0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views34 pagesJava Packages & Classes Guide
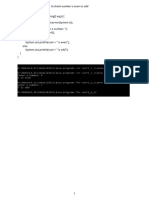
The document discusses Java packages and classes. It explains that packages are used to group related classes and interfaces. The java.lang package contains fundamental classes like Object, String, Integer, and Double. Other classes discussed include Vector, Stack, and Scanner. Examples are provided to demonstrate using various methods of these classes like add(), pop(), and next().
Uploaded by
Dragan IvanovCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views34 pagesJava Packages & Classes Guide
The document discusses Java packages and classes. It explains that packages are used to group related classes and interfaces. The java.lang package contains fundamental classes like Object, String, Integer, and Double. Other classes discussed include Vector, Stack, and Scanner. Examples are provided to demonstrate using various methods of these classes like add(), pop(), and next().
Uploaded by
Dragan IvanovCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 34