Exploring Greenhouse Structures
Warm Up
What building material can you recognize in this
photo?
�Essential Question
What are the common greenhouse designs?
�Common Green House
Designs
4 Common designs
Lean-to
Even-Span
Uneven-Span
Ridge and Furrow
�Lean-to Greenhouse
shares a wall with a building and relies on the
building structure to provide some support for
the greenhouse roof.
�Even-span Greenhouse
Single houses that have roofs with an even pitch and
an even width.
Hoop House/Quonset: common even-span greenhouse
that uses arching pipes for the framework
�Uneven-Span Greenhouse
Have unequal pitches and widths.
Limited to hillside use
Rarely Built
�Ridge and Furrow
Greenhouse
Structures consist of
a number of
greenhouses
connected along the
length of the house.
Shared interior walls
reduce energy costs
and allow for large
interior spaces.
Best oriented north
and south to reduce
permanent shadows on
the crops created by
the gutters.
�Types of
Greenhouses
Expanded
�Greenhouse Framework
Supports the greenhouse
covering material
Should be:
Strong, allow for
maximum amount of light
to enter, require little
maintenence
Aluminum is most popular
Other materials include
wood, steel, angle iron
�Greenhouse Covering
Covering= glazing
Considerations
Durable, light transmission, cost, heating
effectiveness
Possible materials
Polyethylene
Stretched over greenhouse framework, cheap, not
durable, not expensive
Structured
sheets
polycarbonate, acrylic, and fiberglass materials have
grown in popularity. Multi sheets= good insulation
�Structured Sheets
Polycarbonate structured sheets
most widely used, good light transmission, resist
hail damage, easy to work with
Acrylic structured sheets
high light transmission, costly, prone to hail
damage, and are less flexible
Fiberglass
discolors after 7 to 10 years, is flammable,and
provides poor insulation
�Glass
Considered best greenhouse glazing (covering)
material
Highest light transmission
Long lasting
�Headhouse
Attached to the greenhouse
Used as a storage area, a potting area, an office,
and/or a shipping area.
�Retractable Roof
Greenhouses
Designs allow the roof to be opened and closed.
Gives plants protection from weather when needed
Reduced watering, rainwater can be used
�Greenhouse Benches
Holds the plants above the ground.
Materials include:
galvanized steel, aluminum, plastic, and rot
resistant wood.
Arranged in greenhouse with aisle space to walk
Rolling Benches:
movable bench used to maximize growing space by
limiting space for aisles
benches are placed on pipes, which allows them to
be easily moved from side to side.
�Rolling Bench
�Vocabulary
�Activities
Review Quiz 1
Go over Review Quiz
Hand out project worksheet
�Controlling Greenhouse Climate
�Warm Up
Why is this plant wilting? What does wilting
mean?
�Essential Question
What are the common greenhouse climate control
systems?
�Heating
Hot water heat system
heating water in a boiler and pumping the hot water
through pipes located in the greenhouse located
under benches, low maintenance, even heat
Steam heat
boilers that bring water to a boil and the resulting
steam flows through pipes in the greenhouse
�Heating
Unit heaters
heat air within the unit, then blow the air
throughout the greenhouse. Polyethylene tubes
evenly distribute air flow, cost more to operate
Infrared heat systems
produce heat energy that is absorbed by the
plants, media, and benches, do not heat the air,
suited for high greenhouses
�Cooling
Fan and pad cooling system
Number 1 system, based on evaporation of water,
pads at one end of the house are kept wet, fans at
the other end of the house pull air through the
pads. Air entering the house is cooled as water in
the pads evaporates.
�Cooling
Fog systems
involve an atomizer
that produces water
vapor, flash
evaporation of this
water cools the
greenhouse.
Vents
consist of panels that
open and allow air
exchange with the
outside, Natural
cooling
�Energy Curtain
Automated systems using fabrics that can
insulate a greenhouse at night and shade the
crops during the day
Installed gutter to gutter, run by computers
Short-day curtains
Similar to energy curtains, provides darkness that
will simulate a short-day effect.
�Climate Control Systems
Environmental controls
Devices used to turn greenhouse systems on and
off, including heating and cooling systems.
Includes:
Thermostats
Analog
controls
Computer controls
Computerized environmental management systems
�Climate Control Systems
Thermostats are low cost, easy to install
environmental controls.
On-off thermostats control fans, heaters, and
vents with the change of temperatures.
Analog controls use proportioning thermostats to
run amplifiers and electronic circuitry.
heating and cooling operations are integrated
resulting in better performance
�Climate Control systems
Computer controls use microprocessors to make
complex judgments based on information from a
number of sensors.
Computerized environmental management
systems, although expensive, are accurate and can
control all the automated systems together.
�Vocabulary
Analog controls
Computer controls
Computerized environmental
management systems
Energy curtains
Environmental controls
Fan and pad cooling system
Fog system
Hot water heat system
Infrared heat system
Polyethylene tubes
Short-day curtains
Steam heat
Thermostats
Unit heaters
Vents
�Activities
Represent Heating and Cooling and Systems
Draw them on a separate piece of paper from your
notes. This will be turned in.
Review Quiz 2
Go over Review Quiz
�Automated Greenhouse Systems
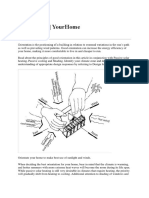
�Warm Up
What does this machine do? Why is it convenient?
�Essential Question
What are some advantages of automated
systems?
�Automated Systems
Incorporate technological developments in the
production of greenhouse crops.
Automated systems cut down labor costs
Automated systems allow for larger crops
�Automated SystemsPlanting
Automated pot fillers
used to fill pots with medium, medium is lightly
packed, and the pots are stacked or move down a
conveyor for planting.
Automated seeders
permit the sowing of entire flats or plug trays in a
few moments, trays move down a conveyor to a
germination room or move to the greenhouse
Automated transplanters
remove small plants from plug trays and transplant
them directly to pots.
�Automated SystemsTransporting
Transporting= most labor intensive part
Conveyor belt systems are used to move plants
from one area of the greenhouse to another.
Tray mechanization, has grown in popularity in
the U.S.
Individual trays or palletized benches that hold 100
pots or more roll on a series of rails from one area
to another.
�Automated Systems:
Watering
Spaghetti tubing
Automated system
that involves small
tubes connected to a
main line
End of each small tube
is placed in a pot, and
when functioning,
dribbles water onto
the medium.
Allows flowers and
foliage to stay dry
�Automated : Watering
Drip irrigation
a system like spaghetti
tubing
differs = provides a
slow steady drip
Used with hanging
baskets
Wastes less !!
�Automated: Watering
Ebb and flood
Watering involves watertight benches in which
pots are set
Water or nutrient solutions are pumped into the
bench, the medium absorbs the water, and the
water drains away.
Little water loss, nutrient levels are easily
adjusted, plant foliage kept dry
�Automated: Watering
Capillary mats
consist of porous
mats placed on a
bench and wetted.
The medium in the
pots absorbs the
water through
capillary action.
Foliage stays dry,
high humidity
provided
�Automated: Watering
Irrigation booms
Move across the
entire bench and
well-placed nozzles
flood the pots below
as they pass over the
plants
Commonly used with
bedding plants, plug
trays, and some
potted flowering
crops.
�Automated: Watering
Overhead sprinklers
Stationary sprinkler heads placed throughout the
growing space
Large amount of water in a short period of time
Often used with bedding plants.
�Automated: Watering
Intermittent mist
systems
Produce tiny droplets
in the air for the
purpose of keeping
plant material wet
Commonly used in the
propagation phase of
production to reduce
water stress on
cuttings
Continuous or
programmed times
�Vocabulary
Automated pot fillers
Automated seeders
Automated transplanters
Capillary mats
Conveyor belt system
Drip irrigation
Ebb and flood
Intermittent mist system
Irrigation booms
Overhead sprinklers
Spaghetti tubing
Tray mechanization
�Activities
Research Project
1 page SINGLE space paper, size 12 font, times new
roman or comic sans
Which automated watering system is the best and
why?
Review Quiz 3
Go over Review Quiz
�Managing a Greenhouse Business
�Warm Up
What types of jobs are conducted in a
greenhouse?
�Essential Question
What are the types of greenhouse businesses?
�Greenhouse Businesses
3 categories
Specialty Growers
Wholesale Growers
Retail Growers
�Specialty Growers
Produce crops sold to wholesale or retail
greenhouse growers
Specialize in one, or multiple crops
Can specialize in:
Rooted cuttings
Seed production
Bulbs for forcing
�Wholesale Growers
Produce a limited number of crops
Can Produce
Cut roses
Foliage Plants
Potted flowering plants
Products are sold to retail stores
�Retail Growers
Generally produce a variety of crops sold directly
to the public through their own retail outlet.
�Common Costs
Direct materials costs
those costs including plant materials, pots,
chemicals, and growing media.
Direct labor costs
based on production activities such as planting
crops, spacing crops, watering and fertilizing crops
and managing pests and diseases.
�Common Costs Continued
Overhead costs
do not have a direct impact on the production of
the crops.
heating fuel, office management and secretarial support,
taxes, depreciation, insurance, and utilities
Marketing costs
associated with advertising, packaging products,
shipping, and billing.
�Career Opportunities
Greenhouse Manager
responsible for the total greenhouse operation
Grower
charge of the day to day tasks involved in producing
one or more crops.
Marketing managers
sell the crops
Shipping room manager
handling a crop from the time it leaves the
greenhouse until it is shipped.
�Skills Required
Understand crops and how to care for them
Mechanical Skills
Understand the market
Deliver plants in a healthy state
Administrative Skills
Good understanding of local, state, and national
laws pertaining to plant growing, sale, and
transport
�Direct labor costs
Direct materials costs
Greenhouse manager
Grower
Marketing costs
Marketing manager
Overhead costs
Production manager
Propagator
Retail growers
Shipping room manager
Specialty growers
Wholesale growers
Vocabulary
�Activities
Review Quiz 4
�Vocabulary
Analog controls
Computer controls
Computerized
environmental
management systems
Energy curtains
Environmental controls
Fan and pad cooling
system
Fog system
Hot water heat system
Infrared heat system
Polyethylene tubes
Short-day curtains
Steam heat
Thermostats
Unit heaters
Vents
Automated pot
fillers
Automated seeders
Automated
transplanters
Capillary mats
Conveyor belt
system
Drip irrigation
Ebb and flood
Intermittent mist
system
Irrigation booms
Overhead sprinklers
Spaghetti tubing
Tray mechanization
Direct labor costs
Direct materials costs
Greenhouse manager
Grower
Marketing costs
Marketing manager
Overhead costs
Production manager
Propagator
Retail growers
Shipping room manager
Specialty growers
Wholesale growers
�Growing Potted Flowering Plants
�Warm Up
�Essential Question
What is one important aspect to keep in mind
while growing flowering potted plants?