Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cranes: OSHA Office of Training & Education 1
Cranes: OSHA Office of Training & Education 1
Uploaded by
ajayjanardhankasle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views38 pagescrane safety
Original Title
Cranes-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcrane safety
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views38 pagesCranes: OSHA Office of Training & Education 1
Cranes: OSHA Office of Training & Education 1
Uploaded by
ajayjanardhankaslecrane safety
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 38
Cranes
OSHA Office of Training & 1
Major Causes of Crane Accidents
• Contact with power lines
• Overturns
• Falls
• Mechanical failures
OSHA Office of Training & 2
How Do Accidents Occur?
• Instability – unsecured load, load
capacity exceeded, or ground not level
or too soft
• Lack of communication - the point of
operation is a distance from the crane
operator or not in full view of the
operator
• Lack of training
• Inadequate maintenance or inspection
OSHA Office of Training & 3
Who is at Risk
• Operators
• Persons at
Crane Site
OSHA Office of Training & 4
Definitions
• Crane – Consists of a rotating structure for lifting and
lowering horizontally on rubber tires or crawler treads
• Hoist - Used to lift and lower load.
• Boom – An inclined spar, strut, or other long member
supporting the hoisting tackle
• Boom stops – A device used to limit the angle of the
boom at its highest position
• Brake – To slow or stop motion by friction or power
• Block – Sheaves or grooved pulleys in a frame with
hook, eye and strap
• Jib – Extension attached to the boom point to provide
added boom length for lifting specified loads.
OSHA Office of Training & 5
Crane Parts
OSHA Office of Training & 6
Types of Cranes
• Mobile
• Hydraulic
• Overhead
• Gantry
• Tower
OSHA Office of Training & 7
Crane Hazards
• Improper load • Working too close to
rating power lines
• Excessive speeds • Improper exhaust
• No hand signals system
• Inadequate • Shattered windows
inspection and • No steps/guardrails
maintenance walkways
• Unguarded parts • No boom angle
• Unguarded swing indicator
radius • Not using outriggers
OSHA Office of Training & 8
Planning Before Start-Up
• Level the crane and ensure support surface is firm
and able to support the load
• Contact power line owners and determine
precautions. Know the location and voltage of
overhead power lines.
• Know the basic crane capacities, limitations, and
job site restrictions, such as the location of power
lines, unstable soil, or high winds.
• Make other personnel aware of hoisting activities.
• Barricade areas within swing radius.
• Ensure proper maintenance and inspections.
• Determine safe areas to store materials and place
machinery.
OSHA Office of Training & 9
Competent Person
The competent person must
inspect all machinery and
equipment prior to each
use, and during use, to
make sure it is in safe
operating condition.
If it needs fixing, take it out
of service and don’t use it Broken
until it is fixed
Track
OSHA Office of Training & 10
Load Capacity - Speed - Warnings
• Make sure the crane
operator can see the:
➢ Rated Load
Capacities
➢ Operating Speeds
➢ Special Hazard
Warning or
Instruction
Load Rating Chart
OSHA Office of Training & 11
Know the Weight of the Load
• Refer to shipping ticket or other
documentation
• Ensure lift calculations are correct
• Ensure load is within load chart rating for
boom length and load radius of crane
• Crane is rated by the maximum weight it
will lift at a minimum radius and minimum
boom length – the further from its
centerpoint, the less it will lift
OSHA Office of Training & 12
Load Limiting Factors
• Not level
• Wind
• Side loads
• On its wheels
• Lifting over the side
• Use of extensions, jibs and other
attachments
• Limits of wire rope, slings and lifting devices
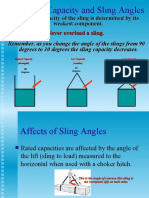
OSHA Office of Training & 13
Mobile Cranes –
Lifting Principles
• Center of Gravity
• Leverage
• Stability
• Structural Integrity
OSHA Office of Training & 14
Load Example –
30 ton crane
• Will lift 60,000 pounds at 10 feet from the
center pin of the crane
• Based on level surface, no wind, and
outriggers fully extended
• At 25 feet from the center pin with an 80 foot
boom, the capacity is only 14,950 pounds
• At 74 feet from the center pin, the capacity
is only 4,800 pounds
OSHA Office of Training & 15
Improper Load
Improper loads or speeds can result
in the tipping of the crane
OSHA Office of Training & 16
Improper Load
OSHA Office of Training & 17
Improper Load
OSHA Office of Training & 18
Power Lines
Stay clear
from power
lines at least
10 feet
OSHA Office of Training & 19
Hand Signals
An illustration of
the signals must
be posted at the
job site
OSHA Office of Training & 20
Guard Moving Parts
Unguarded
Chain Drive
Guard moving parts such as gears or belts
OSHA Office of Training & 21
Swing Radius
Stay out of the swing radius of the crane –
Make sure there are barrier guards showing swing radius
OSHA Office of Training & 22
Operator Visibility
Broken Window
Make sure broken windows or other obstructions
do not prevent the operator from seeing
OSHA Office of Training & 23
Ladders
Ladder
Use ladders to get to the upper portion of the cab
OSHA Office of Training & 24
Guardrails
Runways and steps need to have guardrails,
handholds and slip resistant surfaces
OSHA Office of Training & 25
Suspended Loads
Don’t stand under suspended loads
OSHA Office of Training & 26
Boom Angle Indicator
A boom angle indicator must be on the crane
OSHA Office of Training & 27
Supporting Surface
Cranes must be on a firm supporting
surface and level within 1 percent
OSHA Office of Training & 28
Sheaves
The grooves must be smooth and free from surface
defects which could cause rope damage
OSHA Office of Training & 29
Rigging Equipment Slings
Types of slings include alloy steel chain, wire rope,
metal mesh, natural or synthetic fiber rope, and
synthetic web.
Chain Wire rope Metal mesh Synthetic
OSHA Office of Training & 30
Annual Inspections
Inspection of the
hoisting machinery
must be made by a
competent person
The employer must
maintain a record of
these inspections Crane wasn’t inspected
and tipped over
OSHA Office of Training & 31
What to Inspect
• Correct air pressure and no leaks
• Tires properly inflated
• Clearance for tail swing
• Wire rope wear
• Physical damage to crane
• Loose or missing hardware, nuts, or bolts
• Fluid leaks
OSHA Office of Training & 32
Remove From Service
Immediately remove damaged or
defective slings from service
OSHA Office of Training & 33
Damaged wire rope
Crushed Rope
Broken Strands
Damaged wire rope must be taken out of service
OSHA Office of Training & 34
Worn Part
OSHA Office of Training & 35
Tire Inspections
Conduct
regular
inspections
of tires for
excessive
wear or
damage
OSHA Office of Training & 36
Training
• Operators:
➢must qualify on specific crane type
➢Must include on-the-job training
• Supervisor / competent person
OSHA Office of Training & 37
Summary
• An unstable load, lack of communication, lack of
training, and inadequate maintenance or inspection are
major contributors to crane accidents.
• Operators or others working in the area can be
victims to “struck by" and "caught in" injuries.
• Contact with power lines causes many accidents.
• A competent person must inspect a crane regularly
to insure it is in proper order.
• Planning and training reduces accidents.
OSHA Office of Training & 38
You might also like
- Samuel Francis Lifting Engineer ResumeDocument5 pagesSamuel Francis Lifting Engineer Resumeanthony jamesNo ratings yet
- Cranes Rigging Your Organization Iti - Com r031512Document33 pagesCranes Rigging Your Organization Iti - Com r031512Mohsin Majeed0% (1)
- HoistingRiggingPlan PDFDocument5 pagesHoistingRiggingPlan PDFHadiwinata DjakariaNo ratings yet
- F4a 2020 LEEA Assessments - Information For Members Students Nov 2019Document4 pagesF4a 2020 LEEA Assessments - Information For Members Students Nov 2019VishnuNo ratings yet
- Training Session: Mobile Crane Operator Safety TrainingDocument42 pagesTraining Session: Mobile Crane Operator Safety TrainingAyaz GhouriNo ratings yet
- Serious Near Miss ReportDocument1 pageSerious Near Miss ReportSusan Sese100% (1)
- Careless Act EssayDocument4 pagesCareless Act EssayAzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tire Litigation: A Primer, by Ben BakerDocument118 pagesTire Litigation: A Primer, by Ben BakerBeasley Allen100% (1)
- Phonics and Spelling ProgrammeDocument24 pagesPhonics and Spelling ProgrammeiqadinNo ratings yet
- EXP-MN-SI020-EN-R0 - Measurements in Instrumentation PDFDocument114 pagesEXP-MN-SI020-EN-R0 - Measurements in Instrumentation PDFbali100% (3)
- Critical Lift PlanDocument2 pagesCritical Lift PlanjeffotNo ratings yet
- 06 Crane Operations and AssociatesDocument86 pages06 Crane Operations and AssociatesMasjoko WaeNo ratings yet
- LEI - 3 Day Course-Thorough ExaminationDocument3 pagesLEI - 3 Day Course-Thorough ExaminationmossamorrisNo ratings yet
- Title: 2210 Industrial Crane Safety: Powerpoint PresentationDocument3 pagesTitle: 2210 Industrial Crane Safety: Powerpoint PresentationbangladragosNo ratings yet
- Lifting Operation Rev2Document29 pagesLifting Operation Rev2Chong Yun QingNo ratings yet
- Crane & Sling 2Document29 pagesCrane & Sling 2g5nb100% (2)
- Lifting and Handling EquipmentsDocument54 pagesLifting and Handling Equipmentsalvin100% (1)
- Lifting ArrangementDocument2 pagesLifting ArrangementHerruSetiawanNo ratings yet
- Safe Lifting PracticesDocument69 pagesSafe Lifting Practicesvikas verma100% (1)
- Lifting PlanDocument2 pagesLifting PlanMidhunRameshThuvasseryNo ratings yet
- Sling Rigger TrainingDocument12 pagesSling Rigger Trainingegy pureNo ratings yet
- Anfal Sandwich Panel Data SheetDocument2 pagesAnfal Sandwich Panel Data SheetAshuu MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lifting Equipments and Procedure: Compiled by Safety Trainees PeclDocument83 pagesLifting Equipments and Procedure: Compiled by Safety Trainees PeclvarunstuffNo ratings yet
- API RP 2D Rigger Safety (2 Day) (API-U Approved)Document1 pageAPI RP 2D Rigger Safety (2 Day) (API-U Approved)idris100% (1)
- Assessment of General Metal Loss Level 1&2Document2 pagesAssessment of General Metal Loss Level 1&2erick CfNo ratings yet
- Pre Crane Lift ChecklistDocument1 pagePre Crane Lift Checklistg665013No ratings yet
- Industrial Safety of Lifting ProcedureDocument83 pagesIndustrial Safety of Lifting Proceduresaravanan_c1No ratings yet
- Rigging EquipmentDocument23 pagesRigging EquipmentAldi SetiadiNo ratings yet
- CraneDocument24 pagesCranezawmoe aungNo ratings yet
- Chain Pulley InspectionDocument1 pageChain Pulley InspectionLwandziso DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Crane & Sling 1Document80 pagesCrane & Sling 1pramodtryNo ratings yet
- Planning Lifting Operations Cosalt OriginalDocument89 pagesPlanning Lifting Operations Cosalt Originalmohamed fahsNo ratings yet
- 2009 Crane Start Up Inspection FormDocument3 pages2009 Crane Start Up Inspection Formsaeed ghafooriNo ratings yet
- Crosby Catalog 2008 - Page 76 To 88Document13 pagesCrosby Catalog 2008 - Page 76 To 88Prejit RadhakrishnaNo ratings yet
- 007 Mobile Crane ChecklistDocument2 pages007 Mobile Crane ChecklistJoshua ThomasNo ratings yet
- PR-1709 - Lifting and Hoisting Procedure Lift Planning ExecutionDocument31 pagesPR-1709 - Lifting and Hoisting Procedure Lift Planning ExecutionAdnanNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Hpg1034Document1 pageFlowchart Hpg1034SharulNo ratings yet
- F4a 2018 LEEA Assessments - Information For Members & Students Version 2 December 2017Document4 pagesF4a 2018 LEEA Assessments - Information For Members & Students Version 2 December 2017VishnuNo ratings yet
- RiggingDocument129 pagesRiggingInnocent BhaikwaNo ratings yet
- Crane 3612 LoadChartDocument6 pagesCrane 3612 LoadChartZura RamliNo ratings yet
- Lifting Hazards & Crane SafetyDocument26 pagesLifting Hazards & Crane SafetynincatNo ratings yet
- Rigger III PDFDocument1 pageRigger III PDFMohamed Hameem DeenNo ratings yet
- ABB Scaffold Competent TestDocument4 pagesABB Scaffold Competent Testvasucristal100% (2)
- Api 570 PreDocument3 pagesApi 570 PreBhargava NaiduNo ratings yet
- Technical Test Theory: Compact Crane A66Document6 pagesTechnical Test Theory: Compact Crane A66memoNo ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar LOP PDFDocument45 pagesDasar Dasar LOP PDFMuhamad Syarifudin100% (1)
- Lifting Plan of SpoolDocument1 pageLifting Plan of SpoolhazopengineerNo ratings yet
- Tandem Lifting Container SWGDocument1 pageTandem Lifting Container SWGarifNo ratings yet
- Overhead Crane SadDocument30 pagesOverhead Crane SadVicky GautamNo ratings yet
- Klasifikasi Pesawat Angkat Dan Pesawat Angkut: Oleh: Arief SuponoDocument80 pagesKlasifikasi Pesawat Angkat Dan Pesawat Angkut: Oleh: Arief SuponoAhmad MultidasaNo ratings yet
- Crane SafetyDocument22 pagesCrane SafetynincatNo ratings yet
- Lifting and Rigging Training Session 1 - 2021 01 22Document25 pagesLifting and Rigging Training Session 1 - 2021 01 22ELMLEMROZINo ratings yet
- Lifting MaterialsDocument6 pagesLifting MaterialsRoselyn SharronNo ratings yet
- Lift Planning Doug Swenson 10.10.2019Document138 pagesLift Planning Doug Swenson 10.10.2019Alex Sandro Borges PereiraNo ratings yet
- Critical Lift ChecklistDocument4 pagesCritical Lift ChecklistUdha Pengen SuksesNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Safety Presentation OSDocument25 pagesConfined Space Safety Presentation OSSajjad AfzalNo ratings yet
- Hands Free LiftingDocument4 pagesHands Free Liftingromerov24100% (1)
- Lifting Gear Inspection & Maintenance PDFDocument14 pagesLifting Gear Inspection & Maintenance PDFArgonauta_navegadorNo ratings yet
- Crane Safety During Edc VCM Errction by Ank 1221024516777948 8Document39 pagesCrane Safety During Edc VCM Errction by Ank 1221024516777948 8sujiyakhanNo ratings yet
- CranesDocument39 pagesCranesMajji SatishNo ratings yet
- Cranes: OSHA Office of Training & Education 1Document38 pagesCranes: OSHA Office of Training & Education 1unbridledsuccessNo ratings yet
- الأوناش عربيDocument38 pagesالأوناش عربيYasser Mahmoud100% (1)
- 2COSH Crane SafetyDocument59 pages2COSH Crane SafetyEunice GayetaNo ratings yet
- 1 Crane SafetyDocument44 pages1 Crane SafetyraezenbukalNo ratings yet
- Safety AwarenessDocument43 pagesSafety AwarenessTuesday EscabarteNo ratings yet
- Health Safety & Environment: Deco InteriorsDocument2 pagesHealth Safety & Environment: Deco InteriorsSusan SeseNo ratings yet
- Sample IGC3#2Document16 pagesSample IGC3#2Susan Sese100% (2)
- Personal Protective Equipment: For General IndustryDocument28 pagesPersonal Protective Equipment: For General IndustryXozanNo ratings yet
- Safe Working ProceduresDocument2 pagesSafe Working ProceduresSusan SeseNo ratings yet
- Thorp T-18 and Turner T-40 Flutter TestingDocument5 pagesThorp T-18 and Turner T-40 Flutter TestingjsgolightlyNo ratings yet
- Freeway and Expressway OperationsDocument22 pagesFreeway and Expressway Operationsrex tanongNo ratings yet
- Monthly HSE Report-May 2020Document2 pagesMonthly HSE Report-May 2020gk100% (1)
- SciChair Balancing Electric ChairDocument13 pagesSciChair Balancing Electric ChairjumpupdnbdjNo ratings yet
- A: Oh, No! How - It - ?: B: Well, I Home When My SisterDocument1 pageA: Oh, No! How - It - ?: B: Well, I Home When My SistervanesaNo ratings yet
- Kenr6239 00Document28 pagesKenr6239 00Boris BabicNo ratings yet
- Seat Belt Synopsis ReportDocument28 pagesSeat Belt Synopsis ReportVinodh JeevaNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Work Energy Power AllDocument15 pages9702 p1 Work Energy Power AllkwaikunNo ratings yet
- ARFFDocument6 pagesARFFMatt GarrettNo ratings yet
- ZeTo RulesDocument47 pagesZeTo RulesPok Itam100% (1)
- Aire y Frenos Especificaciones 140HDocument18 pagesAire y Frenos Especificaciones 140Hlark_No ratings yet
- Emergency Wreck Marking BuoyDocument1 pageEmergency Wreck Marking BuoyChockalingam Ganesh K RNo ratings yet
- The Bone Queen by Alison Croggon Chapter SamplerDocument32 pagesThe Bone Queen by Alison Croggon Chapter SamplerCandlewick Press33% (3)
- Current State of Scaffolding Unsafe Factor: A Thematic ReviewDocument19 pagesCurrent State of Scaffolding Unsafe Factor: A Thematic ReviewMimi SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis On Accident RateDocument30 pagesStatistical Analysis On Accident RateOladosu muritala100% (1)
- Fall Hazard ManualDocument53 pagesFall Hazard ManualAviects Avie JaroNo ratings yet
- Manual Cheerson Cx20Document1 pageManual Cheerson Cx20cgouveiaNo ratings yet
- Accident ReportDocument10 pagesAccident ReportVenkata Ramana100% (1)
- 1 3 - 3 EN1991 1 7 Bridge Design Provisions of UK NA For EN1991 1 7 and PD6688 1 7Document14 pages1 3 - 3 EN1991 1 7 Bridge Design Provisions of UK NA For EN1991 1 7 and PD6688 1 7tim_lim12No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 Fin610Document22 pagesCHAPTER 9 Fin610anisya_rad9161No ratings yet
- Serra Mármore - DeWALT - DW860 - Manual de InstruçõesDocument28 pagesSerra Mármore - DeWALT - DW860 - Manual de Instruçõesmazzalimania0% (1)
- Flight Operations Briefing NotesDocument7 pagesFlight Operations Briefing Notesa320No ratings yet
- RM & I Detailed PDFDocument187 pagesRM & I Detailed PDFDevikaNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Vessels That Sank in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesTimeline of Vessels That Sank in The PhilippinesChin-Chin AbejarNo ratings yet
- UAS Genap Bhs. Inggris Kelas 10Document7 pagesUAS Genap Bhs. Inggris Kelas 10Nendra BeluciNo ratings yet
- Extra PracticeDocument2 pagesExtra PracticeКатарина ПетковићNo ratings yet