Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pin Description For Maximum Mode
Uploaded by
Radhwan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesmmm
Original Title
Pin Description for Maximum Mode
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmmm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesPin Description For Maximum Mode
Uploaded by
Radhwanmmm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
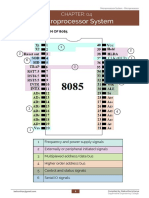
Pin Description for Maximum
Mode
Gursharan Singh Tatla www.eazynotes.com 1
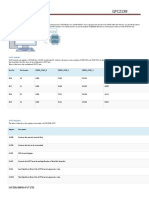
QS1 and QS0
Pin 24 and 25 (Output)
These pins provide the
status of instruction
queue.
QS1 QS0 Status
0 0 No operation
0 1 1st byte of opcode from queue
1 0 Empty queue
1 1 Subsequent byte from queue
Gursharan Singh Tatla www.eazynotes.com 2
S0, S1, S2
Pin 26, 27, 28 (Output)
These status signals
indicate the operation
being done by the
microprocessor.
This information is
required by the Bus
Controller 8288.
Bus controller 8288
generates all memory and
I/O control signals.
Gursharan Singh Tatla www.eazynotes.com 3
S0, S1, S2
Pin 26, 27, 28 (Output)
S2 S1 S0 Status
0 0 0 Interrupt Acknowledge
0 0 1 I/O Read
0 1 0 I/O Write
0 1 1 Halt
1 0 0 Opcode Fetch
1 0 1 Memory Read
1 1 0 Memory Write
1 1 1 Passive
Gursharan Singh Tatla www.eazynotes.com 4
LOCK
Pin 29 (Output)
This signal indicates that
other processors should not
ask CPU to relinquish the
system bus.
When it goes low, all
interrupts are masked and
HOLD request is not
granted.
This pin is activated by using
LOCK prefix on any
instruction.
Gursharan Singh Tatla www.eazynotes.com 5
RQ/GT1 and RQ/GT0
Pin 30 and 31 (Bi-directional)
These are Request/Grant
pins.
Other processors request the
CPU through these lines to
release the system bus.
After receiving the request,
CPU sends acknowledge
signal on the same lines.
RQ/GT0 has higher priority
than RQ/GT1.
Gursharan Singh Tatla www.eazynotes.com 6
You might also like
- Microprocessor - 8086 Pin Configuration - TutorialspointDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor - 8086 Pin Configuration - TutorialspointSadikuzzaman lalinNo ratings yet
- 8086 MicroprocessorDocument19 pages8086 MicroprocessorAchyut TripathiNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument4 pagesMicroprocessork lakshmi prasannaNo ratings yet
- Pinout Diag. 8086Document8 pagesPinout Diag. 8086ROCKING STYLENo ratings yet
- MIC (22415) UNIT - 1 NotesDocument17 pagesMIC (22415) UNIT - 1 NotesGaurang RaneNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8086 Pin ConfigurationDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor - 8086 Pin ConfigurationShahanasNo ratings yet
- 8086 SignalsDocument12 pages8086 SignalsY MARY REEJANo ratings yet
- Pin Diagram of 8086Document34 pagesPin Diagram of 8086vinayaaaNo ratings yet
- 8086 Microprocessor: Lec. 4: 8086 Pin Description Omar ZyadDocument14 pages8086 Microprocessor: Lec. 4: 8086 Pin Description Omar Zyadالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- 8086 MIC - Unit 1 - NotesDocument31 pages8086 MIC - Unit 1 - Notesviraj babarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 8086 16 Bit MicroprocessorDocument17 pagesUnit 1 8086 16 Bit MicroprocessorManofwarrior100% (1)
- Lecture 4 - 5 - 6 - CSE - Microprocessor and Assembly LanguageDocument63 pagesLecture 4 - 5 - 6 - CSE - Microprocessor and Assembly LanguagefaridulNo ratings yet
- Memory SegmentationDocument38 pagesMemory SegmentationVinaya SreeNo ratings yet
- The 8086 Pin ConfigurationDocument32 pagesThe 8086 Pin ConfigurationTeo JavaNo ratings yet
- Pin Diagram of 8085Document48 pagesPin Diagram of 8085api-247714257No ratings yet
- Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument1 pageMicroprocessor and MicrocontrollerJitendraNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor: Based, Multipurpose, ProgrammableDocument61 pagesMicroprocessor: Based, Multipurpose, ProgrammableSiddhant MittalNo ratings yet
- Pin Diagram of 8085 MicroprocesoorDocument52 pagesPin Diagram of 8085 MicroprocesoorSkanda GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2-16 Bit Microprocessor 8086Document20 pages2-16 Bit Microprocessor 8086afzal_a75% (4)
- UNIT1Document48 pagesUNIT1mohit mishraNo ratings yet
- Sigals 8086Document31 pagesSigals 8086RajaRaman.GNo ratings yet
- 8086 Hardware Specification: Segment 5Document19 pages8086 Hardware Specification: Segment 5Tigabu YayaNo ratings yet
- 02 The 8085 MicroprocessorDocument27 pages02 The 8085 MicroprocessorSheena Ann StonehillNo ratings yet
- Advanced Microprocessors: Date: 16/11/2005 Prof. S. JagannathanDocument39 pagesAdvanced Microprocessors: Date: 16/11/2005 Prof. S. JagannathanVinoda DhayanitheNo ratings yet
- PIN DIAGRAM of 8086:: Maximum Mode - Pin 1,20 (GND) : Connected To GroundDocument4 pagesPIN DIAGRAM of 8086:: Maximum Mode - Pin 1,20 (GND) : Connected To GroundvishwanathNo ratings yet
- MP 8086 PPTDocument18 pagesMP 8086 PPTcompstudent2024No ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086 - Min and Max ModesDocument25 pagesMicroprocessor 8086 - Min and Max ModesE.VigneshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingDocument29 pagesUnit 3 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingDere JesusNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller PDFDocument31 pages8051 Microcontroller PDFHarshitha bottaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 8086 System Bus Structures FullunitDocument36 pagesUnit 2 8086 System Bus Structures Fullunitlauro eugin brittoNo ratings yet
- 8086 Pin ConfigurationsDocument24 pages8086 Pin ConfigurationsVeena mitraNo ratings yet
- LPC2148 UART ProgrammingDocument8 pagesLPC2148 UART ProgrammingvaibhavNo ratings yet
- 8086 Min and Max Mode: Course Code BM 502 Microcontroller and BioelectronicsDocument42 pages8086 Min and Max Mode: Course Code BM 502 Microcontroller and BioelectronicsVeena mitraNo ratings yet
- Unit III 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingDocument26 pagesUnit III 8086 Microprocessor InterfacingRammanohar Lokiya100% (1)
- Overview or Features of 8086: It Is A 16-Bit MicroprocessorDocument33 pagesOverview or Features of 8086: It Is A 16-Bit MicroprocessorSamuel KuantumNo ratings yet
- Set 8088 IntelDocument30 pagesSet 8088 IntelVictor UV VelardeNo ratings yet
- ARM Experiment ProgrammsDocument52 pagesARM Experiment ProgrammsShweta KulkarniNo ratings yet
- LPC2148 UART ProgrammingDocument5 pagesLPC2148 UART Programmingkbmn2No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - MP DSBDocument42 pagesChapter 4 - MP DSBsheham ihjamNo ratings yet
- 8086 Pin ConfigurationDocument83 pages8086 Pin ConfigurationVenkata Krishnakanth ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- Ifm 00057F 20210318 IODD11 enDocument34 pagesIfm 00057F 20210318 IODD11 enmulabunsNo ratings yet
- 8086 Miccro ControllerDocument41 pages8086 Miccro ControllerqwertyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document20 pagesChapter 9sandeep4672kvkNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller With 2K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash: FeaturesDocument17 pagesMicrocontroller With 2K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash: FeaturesGomzalez Bin GembozNo ratings yet
- Mp&i Course File - unit-IIIDocument23 pagesMp&i Course File - unit-IIIvenkateshrachaNo ratings yet
- RX3i Discrete Modules DatasheetDocument3 pagesRX3i Discrete Modules Datasheetcomercial mox asesoriaNo ratings yet
- Manual SIWAREX WP521 WP522 en - PDF Page 87Document1 pageManual SIWAREX WP521 WP522 en - PDF Page 87Cr SeNo ratings yet
- U3 8086 MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesU3 8086 MicroprocessorNishant Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- The 8051 Microcontroller: Hsabaghianb at Kashanu - Ac.irDocument141 pagesThe 8051 Microcontroller: Hsabaghianb at Kashanu - Ac.irShraddha Parmar100% (1)
- 8086 Pin DiagramDocument7 pages8086 Pin DiagramTsy Less DahalNo ratings yet
- Pin ConfigurationDocument27 pagesPin ConfigurationShanmukh SudheendraNo ratings yet
- 1a. CS602 Microprocessor and Microcontroller - HardwareDocument16 pages1a. CS602 Microprocessor and Microcontroller - HardwareRehan NightNo ratings yet
- Micro CH 04Document38 pagesMicro CH 04Denis RijalNo ratings yet
- Mic Unit1Document21 pagesMic Unit1xboyxman1000No ratings yet
- 8085 Pin DiagramDocument48 pages8085 Pin DiagramJaydev BhadeliyaNo ratings yet
- My Lecture 4Document9 pagesMy Lecture 4Kashif KhanNo ratings yet
- Microcomputer Components: 16-Bit CMOS Single-Chip MicrocontrollerDocument52 pagesMicrocomputer Components: 16-Bit CMOS Single-Chip MicrocontrollerMathias GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 8085 Pin DiagramDocument4 pages8085 Pin Diagrammohan babuNo ratings yet
- 8085 Pin DiagramDocument4 pages8085 Pin Diagramksp27febNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Architectures and Systems: RISC, CISC and DSPFrom EverandMicroprocessor Architectures and Systems: RISC, CISC and DSPRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Lab.1 Assembly Language: RAM Is A Place To Where The Programs Are Loaded in Order To Be Executed. TheDocument6 pagesLab.1 Assembly Language: RAM Is A Place To Where The Programs Are Loaded in Order To Be Executed. TheRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Lenguaje EnsambladorDocument115 pagesLenguaje EnsambladorFidel SalavarriaNo ratings yet
- Lec c.1 Gene Eral Intro Oduction: Co Omputer PartsDocument5 pagesLec c.1 Gene Eral Intro Oduction: Co Omputer PartsRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Emu 8086Document191 pagesEmu 8086qazed222No ratings yet
- Emu 8086Document191 pagesEmu 8086qazed222No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: SRM UniversityDocument59 pagesLaboratory Manual: SRM UniversityRadhwanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085 & 8086 ProgramsDocument141 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 & 8086 ProgramsDwane Almeida100% (1)
- Laboratory Manual: SRM UniversityDocument59 pagesLaboratory Manual: SRM UniversityRadhwanNo ratings yet
- EC6513 Microprocessor Microcontroller Lab 1 2013 RegulationDocument92 pagesEC6513 Microprocessor Microcontroller Lab 1 2013 RegulationvijaykannamallaNo ratings yet
- Lect 4Document12 pagesLect 4RadhwanNo ratings yet