Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.bones of Upper Limb
Uploaded by
rahul maurya0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
48 views32 pagesThe document summarizes key bones and features of the upper limb, including the clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. It describes the structures and articulations of these bones, common sites of fractures like Colles' fracture, and methods to identify the anterior, medial and superior surfaces of certain bones.
Original Description:
rahul maurya
Original Title
4.Bones of Upper Limb (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key bones and features of the upper limb, including the clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. It describes the structures and articulations of these bones, common sites of fractures like Colles' fracture, and methods to identify the anterior, medial and superior surfaces of certain bones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
48 views32 pages4.bones of Upper Limb
Uploaded by
rahul mauryaThe document summarizes key bones and features of the upper limb, including the clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. It describes the structures and articulations of these bones, common sites of fractures like Colles' fracture, and methods to identify the anterior, medial and superior surfaces of certain bones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
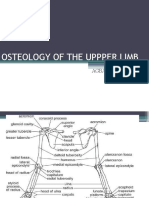
Bones of Upper Limb
Clavicle
First to start its ossification and last to
complete it.
No medullary cavity
Develops in membrane
Common site of fracture is the junction of
its medial two-thirds and lateral one-third.
Clavicle
Has 3 functions :
To transmit forces from the upper limb
to axial skeleton
To act as strut holding the arm free
from trunk, to hang
To provide attachment for muscles
Clavicle
Sternal end - Articulates sternum
(manubrium)
Acromial end - Articulates scapula
Scapula
Scapula
Structure (triangle; three sides and angles)
Acromionanterior projection of spine; articulation with
clavicle
Coracoid processanterior projection of superior scapular
border; anchors bicep muscle
Glenoid cavityarticulates with humerous
Suprascapular notchnerve passage
Superior, lateral and inferior angle
Spineposterior surface
Infraspinous, supraspinous and subscapular fossashallow
depressions
Superior, medial and lateral borders
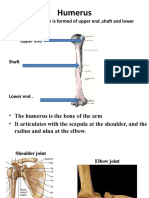
Humerus
Humerus
Humerus
a. Head
b. Anatomical neck
c. Greater and lesser tubercles
i. Separated by intertubercle groove
d. Surgical neck (most likely site of fracture)
e. Deltoid tuberosity
i. Attachment site of deltoid muscle
f. Radial groove - mid shaft of humerus
i. Course of radial nerve
g. Condyles
i. Trochlea (medial): articulates with ulna
ii. Capitulum: articulates with radius
Humerus
Surgical neck axillary nerve (&
circumflex vessels)
Radial / spiral groove radial nerve (&
profunda brachii vessels)
Distal end of humerus median nerve
Medial epicondyle ulnar nerve
Radius and Ulna
a. Two parallel long bones: ulna and
radius
b. Articulations
i. Proximal: humerus
ii. Distal: bones of wrist
iii. Radioulnar joints: radius
and ulna both proximally and distally
Radius and Ulna
Radius and Ulna
Ulna: forms elbow joint with humerus; wide at proximal end, narrow at
distal
a. Olecranon and coronoid processes
i. Grip trochlea of humerus to form a stable hinge joint
ii. At full extension, olecranon process locks to prevent
hyperextension
b. Radial notch: articulates with radius
c. Head (wrist end): articulates with radius
d. Styloid process: attachment for wrist ligaments
Radius: narrow proximally, wide distally
a. Head (humerus end)
i. Superior surface articulates with capitulum of humerus
ii. Medial surface articulates with ulna
b. Radial tuberosity: anchors biceps muscle
c. Styloid process: attachment for wrist ligaments
Skeleton of Hand
Skeleton of Hand
1. Carpus: proximal structure of hand
a. Group of 8 bones (carpals) tied together with ligaments
b. Two irregular rows of four bones each
i. Proximal row: scaphoid, lunate, triquetral and pisiform
ii. Distal row: Trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and hamate
2. Metacarpus (5 wrist-like spokes)
a. No names; numbers (1-5) instead; 1 on thumb side
b. Articulations
i. Bases with carpals
ii. Heads with phalanges
3. Phalanges (fingers or digits): 14 bones
a. Numbered 1-5 beginning with pollex (thumb)
b. Distal, middle and proximal phalanges for each digit
c. No middle phalanx for pollex
Colles transverse fracture of distal end
of radius distal fragment is displaced
posteriorly. (fall with outstretched arms)
Opposite of Colles is Smiths (falling with wrists flexed)
Colles fracture
- Dinner fork deformity
Colles fracture
Boxers fracture
Scaphoid fracture
Results from a fall on the palm of the hand
When the hand is abducted across the narrow
part of scaphoid
May result in avascular necrosis of proximal fragment.
1. Acromial end
2. Conoid tubercle
3. Sternal end
1. Acromion process
2. Coracoid process
3. Glenoid fossa
4. Subcapsular fossa
1. Lesser tubercle
2. Intertubercular
groove/ bicipital
sulcus
3. Medial
epicondyle
4. Coronoid fossa
1. Radial tuberosity
2. Styloid process of radius
3. Coronoid process
4. Trochelar notch
1. Capitulum
2. Radiocarpal joint
3. Proximal radio-ulnar joint
1. Scaphoid
2. Hook of hamate
3. Pisiform
4. Lunate
Side identification
Clavicle
Medial - enlarged sternal end
Anterior curvature is convexo-concave from
medial to lateral
Inferior conoid tubercle
Scapula
Posterior spine
Superior and lateral glenoid cavity
Humerus
Superior and medial head
Posterior olecranon fossa
You might also like
- 100 TOP Orthopaedics MCQ and AnswersDocument18 pages100 TOP Orthopaedics MCQ and AnswersAhmed Noori89% (157)
- Jin Goo Kim - Knee Arthroscopy - An Up-to-Date Guide-Springer (2021)Document370 pagesJin Goo Kim - Knee Arthroscopy - An Up-to-Date Guide-Springer (2021)Fernando FernandezNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD. PH.DDocument26 pagesBones of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD. PH.DTodesengelNo ratings yet
- L - Upper Extremity (Bones and Muscles)Document56 pagesL - Upper Extremity (Bones and Muscles)Riyadh Ali nasser Al.Sharekh 0252No ratings yet
- 2 Bones of Upper Limb 2Document29 pages2 Bones of Upper Limb 2Abdelrhman AbubakrNo ratings yet
- General Arthrology, Joints of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDDocument33 pagesGeneral Arthrology, Joints of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDTodesengelNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb by SheheryarDocument15 pagesUpper Limb by SheheryarsfrtrNo ratings yet
- Joints of Upper ExtremityDocument28 pagesJoints of Upper ExtremityIzabella MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Bones of The Upper LimbsDocument38 pagesLecture 4 - Bones of The Upper LimbsTheLegendKiller337No ratings yet
- Anatomy ReviewDocument283 pagesAnatomy ReviewmmbrewNo ratings yet
- Katz Sandor enDocument49 pagesKatz Sandor enAlexNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Study Table 2Document55 pagesAnatomy Study Table 2Austin KellyNo ratings yet
- RaddaaDocument69 pagesRaddaasravanthreddy44No ratings yet
- Brachium, Cubital Fossa and UmDocument24 pagesBrachium, Cubital Fossa and UmartikslennonNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Skeleton StdsDocument40 pagesAppendicular Skeleton StdsNaveelaNo ratings yet
- The SkullDocument123 pagesThe SkullAnonymous k8rDEsJsU1No ratings yet
- BonesDocument27 pagesBonesADELAJA SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Upper ExtremityDocument216 pagesUpper ExtremityChester VergilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Upper Limb-1 EDITAN HEMATDocument49 pagesAnatomy of Upper Limb-1 EDITAN HEMATFriska Penri UtamiNo ratings yet
- NeckdissectionsDocument130 pagesNeckdissectionsAlvaro RivCalleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab 1Document31 pagesAnatomy Lab 1Spotify IraqNo ratings yet
- Osteology of Upper Limb 2023Document44 pagesOsteology of Upper Limb 2023Satrumin ShirimaNo ratings yet
- NeckDocument215 pagesNeckpilot abdi baariNo ratings yet
- Fractures Around The Elbow JointDocument31 pagesFractures Around The Elbow Jointalimran MahmudNo ratings yet
- Bones of Upper LimbsDocument33 pagesBones of Upper LimbsGyori ZsoltNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms Used in Description of BonesDocument29 pagesAnatomical Terms Used in Description of Bonesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- ANA L4 - Bones, Joints Muscles of The Upper Limb IIIDocument24 pagesANA L4 - Bones, Joints Muscles of The Upper Limb IIIjexshimadaNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument69 pagesAxial SkeletonKharisulNo ratings yet
- Ul PDFDocument8 pagesUl PDFNourhan ShabanNo ratings yet
- Vertebrae and Appendicular ANAPHY AND PHYSIODocument10 pagesVertebrae and Appendicular ANAPHY AND PHYSIOshannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- Thoracic ESDocument237 pagesThoracic ESAbel Belete100% (1)
- 5-Scapular RegionDocument36 pages5-Scapular Regionsama rasmyNo ratings yet
- The Shoulder Anatomy & Approaches: Abdulaziz F. Ahmed, MBBS PGY-2Document61 pagesThe Shoulder Anatomy & Approaches: Abdulaziz F. Ahmed, MBBS PGY-2Abdulaziz Al-Akhras100% (1)
- Lecture Note - Medical Course, 353241 Musculoskeletal SystemDocument107 pagesLecture Note - Medical Course, 353241 Musculoskeletal SystemKitchanan KosalathipNo ratings yet
- 02 Appendicular SkeletonDocument40 pages02 Appendicular SkeletonkalyanNo ratings yet
- Radiography of Shoulder and ArmDocument81 pagesRadiography of Shoulder and ArmKristina ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Appendicular Skeleton 1-1Document117 pagesAppendicular Skeleton 1-1Anania EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- ZOO3731 chptr.6-8Document55 pagesZOO3731 chptr.6-8Raylax2sik24No ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument84 pagesUpper LimbJinnah SheriffNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System: Cebu Doctors' University - CAMS Department of Medical TechnologyDocument46 pagesSkeletal System: Cebu Doctors' University - CAMS Department of Medical TechnologyJoshua CodillaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument72 pagesAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- Osteology of The Upper ExtremityDocument75 pagesOsteology of The Upper ExtremityKevo YoungNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Practical I: Limbs I and II Annie Kim September 21, 2015Document65 pagesAnatomy Practical I: Limbs I and II Annie Kim September 21, 2015Nijo JacobNo ratings yet
- Superior Extremities & Vertebrae OsteologyDocument48 pagesSuperior Extremities & Vertebrae OsteologyPokena EmaNo ratings yet
- Joints of Skull and Axial Skeleton.Document29 pagesJoints of Skull and Axial Skeleton.fdgmffv5mpNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocument12 pagesBones of The Upper LimbShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Kartu Hapalan Osteology Anatomy 2018: Nama: .. NIM: .. PembimbingDocument8 pagesKartu Hapalan Osteology Anatomy 2018: Nama: .. NIM: .. PembimbingzannubanabilahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Chart2Document16 pagesAnatomy Chart2Jeff WuNo ratings yet
- Osteology of Upper LimbDocument63 pagesOsteology of Upper LimbAkomolede AbosedeNo ratings yet
- Lab Practical 2 ReviewDocument2 pagesLab Practical 2 ReviewlogonautNo ratings yet
- 1 Bones of The Upper LimbDocument28 pages1 Bones of The Upper LimbForwardNo ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy of The Upper LimbDocument23 pagesSurface Anatomy of The Upper LimbSherifaNo ratings yet
- Bones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9Document41 pagesBones of Limbs - Pharmacy - 12-9安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Modul Anatomy Blok 2-2Document46 pagesModul Anatomy Blok 2-2AyuNo ratings yet
- Final W5 L2 Shoulder JointDocument36 pagesFinal W5 L2 Shoulder JointOmar OsamaNo ratings yet
- 7 Anatomy of The Anterior Compartment of Forearm DiyaDocument22 pages7 Anatomy of The Anterior Compartment of Forearm DiyaADELAJA SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Hand: Khalid AyoubDocument53 pagesAnatomy of The Hand: Khalid Ayoubvaikunthan100% (2)
- Anatomi Dan Kinesiologi: Tangan (1) : Dr. Ika Ayu Paramita Supervised By: Dr. Rahmat Zulkarnain G, SPKFRDocument66 pagesAnatomi Dan Kinesiologi: Tangan (1) : Dr. Ika Ayu Paramita Supervised By: Dr. Rahmat Zulkarnain G, SPKFRIka Ayu ParamitaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Anatomy of Thoracic Walls, Lower Respiratory TractDocument36 pagesLab 1 - Anatomy of Thoracic Walls, Lower Respiratory TractMe MyselfNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument31 pagesUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- A New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasFrom EverandA New Order of Fishlike Amphibia From the Pennsylvanian of KansasNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy Protocols For Conditions of Shoulder RegionDocument111 pagesPhysical Therapy Protocols For Conditions of Shoulder RegionPieng Napa100% (1)
- Elbow Special TestDocument4 pagesElbow Special TestEllaiza Astacaan100% (1)
- Orthopedic Chart 3-3Document9 pagesOrthopedic Chart 3-3elaine daiNo ratings yet
- Periarthritis ShoulderDocument76 pagesPeriarthritis Shouldervijay1234568883No ratings yet
- Posterior Compartment of The ThighDocument1 pagePosterior Compartment of The ThighLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- ABOS Sports Acceptable CPT CodesDocument13 pagesABOS Sports Acceptable CPT CodesFrank CookNo ratings yet
- Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Over-the-Top TechniquesDocument12 pagesArthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Over-the-Top TechniquesSang PhạmNo ratings yet
- The Strength Coach's Guide To Shoulder TrainingDocument86 pagesThe Strength Coach's Guide To Shoulder TrainingShaleen Dalal96% (23)
- 14th Forum Program Rundown Final v2Document2 pages14th Forum Program Rundown Final v2Ray Li Shing KitNo ratings yet
- Cuadricepsplastia MipiDocument5 pagesCuadricepsplastia MipiVictor HernandezNo ratings yet
- OU Shoulder and Elbow OITE Review: September 23, 2015 Betsy M. Nolan MDDocument159 pagesOU Shoulder and Elbow OITE Review: September 23, 2015 Betsy M. Nolan MDJayNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy For ArtistsDocument223 pagesHuman Anatomy For Artistst. MaellnerNo ratings yet
- MobilisationDocument97 pagesMobilisationMegha Patani100% (1)
- Anatomical Anaylsis Tables For HittingDocument5 pagesAnatomical Anaylsis Tables For HittingDamien wallaceNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive UL MM Table - Sheet1Document5 pagesComprehensive UL MM Table - Sheet1Teodora MunteanuNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Shoulder Injuries in Overhead AthletesDocument9 pagesPrevention of Shoulder Injuries in Overhead AthletesLeonardiniNo ratings yet
- American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery: Acceptable CPT Codes For Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Subspecialty Case ListDocument13 pagesAmerican Board of Orthopaedic Surgery: Acceptable CPT Codes For Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Subspecialty Case ListKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Musculoskeletal SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Musculoskeletal SystemDevi AswandiNo ratings yet
- Price List EuroDocument6 pagesPrice List Euromnegrilam2002No ratings yet
- GoniometryDocument22 pagesGoniometryDuppala Sateesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Nursing Actions (Dops)Document5 pagesAnalysis of Nursing Actions (Dops)mutia aNo ratings yet
- Do Changes in Hand Grip Strength Correlate With Shoulder Rotator Cuff Function?Document6 pagesDo Changes in Hand Grip Strength Correlate With Shoulder Rotator Cuff Function?soylahijadeunvampiroNo ratings yet
- RECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATION NewDocument93 pagesRECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATION NewAjayi FolamiNo ratings yet
- Shoulder PresentationDocument22 pagesShoulder Presentationapi-664376361No ratings yet
- Positioning and Moving of Hemiplegic Pt. Bed Mobility ExercisesDocument133 pagesPositioning and Moving of Hemiplegic Pt. Bed Mobility Exercisesktin17100% (1)
- Rehabilitation Guidelines For Proximal Humerus Fracture - OrifDocument4 pagesRehabilitation Guidelines For Proximal Humerus Fracture - OrifIlie OnuNo ratings yet
- Knee MCL and LCL InjuriesDocument90 pagesKnee MCL and LCL InjuriesImam SurkaniNo ratings yet
- Dislocation of Hip Joint: DR - PonnilavanDocument38 pagesDislocation of Hip Joint: DR - PonnilavanPankaj VatsaNo ratings yet