram ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Molecules 24 02822Document12 pagesMolecules 24 02822Aman AmanNo ratings yet
- Application of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry: International Series in Organic ChemistryFrom EverandApplication of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry: International Series in Organic ChemistryRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Mathematical Modeling and Physical Reality in Noncovalent InteractionsDocument30 pagesMathematical Modeling and Physical Reality in Noncovalent Interactionsnisa fitri andriyantiNo ratings yet
- FtirDocument3 pagesFtirRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- PEM Water Electrolysis-Fundamentals Prof. TsiplakidesDocument37 pagesPEM Water Electrolysis-Fundamentals Prof. TsiplakidesRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- Needle ValvesDocument38 pagesNeedle ValvesRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- Sampling CylindersDocument14 pagesSampling CylindersRavichandran Mohan100% (1)
- Catalog Sample BootleDocument4 pagesCatalog Sample BootleRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar ElectrolysisDocument19 pagesBipolar ElectrolysisRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- Water ElctrolysisDocument4 pagesWater ElctrolysisRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- Section 11Document16 pagesSection 11Shanna GarciaNo ratings yet
- 4-pH METERDocument3 pages4-pH METERRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- Home Made Medecine For CancerDocument2 pagesHome Made Medecine For CancerRavichandran MohanNo ratings yet
- Photochemistry RevisedDocument41 pagesPhotochemistry RevisedRSLNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument22 pagesIsomerismShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Class: Xi Inorganic Chemistry DPP. NO.-9Document2 pagesClass: Xi Inorganic Chemistry DPP. NO.-9Radhika MohataNo ratings yet
- L1-L3 StereochemistryDocument64 pagesL1-L3 Stereochemistryvanwani.mozeelNo ratings yet
- (David Morris) Stereochemistry Tutorial Chemistry PDFDocument182 pages(David Morris) Stereochemistry Tutorial Chemistry PDFAditya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Conformational analysis of cycloalkanesDocument30 pagesConformational analysis of cycloalkanesNimra MalikNo ratings yet
- Organic Isomers Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesOrganic Isomers Multiple Choice QuestionsrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Conformations and Strains of Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument92 pagesConformations and Strains of Alkanes and CycloalkanesMutia HadiyantiNo ratings yet
- IIT Bombay Organic Chemistry End-Semester ExamDocument2 pagesIIT Bombay Organic Chemistry End-Semester ExamRutul JainNo ratings yet
- Organic Stereochemistry Practice ProblemsDocument7 pagesOrganic Stereochemistry Practice Problemsserenity1290100% (1)
- Problems in IsomerismDocument5 pagesProblems in IsomerismAt Tanwi100% (1)
- LG 1.5 Isomerism Part II (Stereoisomerism)Document10 pagesLG 1.5 Isomerism Part II (Stereoisomerism)wangmorisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - StereochemistryDocument82 pagesChapter 2 - StereochemistryMELVINDO JACOBNo ratings yet
- 6417 Topper 21 129 510 2 8532 Isomerism Up201612091817 1481287659 483 PDFDocument41 pages6417 Topper 21 129 510 2 8532 Isomerism Up201612091817 1481287659 483 PDFMd Waquar SalisNo ratings yet
- Organic - Class 7Document27 pagesOrganic - Class 7Sajan Singh LUCKYNo ratings yet
- RS Configuration DL NomenclatureDocument9 pagesRS Configuration DL NomenclatureDanny юрьевич Usvyat50% (2)
- Ch. 11 Review Power Point CHEM 180Document15 pagesCh. 11 Review Power Point CHEM 180Muhammad Nazif AzmiNo ratings yet
- Vsepr ChartDocument2 pagesVsepr Chartapi-239855791No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document20 pagesChapter 4Simran Saiinii0% (1)
- Chapter05 Smith3e PPTDocument57 pagesChapter05 Smith3e PPTLuisa Palomo100% (1)
- CH 7 - Isomer TypesDocument4 pagesCH 7 - Isomer Typesharshm_39No ratings yet
- Optical IsomerismDocument12 pagesOptical IsomerismgcantaluppiNo ratings yet
- Isomerism and Stereochemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDocument15 pagesIsomerism and Stereochemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDana CapbunNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry (2.1, 2.2)Document12 pagesStereochemistry (2.1, 2.2)VIGHNESH BALKRISHNA LOKARENo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry 1Document97 pagesStereochemistry 1Babi Kumar KafleNo ratings yet
- Absolute Configuration RSDocument13 pagesAbsolute Configuration RSSubhasish SauNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry FBM 2014 May 1 Baskar PDFDocument18 pagesStereochemistry FBM 2014 May 1 Baskar PDFatulbakshimickey100% (1)
- Stereochemistry Notes For CHM 102Document4 pagesStereochemistry Notes For CHM 102faborodeharyomideNo ratings yet