Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
Heat loss calculation
Standard CSN EN 12831 Method for calculation of the design heat load
Assignment 4
Design heating system in two variants. Design local heating system equipped with local boiler in
your flat as first variant and central system for entire building as second variant.
Working steps:
1) Calculate total design heat load for all rooms in your flat at first floor. Use the simplified
method from CSN EN 12831.
2) Calculate total heat losses of entire building. Use the envelope method.
3) Design of heat emitters in your flat according to results from step 1.
4) Prepare local heating system. Draw plan of the system. This is the first variant.
5) Calculate pressure drop of main branch. Design proper pump. Update plan of local heating
system due to calculation results (dimensions).
6) Draw ground floor and first floor plans and section of central heating system. This is the
second variant.
7) Design central boiler in the boiler room. Use results from envelope method (step 2).
8) Draw plan and scheme of boiler room.
9) Calculate expansion vessel and pressure relief valve.
10) Calculate heating and hot water annual energy consumption of the whole building.
TEXT PART
Total design heat load calculation all rooms in your flat (Heat loss-Example, tables)
Total heat loss calculation - whole building, simple envelope method
Heat emitters design entire flat (Heat emitters design), (Heat emitters design-example)
Calculation of pressure drop of main branch in local heating system, design of pump
(variant 1).
Design of central boiler - variant 2.
Calculation of expansion vessel and pressure relief valve - variant 2.
Calculation of annual energy consumption - variant 2.
DRAWINGS
Plan of your flat with local heating system variant 1. (Heating system-flat_A , Heating
system-flat_B)
Plan of your flat with central energy source variant 2
Plan of ground floor with central heating system variant 2
Section of central heating system variant 2
Plan and section of boiler room variant 2
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
SIMPLE METHOD (residential buildings only)
TOTAL DESIGN HEAT LOSS
DESIGN TRANSMISSION HEAT LOSS
e.external air temperature (C). Czech Republic -12, -15, -18C
CSN 730540 Heat transfer coefficient (Czech national standard)
Heat transfer coefficient in
buildings with outbalanced
temperature 20C (W/m2.K)
Construction description
Required
Recommended
values
values
Flat roof, sloping roof to 45
0,24
0,16
Ceiling, floor above exterior
External wall, sloping roof over 45
light
0,30
0,20
wall adjacent to unheated attic
heavy
0,38
0,25
Floor / wall adjacent with earth
0,45
0,30
Internal wall heated to unheated space
0,60
0,40
Internal ceiling-temperature difference 10C
1,05
0,7
Internal wall-temperature difference 10C
1,3
0,9
Internal ceiling-temperature difference 5C
2,2
1,45
Internal wall-temperature difference 5C
2,7
1,8
Window, door in external wall-heated space to
1,7
1,2
2
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
exterior
Window in sloping wall to 45
1,5
1,2
DESIGN VENTILATION HEAT LOSS
Note 1: If you have kitchen as a part of living room, consider air exchange 0.5 1/h.
Note 2: Bathroom air supply is usually from hall of flat, not from exterior, so design temperature
difference is (int,BATH int,HALL) = (24 20)C.
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
TOTAL DESIGN HEAT LOAD
Residential building
Night setback max. 8h
TOTAL DESIGN HEAT LOAD FOR A BUILDING ENTITY OR A BUILDING
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
EXAMPLE:
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
INPUT DATA:
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
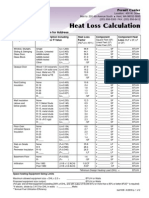
HOBBY ROOM CALCULATION:
�Czech Technical University in Prague
Department of Microenvironmental and Building Services Engineering
http://tzb.fsv.cvut.cz
BEE1 Heating
Room name
Temperature data
Design external temperature
qe
Design internal temperature
qint,i
qint,i-qe
fk
p.u.
Ak
2
m
Design temperature difference
Transmission heat losses
Code
Building
element
Uk
2
W/m K
External wall
External wall
Window
Window
Internal wall
Internal wall
Internal wall
Door
Floor
Total transmission heat loss coefficient
Total transmission heat loss
Ventilation heat losses
HT,i=k fkAkUk
W/K
FT,i=HT,i (qint,i-qe)
0,00
W
0,00
W
W
0
0
FRH,i=AifRH
FHL,i=Fi+FRH,i
Vi
Minimum air exchange rate
nmin
Total ventilation heat loss coefficient
Total ventilation heat loss
Total ventilation and transmission heat loss
HV,i=0,34Vinmin
W/K
FV,i=HV,i (qint,i-qe)
FT,i+FV,i
Internal volume
Correction factor for higher temperature
fq
-1
p.u.
Fi=(FT,i+FV,i)fq
Design ventilation and transmission heat loss
Heating-up capacity
Floor area
Reheat factor
Total heating-up capacity
fRH
Total design heat load
fkAkUk
W/K
0,00
0,00
0,00
0,00
0,00
0,00
0,00
0,00
0,00
m
2
W/m