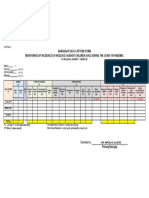
50% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views31 pagesChapter13 Gender Stratification
The document discusses gender stratification and inequality between men and women from a sociological perspective. It addresses how gender roles are socially constructed and vary globally. Key topics covered include patriarchy and sexism, gender socialization, family and peer influences on gender, media portrayals of gender, occupational segregation, women's increasing roles in education and politics, violence against women and men, sexual harassment, and different types of feminism as an approach to addressing gender inequality.
Uploaded by
Siti Yudha AminahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
50% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views31 pagesChapter13 Gender Stratification
The document discusses gender stratification and inequality between men and women from a sociological perspective. It addresses how gender roles are socially constructed and vary globally. Key topics covered include patriarchy and sexism, gender socialization, family and peer influences on gender, media portrayals of gender, occupational segregation, women's increasing roles in education and politics, violence against women and men, sexual harassment, and different types of feminism as an approach to addressing gender inequality.
Uploaded by
Siti Yudha AminahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Gender Stratification: An overview of the concept of gender stratification and its implications across societies.
- Gender and Inequality: Explores gender-related inequalities and differences within social structures.
- Gender in a Global Perspective: Examines gender roles and equality on a global scale, incorporating various cultural perspectives.
- Diversity Snapshot: Highlights diverse historical movements that have impacted gender roles and perceptions.
- Patriarchy and Sexism: Discusses the systemic nature of male dominance and the prevalence of sexism across societies.
- Gender and Socialization: Details how societal norms assign roles based on gender, thus shaping identities.
- Gender and the Family: Examines traditional gender roles within the family dynamic, addressing upbringing and roles.
- Gender and Peer Groups: Analyzes how peer groups influence gender roles from childhood through adolescence.
- Gender and the Mass Media: Investigates the portrayal and impact of gender roles through mass media channels.
- Social Stratification: Discusses the division of society into layers based on gender roles and expectations.
- Jobs with the Highest Concentrations of Women: Presents statistical data about occupations largely held by women and the gender implications within work sectors.
- Women in Politics: Chronicles milestones women have achieved in U.S. politics over time.
- Education, Politics, and Military: Evaluates the involvement and representation of women in education, politics, and military services.
- Are Women a Minority?: Explores intersectionality, addressing how gender interplays with other dimensions of disadvantage.
- Violence Against Women: Addresses various forms of gender-linked violence, reflecting on historical and social roots.
- Violence Against Men: Considers societal and cultural factors that may contribute to violence against men.
- Sexual Harassment: Details forms of sexual harassment and the effects on workplace culture and behavior.
- Pornography: Discusses societal views on pornography and its power-related implications.
- Applying Theory - Gender: Compares theoretical approaches to understanding gender roles, focusing on social function and conflict.
- Feminism: Explores the principles and activism of feminism, aimed at achieving gender equality.
- Types of Feminism: Differentiates between various strands of feminism including liberal, socialist, and radical feminisms.
- Applying Theory - Feminism: Discusses how feminist theories apply to societal structures and improve gender equality.
- Opposition to Feminism: Examines resistance to feminist movements and common arguments against gender equality initiatives.