Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Access Layer
Uploaded by
Jerome Fayluga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Network Access Layer.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesNetwork Access Layer
Uploaded by
Jerome FaylugaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Network Access Layer
Rey Angelo E. Elumir
ACON II; CS 351
Definition:
It is the lowest layer of the TCP/IP protocol hierarchy.
It is often ignored by users as it is well hidden by the
better known mid-level protocols such as IP, TCP, and
UDP, and higher level protocols such as SMTP, HTTP,
and FTP.
Usually performed in this level:
Encapsulation of IP datagram's into the frames
transmitted by the network.
Mapping of IP addresses to the physical addresses
used by the network.
Examples of RFCs that define
network access layer protocols
are:
RFC 826, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) :
which maps IP addresses to Ethernet addresses.
RFC 894, A Standard for the Transmission of IP
Datagram's over Ethernet Networks : which
specifies how IP datagram's are encapsulated for
transmission over Ethernet networks
In addition:
As implemented in UNIX, protocols in this layer often
appear as a combination of device drivers and
related programs.
The modules that are identified with network device
names usually encapsulate and deliver the data to
the network, while separate programs perform related
functions such as address mapping.
Source:
1. Hunt, C. (1999, February 03). TCP/IP Network
Administration. Retrieved July 15, 2017, from
https://docstore.mik.ua/orelly/networking/tcpip/ch01_
04.htm
2. Whipple, W. L. (n.d.). Retrieved July 15, 2017, from
http://www.webhart.net/garry/html/TC0200.html
You might also like
- Network Access Layer: Rey Angelo E. Elumir Acon Ii Cs 351Document6 pagesNetwork Access Layer: Rey Angelo E. Elumir Acon Ii Cs 351Jerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Network Chapter ThreeDocument46 pagesNetwork Chapter ThreeDaniel AshagrieNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Fundamentals: Chapter ObjectivesDocument27 pagesTCP/IP Fundamentals: Chapter Objectiveschetana sidigeNo ratings yet
- The OSI Network Model StandardDocument10 pagesThe OSI Network Model Standardcheal_che2No ratings yet
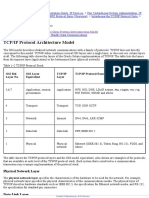
- TCP IP Protocol Architecture ModelDocument6 pagesTCP IP Protocol Architecture Modelayesha chNo ratings yet
- It First ChapterDocument76 pagesIt First ChapterRohan RathoreNo ratings yet
- How TCP-IP WorksDocument29 pagesHow TCP-IP WorksJames GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 00 NetworkReviewDocument26 pages00 NetworkReviewZee ZaboutNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelDocument5 pagesTCP/IP Protocol Architecture Model: Previous: Protocol Layers and The Open Systems Interconnection ModelGreen ZoneNo ratings yet
- MODULE 9 - TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingDocument7 pagesMODULE 9 - TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingGrecu GianiNo ratings yet
- TCPIP OSI ModelDocument3 pagesTCPIP OSI ModelAdarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- List Out The Things To Be Needed To Do Face Make-Up by Self - Steps InvolvedDocument21 pagesList Out The Things To Be Needed To Do Face Make-Up by Self - Steps InvolvedetasureshNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP ProtocolsDocument15 pagesTCP/IP ProtocolsNeha100% (1)
- Tcpi IpDocument97 pagesTcpi Ipcborn99100% (1)
- CCNA 1 Explorer Final Review Fall 2010Document48 pagesCCNA 1 Explorer Final Review Fall 2010Rai ReyesNo ratings yet
- IP Basics and Routing Protocols PDFDocument241 pagesIP Basics and Routing Protocols PDFWubie NegaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TCP IP Reference ModelDocument43 pagesChapter 4 TCP IP Reference Modelamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- (IP) Networks Revision Networks: Communications TechnologyDocument5 pages(IP) Networks Revision Networks: Communications TechnologyAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- CMPN 370 - Handout 3.5 Protocol Suites - TCP/IP: Application LayerDocument5 pagesCMPN 370 - Handout 3.5 Protocol Suites - TCP/IP: Application LayerShania LallNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - History of TCP/IP 4.2 - IP Addressing 4.3 - Name Resolution 4.4 - TCP/IP ProtocolsDocument50 pages4.1 - History of TCP/IP 4.2 - IP Addressing 4.3 - Name Resolution 4.4 - TCP/IP ProtocolsEchezona Uzochukwu AzubikeNo ratings yet
- Over View of TCPDocument15 pagesOver View of TCPMkt RayNo ratings yet
- Internet ProtocolsDocument28 pagesInternet ProtocolsPepeNo ratings yet
- Course Contents: Data Communications Grade Prof. Dr. Hassan H. Soliman Dr. Mostafa Elgayar Part 5 P1Document20 pagesCourse Contents: Data Communications Grade Prof. Dr. Hassan H. Soliman Dr. Mostafa Elgayar Part 5 P1saher waleedNo ratings yet
- Protocols Invovled in TcipDocument23 pagesProtocols Invovled in TcipFiremandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- Protocols and The Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteDocument19 pagesProtocols and The Tcp/Ip Protocol SuiteGeetansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Network Fundamental ConceptsDocument125 pagesChapter 2. Network Fundamental ConceptsBereketNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers - ProtocolsDocument4 pagesQuestions and Answers - ProtocolsVishal PaupiahNo ratings yet
- E.G. File Transfer: CS420/520 Axel Krings Sequence 2Document20 pagesE.G. File Transfer: CS420/520 Axel Krings Sequence 2Anonymous eForKONo ratings yet
- Network Layers: The OSI Network Model StandardDocument4 pagesNetwork Layers: The OSI Network Model StandardPrasanna Venkatesan100% (1)
- Chapter 7Document41 pagesChapter 7Muqeemuddin SyedNo ratings yet
- Networking Notes in HindiDocument29 pagesNetworking Notes in Hindi2abijeet43% (7)
- Internet ProtocolsDocument40 pagesInternet ProtocolsPepeNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - Internet Protocol and IP AddressingDocument22 pagesCH 7 - Internet Protocol and IP Addressingmelkamu debasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document35 pagesLesson 3Bhon-Bhon AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)Document10 pagesTransmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)Sanjoy Basak100% (1)
- W1 HO Networking Concepts PDFDocument31 pagesW1 HO Networking Concepts PDFRttc PuneNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument1 pageOSI Modelsophie10694No ratings yet
- Internet Architecture and Performance MetricsDocument14 pagesInternet Architecture and Performance MetricsnishasomsNo ratings yet
- Internetworking Using TCP/IP: By: Nitin SaraswatDocument16 pagesInternetworking Using TCP/IP: By: Nitin SaraswatdroidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Data CommunicationsDocument47 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Data CommunicationsYihune NegesseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Computer NetworksDocument30 pagesLecture 4 Computer Networksahmedehab1772002No ratings yet
- Curso CCNADocument103 pagesCurso CCNAJORGE LUIS FRANCISCO MORALESNo ratings yet
- Physical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)Document44 pagesPhysical Layer Data Link Layer: Logical Link Control (LLC) Media Access Control (MAC)GauravNo ratings yet
- OSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideDocument28 pagesOSI and TCP - IP Lecture SlideBobby IgbeNo ratings yet
- Link Layer of TCP/IP ProtocolDocument6 pagesLink Layer of TCP/IP Protocolgani525No ratings yet
- IT Notes Unit 5Document14 pagesIT Notes Unit 5Deepankar Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Network Basics: ProtocolsDocument93 pagesUnderstanding Network Basics: Protocolsnishasaiyed2304No ratings yet
- 3.2 TCPIP ModelDocument5 pages3.2 TCPIP ModelSuyasha JainNo ratings yet
- The Internet Protocol SuiteDocument5 pagesThe Internet Protocol SuiteErwinMacaraigNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal JainDocument13 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Ruchi Nanda Diksha Mangal Kajal Jainpooja guptaNo ratings yet
- ProtocolDocument39 pagesProtocolمحمد ياسر محي الدينNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document151 pagesModule 1tharunn6364No ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip: Understanding The Function of ProtocolsDocument10 pagesTcp/Ip: Understanding The Function of Protocolsapurb tewaryNo ratings yet
- OCW - CS601Computer NetworkDocument85 pagesOCW - CS601Computer NetworkRittwik Biswas17No ratings yet
- Communication and Internet TechnologiesDocument9 pagesCommunication and Internet Technologiesmuhammad hussainNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment For 4 Year IT StudentsDocument15 pagesGroup Assignment For 4 Year IT StudentsAnonymous NNRdxSCpNo ratings yet
- Introduction TCP IPDocument42 pagesIntroduction TCP IPballmerNo ratings yet
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisFrom EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Erik E Rikson's: Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument13 pagesErik E Rikson's: Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Moral MaturityDocument12 pagesMoral MaturityJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Colors in SpanishDocument168 pagesColors in SpanishJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- FINALDocument116 pagesFINALJerome Fayluga100% (1)
- Philosophical InquiryDocument9 pagesPhilosophical InquiryJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Are Beards Good For Your HealthDocument2 pagesAre Beards Good For Your HealthJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper in Mindanao Ict Cluster ConferenceDocument1 pageReaction Paper in Mindanao Ict Cluster ConferenceJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- KimDocument22 pagesKimJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Competitors For The 1st National Computer Engineering ChallengeDocument1 pageCompetitors For The 1st National Computer Engineering ChallengeJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Sample Take Home ExamDocument5 pagesSample Take Home ExamJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- State of The Nation Address 2016Document3 pagesState of The Nation Address 2016Jerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Paper - in - Meta - Doc Filename UTF-8''paper in MetaDocument16 pagesPaper - in - Meta - Doc Filename UTF-8''paper in MetaJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Template Module For DebateDocument6 pagesTemplate Module For DebateJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet
- Multiple IntelligencesDocument3 pagesMultiple IntelligencesJerome FaylugaNo ratings yet